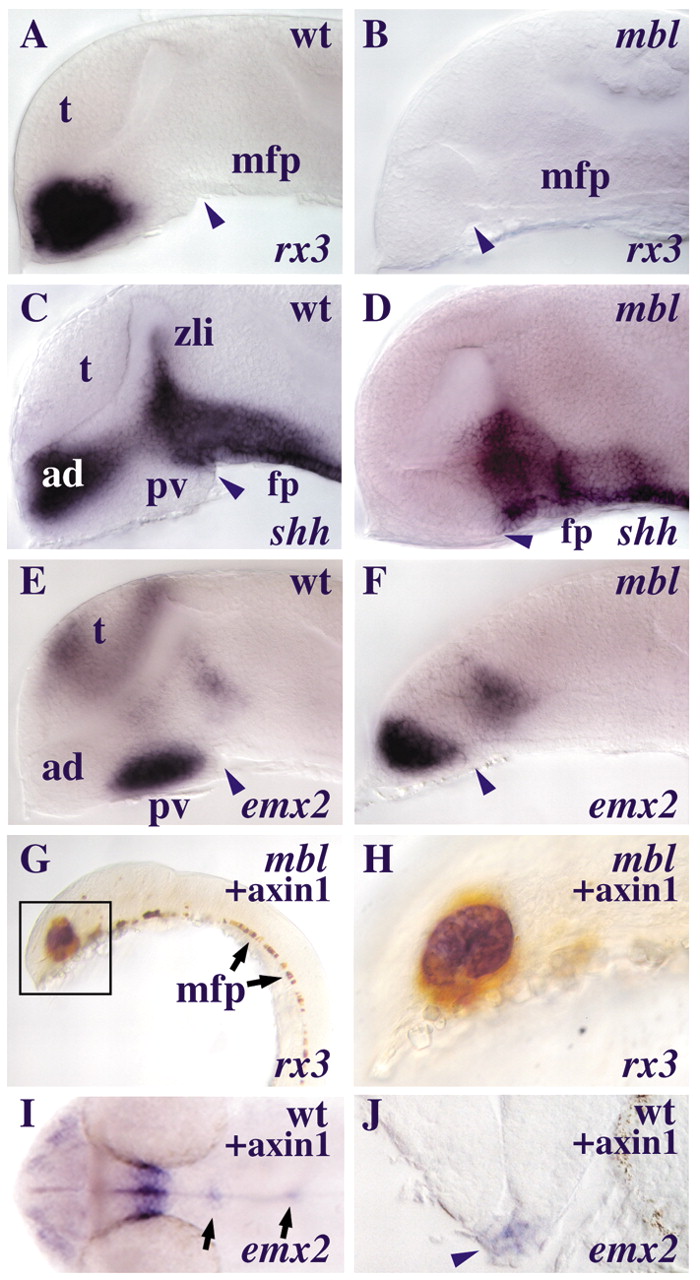
Fig. 5 mbl embryos lose rostral but retain caudal hypothalamic marker gene expression. (A-H) Lateral views of brains of embryos at about 31 somites with anterior to the left. (A-D) The hypothalami of the mbl embryos (B,D) do not express rx3 (B) and lose the anterior domain of shh expression (D) compared to the wild-type embryos (A,C). (E-F) The mbl embryo (F) retains expression of the hypothalamic marker emx2 which is expressed in the caudal hypothalamus of the wild-type embryo (E). Arrowheads point at the caudal limit of the hypothalamus. (G-H) Transplanted cells overexpressing axin1 (brown) that have incorporated into the rostral ventral CNS restore rx3 expression (blue) in the mbl embryo (G). (H) A higher magnification view of the transplant (boxed) of this embryo. (I-J) Some Axin1-overexpressing cells that incorporate into the floorplate domain of a wild-type host ectopically express emx2 (arrows). The transverse section (indicated by the left arrow in I) shows ectopic emx2 expression in the floorplate (arrowhead in J). Abbreviations: ad, anterior-dorsal hypothalamus; fp, floorplate; mfp, medial floorplate; pv, posterior-ventral hypothalamus; t, telencephalon; zli, zona limitans intrathalamica.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development