- Title
-
Sonic hedgehog is not required for the induction of medial floor plate cells in the zebrafish
- Authors
- Schauerte, H.E., van Eeden, F.J.M., Fricke, C., Odenthal, J., Strähle, U., Haffter, P.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
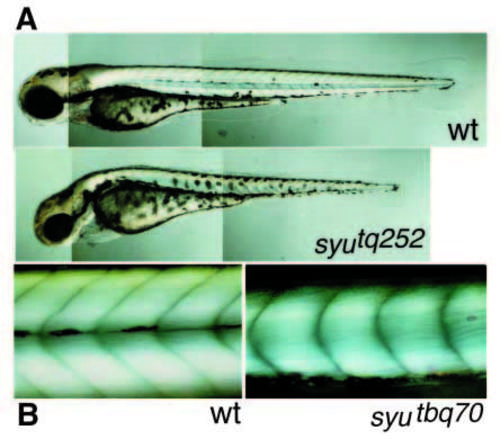
(A) Nomarski picture showing wild-type and syutq252 mutant embryos at 72 hpf in lateral view. The somites are clearly U-shaped and the horizontal myoseptum is missing in the syu mutant embryo, causing the failure of melanophores to assemble in a lateral stripe. (B) Dark-field picture showing the somites of wild-type and syutbq70 mutant embryos at 72 hpf in lateral view. Striated muscle shows a bright birefringence and somite boundaries show as dark lines. Wildtype somites are V-shaped and separated into a dorsal and a ventral part by the horizontal myoseptum. The somites in the syu mutant embryo are reduced in size, clearly U-shaped and lack a horizontal myoseptum. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
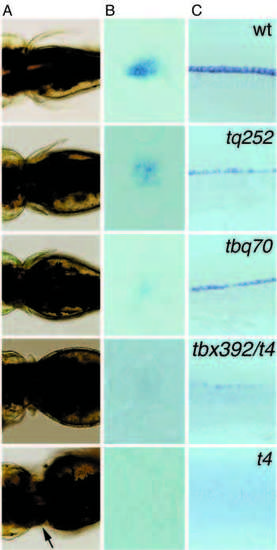
(A) Nomarski pictures showing pectoral fins of wt and syu alleles in dorsal views. In the weak alleles, syutq252 and syutbq70, the pectoral fin phenotype is variable and frequently only the pectoral fin on one side of the embryo is reduced in size. In the strong allele, syutbx392/t4, the pectoral fins on both sides are reproducibly tiny and in the deletion allele syut4 finbuds are established (arrow) but fail to grow out. (B) Pectoral fins; dorsal views of shh whole-mount in situ hybridizations on syu alleles at 36 hpf. (C) Lateral views of shh whole-mount in situ hybridizations on syu alleles at 22 hpf. In the weak alleles, syutq252 and syutbq70, expression of shh is reduced, in embryos that carry syutbx392 over the shh deletion (syut4), it is barely detectable and no shh expression is seen in syut4 mutant embryos. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
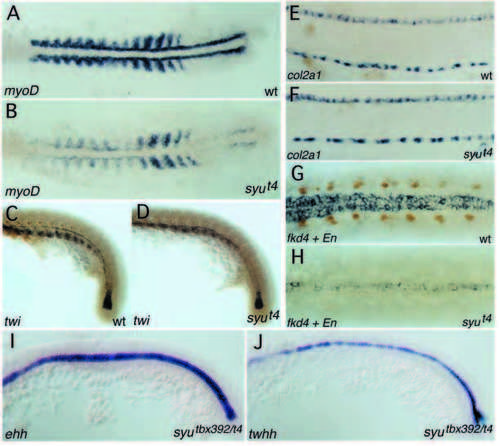
Expression of myoD in a wild-type (A) and a syut4 mutant embryo (B), 14-somite stage, dorsal view on flat-mounted embryo. Expression of myoD is strongly reduced in the adaxial cells, also more lateral expression in the somitic mesoderm is lower. Residual levels of myoD remain detectable in the adaxial cells, especially in the tailbud region. Double staining for twist (in situ hybridization) and Engrailed (4D9 antibody labeling) in wild-type (C) and syut4 mutant (D) embryo, side view on tail, 22 hpf. twist labels the early notochord in the tailbud, the hypochord and the sclerotome visible in the ventral part of the somites (all blue staining). In the syu mutant, twist staining is only slightly reduced and shifted dorsally relative to the notochord due to the abnormal shape of the somites. Engrailed positive muscle pioneers (brown staining) are absent from syu mutant embryos. Expression of col2a1 in wild-type sibling (E) and syut4 mutant embryo (F) at 29 hpf, side view. col2a1 labels both the medial floor plate and the hypochord. syut4 has no effect on medial floor plate staining. Whole-mount antibody and in situ staining for Engrailed (4D9) and fkd4, respectively, of wild-type sibling (G) and syut4 mutant (H) embryo at 24 hpf, dorsal view. Computer composite of two focal planes. One plane shows the nuclei of the muscle pioneers (brown). The second plane shows the cytoplasmic fkd4 staining in the ventral neural tube encompassing medial and lateral floor plate. In syu mutant embryos, muscle pioneers are absent and fkd4 expression is restricted to the medial floor plate itself. Expression of ehh (I) and twhh (J) at 15- to 17-somite stage syutbx392/t4 mutant embryos. The expression of both hedgehog homologs in syu mutant embryos is indistinguishable from wild-type siblings. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
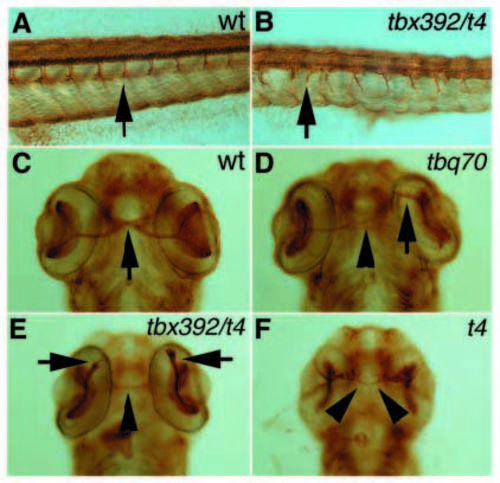
Zn5 antibody staining of secondary motorneurons in a wildtype (A) and a syutbx392/syut4 mutant (B) embryo at 52 hpf. In syu mutant embryos the axons of the secondary motorneurons (indicated by arrows) fail to branch and instead cease to extend or grow further ventrally in an abnormal pattern. Zn5 staining of retinal axon projections in wild-type (C) and syu mutant alleles (D-F) at 52 hpf. In wild-type embryos, the retinal ganglion cell axons have crossed the midline where the optic chiasm is formed (arrow) and grow towards the tectum on the contralateral side. In syu mutant embryos, these retinal axons frequently fail to cross the midline and remain on the ipsilateral side (arrows) or, if they do cross the midline, frequently grow abnormally and in many cases only form very thin axon bundles (arrowheads). |