- Title
-
The ventral and posterior expression of the zebrafish homeobox gene eve1 is perturbed in dorsalized and mutant embryos
- Authors
- Joly, J.S., Joly, C., Schulte-Merker, S., Boulekbache, H., and Condamine, H.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
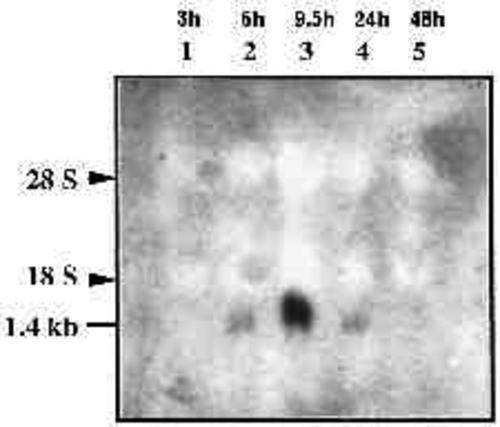
Temporal expression of eve1 in zebrafish embryos as detected by northern blot hybridization. Total RNA (20 µg) from different embryonic stages (hours after fertilization indicated upon lanes number at the top) were run in each lane and hybridized with probe ‘A’ (see Methods). Exposure time was 3 days. Arrowheads indicate the positions of ribosomal RNA. |
|
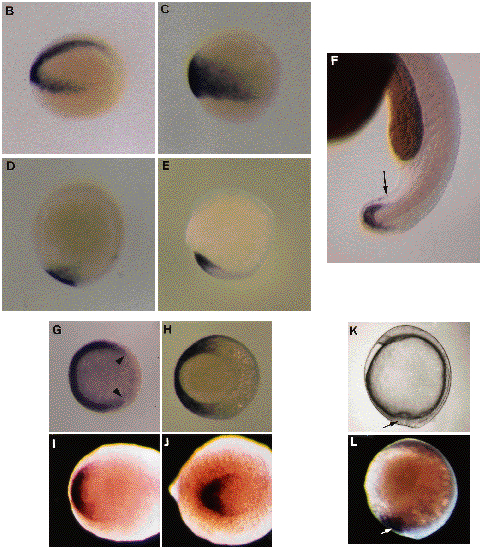
Localization of eve1 RNA in early embryos. (B-J,L). Whole-mount in situ hybridizations using a eve1 probe. Cells expressing eve1 appear in dark purple after an alkalinephosphatase chromogenic reaction. (B-F). Side views of embryos with the same orientation as in A. (B). 30% epiboly (4.7 h) embryo slightly inclined to see the whole arc of positive cells from the vegetal pole. (C). 60% epiboly (7 h). (D). 100% epiboly (9.5 h). (E). 5-somite embryo (12.5 h). (F). 24h embryo. Positive external cells are located around the extremity of the tail (arrow). (G-J). Views from the animal pole in (G), from the vegetal pole in (H) and from the posterior pole in (I,J). Dorsal side on the right. (G). 30% epiboly stage, the positive signal covering more than 270° of arc (limits indicated by arrowheads). (H). 80% epiboly (8.5 h) stage, positive cells in the ventral half of the gastrula. (I). 1-somite embryo (10.5 h). (J). 10-somite embryo (15 h). (K). Micrograph of a living embryo (9.5 h). Side view. Vegetal pole is at the bottom. The dorsal tail bud is on the right from yolkplug closure. Ventral cells (arrow) converge with their dorsal counterparts. (L). Embryo at the same stage and with the same orientation as in (K). The signal (arrow) forms a plaque ventral to the yolk plug closure and to the dorsal tail bud. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
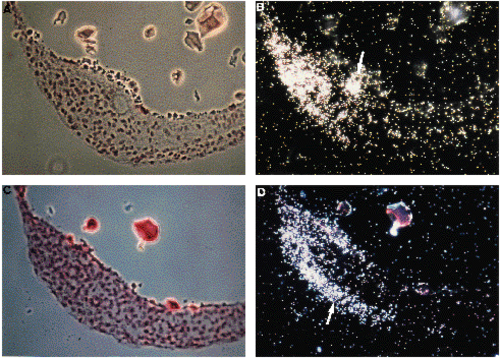
Expression of eve1 in 10-somite embryos (14 h). (A). Bright-field section of a sagittal section passing through the Kupffer’s vesicle. Yolk has mostly disappeared during the manipulations. (B). Corresponding dark-field view. RNA are located at the tip of the tailbud on the left. A small mass of positive cells (arrow) are located behind the Kupffer’s vesicle (which is negative). (C). Bright-field view of a neighbour section (one section thickness is intercalated between the section shown in A,B and this one). (D). Dark-field view of the region seen in (C). eve1 signal forms an extension in an external cell layer (arrow). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
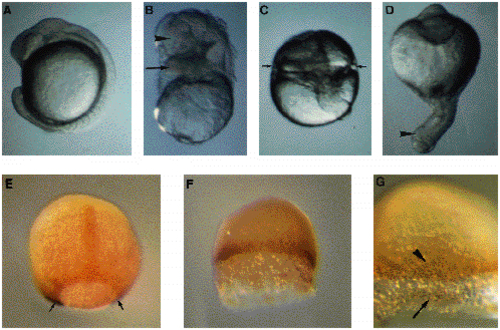
