- Title
-
Zebrafish BID Exerts an Antibacterial Role by Negatively Regulating p53, but in a Caspase-8-Independent Manner
- Authors
- Qi, Z., Yan, D., Cao, L., Xu, Y., Chang, M.
- Source
- Full text @ Front Immunol
|
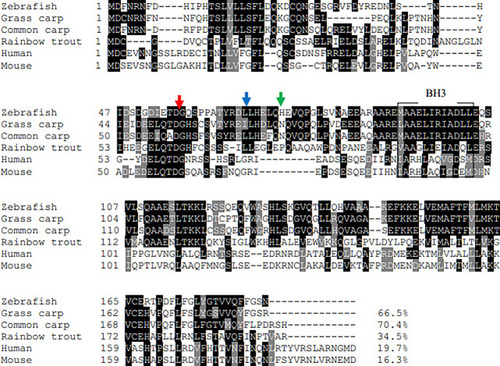
Multiple-sequence alignment of vertebrate Bid. The Bid from each species were aligned using the Clustal O program and decorated with BoxShade software. The conserved BH3 domains were boxed. The caspase-8 cleavage site (LETD), the granzyme B cleavage site (HELQ), and the calpain cleavage site was marked by red arrow, blue arrow, and green arrow, respectively. |
|
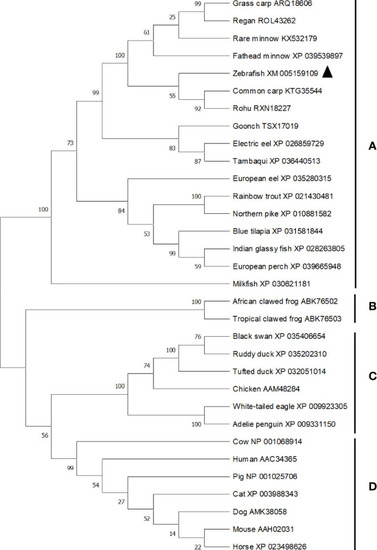
Phylogenetic tree analysis of vertebrates Bid. The phylogenetic tree was constructed using Mega X software using N-J method. Bootstrap was calculated with 10,000 repeats. The tree is divided into four main clades (clade |
|
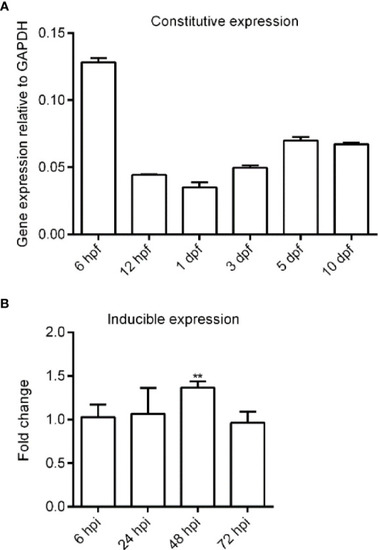
Expression analysis of zebrafish |
|
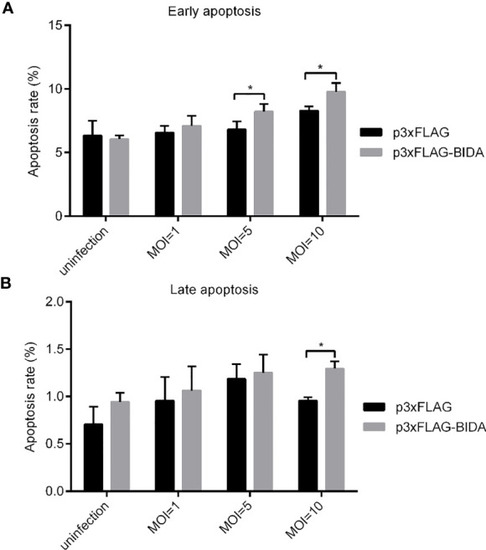
Apoptotic activity of zebrafish Bid at the early apoptosis stage |
|
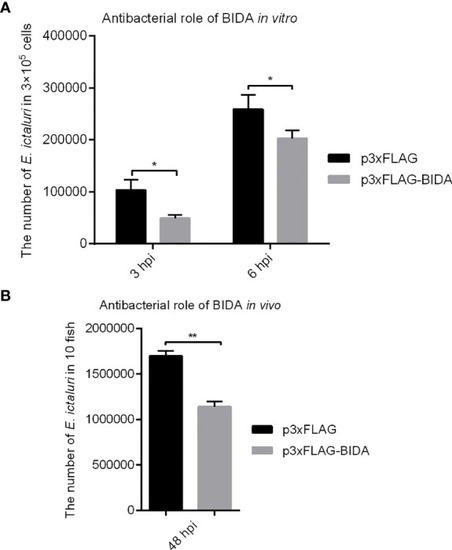
Figure 5 Antibacterial activity of zebrafish Bid in vitro (A) and in vivo (B). For in vitro bacterial invasion assays (A), the EPC cells were transiently transfected with 500 ng p3×FLAG or Bid-FLAG plasmid. At 24 h post-transfection, the cells were infected with E. ictaluri at an MOI of 10. At 1.5 h post-infection, the extracellular bacteria were killed using gentamicin (50 µg/ml). At 3 and 6 hpi, the cells were lysed, and the intracellular bacterial colony-forming units (CFU) were calculated. For in vivo bacterial invasion assays (B), the fertilized eggs were microinjected with 200 ng/μl p3×FLAG or Bid-FLAG. At 4 dpf, the larvae were infected with E. ictaluri at an MOI of 10. At 48 hpi, the fish were ground, and the CFU was calculated. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. |
|
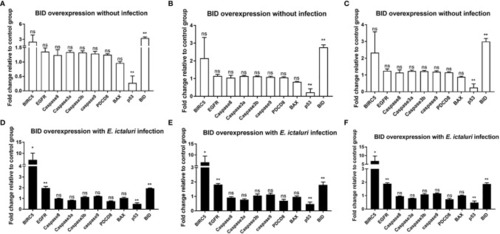
Expression analysis of apoptosis-related genes in |
|
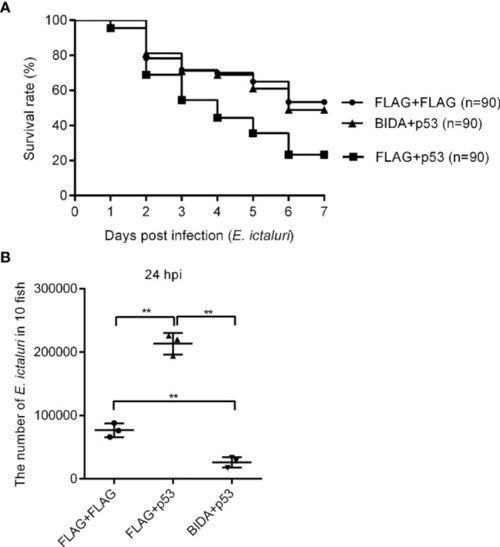
The effects of Bid and p53 on fish survival |
|
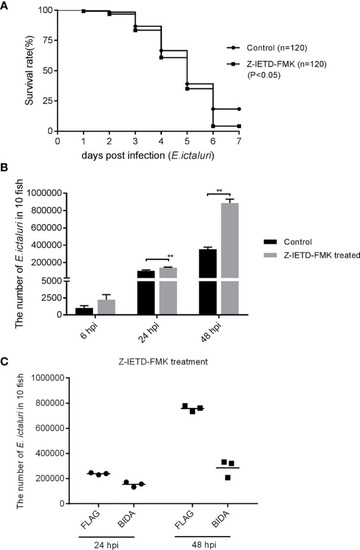
Antibacterial activity of Bid is caspase-8 independent. |
|
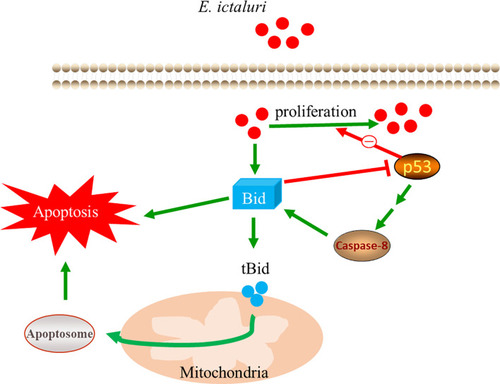
Mechanism of the antibacterial activity of full-length Bid. |