- Title
-
Vessel patterning in the embryo of the zebrafish: guidance by notochord
- Authors
- Fouquet, B., Weinstein, B.M., Serluca, F.C., and Fishman, M.C.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
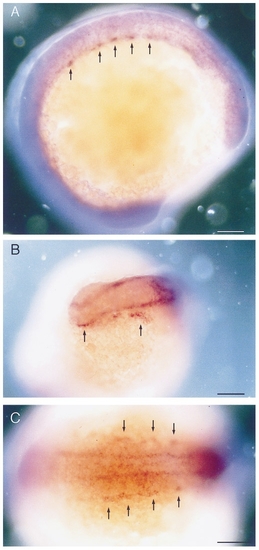
Whole mount RNA in situ hybridization with flk performed on 12 somite stage embryos (15 hpf). (A) Lateral view and (C) dorsal view showing the bilateral angiogenic cell clusters in the trunk (arrows). (B) Anterior view showing the endocardial and cephalic angioblasts (arrows). Dorsal is up (A) and anterior is to the left (A). Bars, 100 μm. |
|
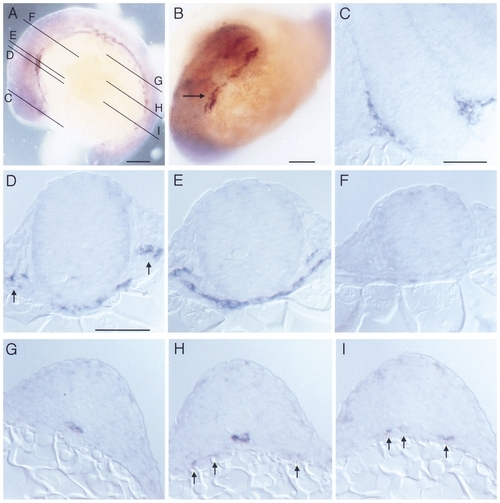
Whole mount RNA in situ hybridization with flk performed on 14 somite stage embryos (16 hpf). (A) Lateral view and (B) anterior view showing angioblastic areas in the embryo. Lines in (A) indicate planes of sectioning for panels C through I. Arrow in (B) indicates position of first aortic arch. (C) Section at the level of the forebrain and eye vesicles, showing angioblastic cells in the ventrally to the brain located plexus. (D) Section at the level of the endocardial primordium which has reached the midline by this stage. Arrows indicate the primordia of the internal carotid artery. (E) Section at the level of the aortic arch primordium. (F) Section at the level of the hindbrain, which lacks flk-positive cells at this stage. (G –I) Sections at various planes through the trunk. Angioblasts have reached the midline below the notochord (G, H) forming the primordium of the dorsal aorta. Other angioblasts are still located laterally close to the yolk (arrows). (I) In the posterior trunk angioblastic cells have not yet reached the midline (arrows). Dorsal is up (A, C–I) and anterior is to the left (A). Bars, 100 μm (A, B), 50 μm (C–I). |
|
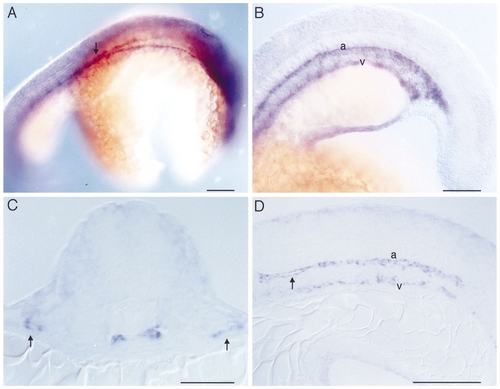
Whole mount RNA in situ hybridization with flk on 24 somite stage embryos (21 hpf). (A) Dorsolateral view showing the paired dorsal aortae in the area of the hindbrain and their junction in the anterior trunk (arrow). (B) Lateral view of the posterior trunk and tail showing the primordia of the dorsal aorta (a) and the axial vein (v). (C) Transverse section through the anterior trunk at the level of the first somite. The two primordia of the dorsal aortae lie just beneath the notochord. Laterally located (arrows) are precursors of the bilateral ducti of Cuvier. (D) Sagittal section of the posterior trunk showing the primordia of the dorsal aorta (a) and the ventral vein (v). Arrow indicates beginning lumen formation in the dorsal aorta. No intersomitic vessels are yet formed. Dorsal is up, and anterior is to the right in (A) and to the left in (B, D). Bars, 100 μm (A, B), 50 μm (C, D). |
|
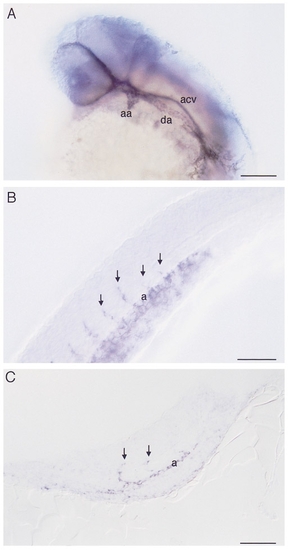