Treatments of blastula stage embryos with LiCl. (A-D) Micrographs of living embryos at 16 h. (A). Side view of a control embryo at the 14-somite stage. (B-D) Phenotypes of embryos treated at the early blastula (32-cell) stage with 0.3 M LiCl for 30 minutes. (B) Embryo with structures located atop yolk, morphologically identified to brain (arrowhead) and heart (arrow). (C) Embryo with a radial constriction (arrows) possibly indicating heart development. A remnant of axis is visible. (D) Radial proboscis embryo with an external proboscis indicated by an arrowhead. (E-G) Immunodetection of the Ntl protein and whole-mount in situ using a eve1 probe. (F,G). Embryos were treated as in B-D and fixed at 9 h. (E) The positive nuclei for Ntl are visible in notochord precursors and around the margin. The ventral eve1 purple signal (arrows) is hardly visible in this embryo viewed from the dorsal side, animal pole at the top. (F,G) Embryo treated with LiCl. Detail in G. Animal pole up. Yolk was accidentally removed during staining experiments probably as a result of a greater fragility of the embryo. In treated embryos, the external YSL is larger than in untreated embryos. There is no staining for eve1. The Ntl-positive nuclei are located at the margin (arrowhead in G) and in detached cells (arrows in G). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
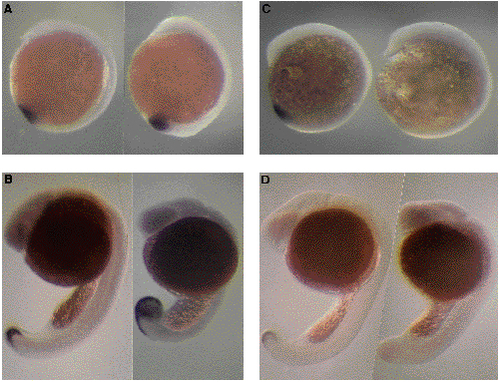
In situ hybridizations of eve1 in wild-type and mutant embryos (whole mounts). Wild types are on the left of each picture and homozygous mutants on the right. Anterior poles at the top. Dorsal sides on the right. (A,B) spadetail mutation. (A) 12.5 h embryos (5- somite stage for the wild type). Beginning of abnormal tail bud swelling can be seen at the bottom of the embryo on the right. (B) 22 h embryo. In spt homozygous mutants, eve1 staining covers the whole swollen tail bud and anterior extension is longer than in wild-types. (C,D) no tail mutation. (C) 5-somite stage (12.5 h). No signal is observed in the mutant embryo. (D) 24 h embryos. Signal begins to fade in the wild-type embryo but is completely absent in the homozygous mutant. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
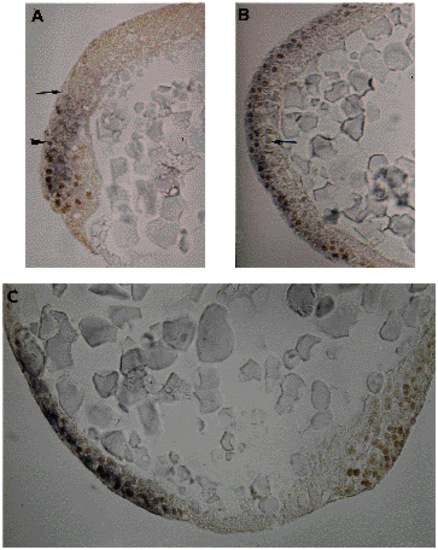
Sections of embryos stained for eve1 and Ntl. The eve1 staining appears as a dark purple cellular coloration after wholemount in situ hybridizations using the chromogenic alkaline phosphatase reaction, while antibody stainings for Ntl give a brown color in nuclei subsequent to a peroxidase detection. (A) Sagittal section through a germ-ring stage embryo. The extents of eve1 or Ntl staining are indicated by an arrow and an arrowhead, respectively. (B) Ventral region of a shield stage embryo. Equatorial section. Epiblast is positive for eve1 and Ntl. In hypoblast, there is no eve1 staining. One nucleus, faintly stained for Ntl, is indicated by an arrow. (C) Sagittal section through the vegetal region of a 90% epiboly embryo. Ntl staining is on both sides of yolk plug, eve1 staining is ventral, on the left side. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|