Fig. 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-070823-10
- Publication
- Rui et al., 2007 - A beta-Catenin-Independent Dorsalization Pathway Activated by Axin/JNK Signaling and Antagonized by Aida
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
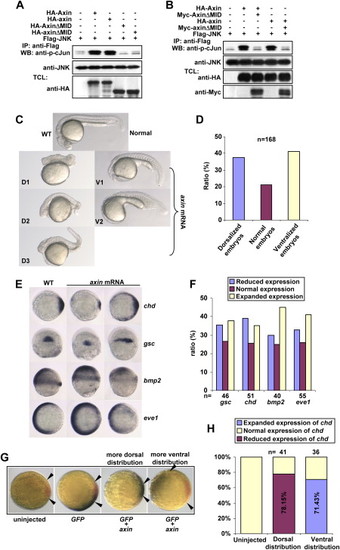
Axin Contains Intrinsic Dorsalizing Activity (A) Zebrafish axin and axinΔMID behave similarly to their mouse counterparts in JNK activation. HEK293T cells were transfected with FLAG-JNK together with other plasmids as indicated. Immunokinase assays were performed as described above. (B) Zebrafish axinΔMID is a dominant-negative form for axin-mediated JNK activation. HEK293T cells were transfected and followed by immunokinase assay at 36 hr posttransfection. (C) Injection of zebrafish axin mRNA induces opposing phenotypic changes in embryos at 24 hpf. axin mRNA was injected into one-cell embryos at a dose of 300 pg. Shown are lateral views of live embryos at 24 hpf. D1, D2, and D3 display characteristic dorsalized phenotypes at 24 hpf. D2 and D3 phenotypes of injected embryos showed shortened tail with the ventral tail fin missing. D1 phenotype was the most severe one. V1 and V2 phenotypes displayed loss of the head and notochord together with enlargement of the blood island. (D) Statistical data for (C). (E) Expression of marker genes in axin-injected embryos. Full-length axin mRNA (300 pg) was injected into one-cell embryos and followed by in situ hybridization at the shield stage. Embryos for chd and eve1 were animal pole views with dorsal to the right; embryos for gsc were dorsal views with animal pole to the top; and embryos for bmp2 were lateral views with dorsal to the right. (F) Statistical data for (E). (G) chd expression changes in an injection-position-dependent manner. Wild-type axin mRNA (250 pg) was coinjected with GFP mRNA (50 pg), and double in situ hybridization was performed at the shield stage for GFP(blue) and chd (red). The blue areas expressing GFP indicated the injection position. Note that when injected mRNAs were distributed into areas proximal to the dorsal side as judged at the shield stage, chd expression was weaker (shorter distance between arrows), whereas ventral distribution gave rise to enhanced expression of chd. (H) The percentage of embryos with reduced chd expression and dorsal distribution of injected GFP mRNA, and the percentage of embryos with enhanced chd expression and ventral distribution of GFP mRNA, were diagramed. |
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 13(2), Rui, Y., Xu, Z., Xiong, B., Cao, Y., Lin, S., Zhang, M., Chan, S.C., Luo, W., Han, Y., Lu, Z., Ye, Z., Zhou, H.M., Han, J., Meng, A., and Lin, S.C., A beta-Catenin-Independent Dorsalization Pathway Activated by Axin/JNK Signaling and Antagonized by Aida, 268-282, Copyright (2007) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell