- Title
-
Growth and Antioxidant-Related Effects of the Reestablished Ascorbic Acid Pathway in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) by Genomic Integration of L-Gulonolactone Oxidase From Cloudy Catshark (Scyliorhinus torazame)
- Authors
- Shanaka, K.A.S.N., Jung, S., Janson, N.D., Jayasingha, J.R.P., Madushani, K.P., Kim, M.J., Lee, J.
- Source
- Full text @ Front. Physiol.
|
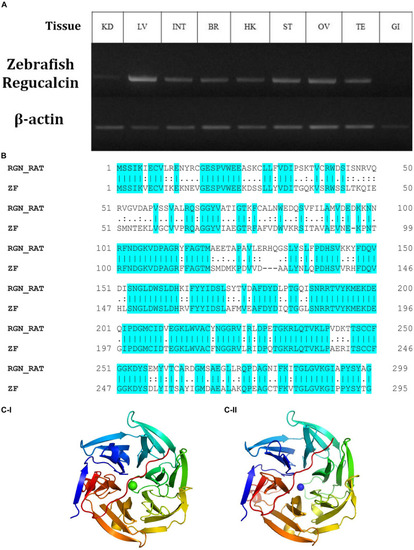
The relative expression of gulonolactonase (Danio rerio) in different tissues and its bioinformatics analysis. (A) Expression of zebrafish gulonolactonase (regucalcin) in KD (kidney), LV (liver), INT (intestine), BR (brain), HK (head-kidney), ST (stomach), OV (ovary), TE (testis), and GI (gill). Zebrafish β-actin (NM_181601.5) was used as the reference gene for RT-PCR analysis. (B) The pairwise sequence alignment between rat (RGN_RAT) (CAA48786.1) and zebrafish (ZF) (NM_205746) gulonolactonase proteins. This alignment indicates high sequence conservation between the rat and zebrafish gulonolactonase proteins. Homology structures for (C-I) Rat and (C-II) Zebrafish gulonolactonase. In both structures, the arrangement of the amino acids is similar, indicating conserved catalytic functions. |
|
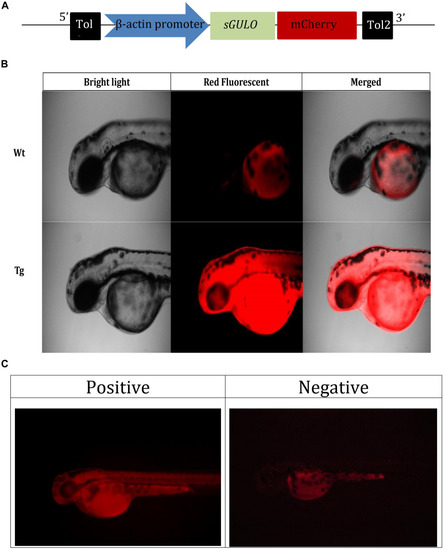
Selection of |
|
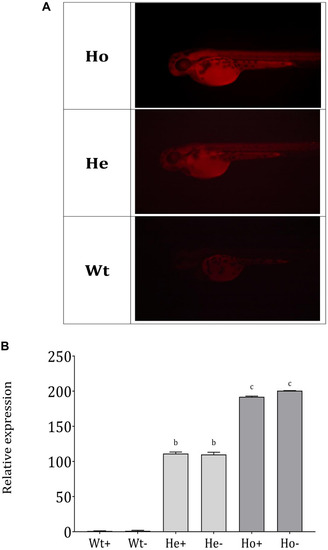
Separation of Ho and He |
|
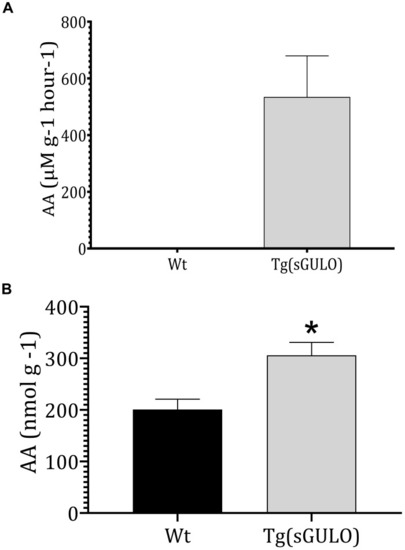
The sGULO enzyme activity and AA level in Wt and |
|
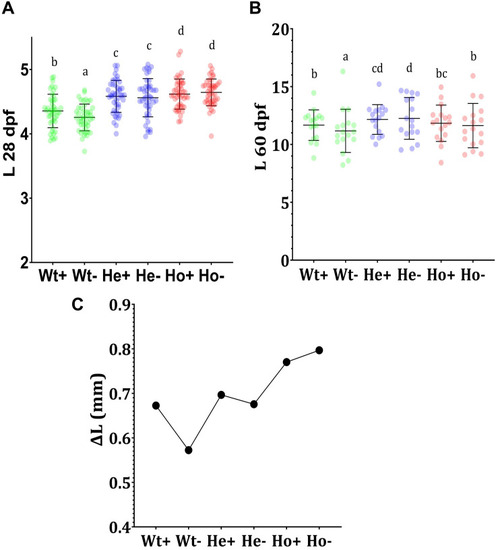
Feeding experiment and evaluation of growth |
|
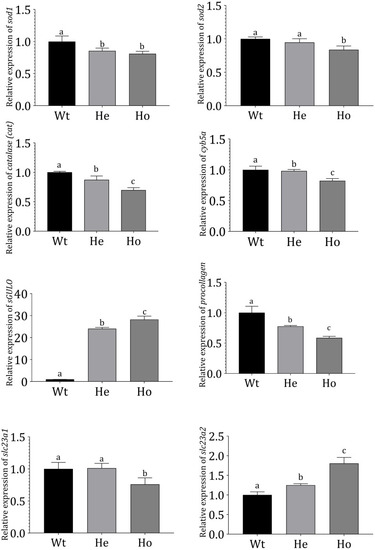
Gene expression profiles in |