Whole mount RNA in situ hybridization with flk on 30 somite stage embryos (24 hpf) showing (A) a view of the head, (B) a lateral view of the trunk, and (C) a sagittal section of the posterior trunk and tail. (A) Clearly visible are the patent first aortic arch (aa) and left dorsal aorta (da). In contrast, the anterior cardinal vein (acv) does not yet possess a lumen. (B, C) In the trunk, intersomitic vessels (arrows) can be seen sprouting from the dorsal aorta (a). Dorsal is up and anterior is to the left. Bars, 100 μm (A), 50 μm (B, C). |
|
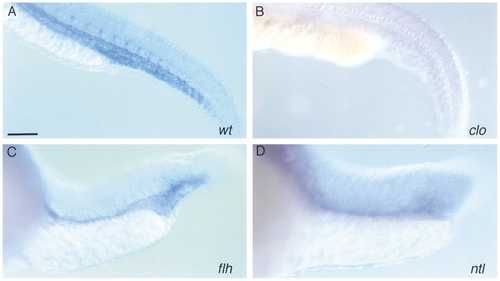
Whole mount RNA in situ hybridization with flk performed on 30 somite stage zebrafish mutant embryos (24 hpf). (A) wildtype, (B) cloche, (C) floating head, (D) no tail. (B) In cloche no flk-expressing cells can be found. (C) flh has few flk-expressing cells in the trunk, but forms a sinus of endothelial cells in the tail. (D) ntl is similar to flh. Dorsal is up and anterior is to the left. Bar, 100 μm. |
|
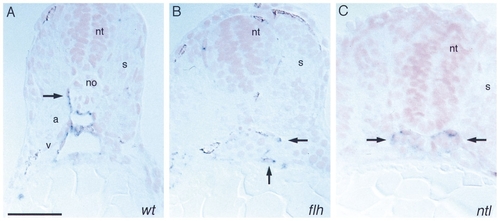
Histological analysis of whole mount RNA in situ hybridization with flk performed on 30 somite stage embryos (24 hpf). (A) Wild type, (B) floating head, (C) no tail. (A) The wild-type embryo clearly shows the two axial vessels, dorsal aorta (a) and axial vein (v) and a sprout of an intersomitic vessel (arrow). (B, C) No axial vessels can be observed in floating head or no tail. Arrows point to flk-expressing cells. Sections were counterstained with Nuclear Fast Red. Dorsal is up. Bar, 50 μm. |
|
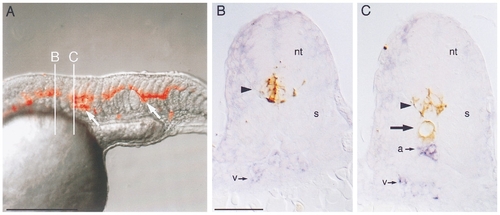
Mosaic analysis of flh embryos transplanted with wild-type cells. (A) Composite rhodamine epifluorescence (red) and Nomarski (gray) videomicrograph of the trunk of a 25 somite flh mutant embryo that was transplanted at the blastoderm stage. In this embryo wildtype cells contributed primarily to neural tube and notochord (arrows). B and C indicate planes of cross-sectioning in panels (B) and (C). (B) Cross section of flh embryo in plane B. Transplanted wild-type cells labeled with biotin– peroxidase (brown, arrowhead) contributed to ventral neural tube (nt). A single population of flk-expressing cells (blue, v) resides ventrally. The somites (s) are fused beneath the neural tube. (C) Cross section of flh embryo in plane C. Transplanted wild-type cells contributed both to ventral neural tube (arrowhead) and to notochord (arrow). There are two populations of flk-expressing cells, a dorsal one (a) just beneath the notochord and a ventral one (v). Somites (s) are not fused. Dorsal is up, anterior is to the left in (A). Bars, 250 μm (A), 50 μm (B, C). |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 183(1), Fouquet, B., Weinstein, B.M., Serluca, F.C., and Fishman, M.C., Vessel patterning in the embryo of the zebrafish: guidance by notochord, 37-48, Copyright (1997) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.