- Title
-
Zebrafish, an In Vivo Platform to Screen Drugs and Proteins for Biomedical Use
- Authors
- Lee, H.C., Lin, C.Y., Tsai, H.J.
- Source
- Full text @ Pharmaceuticals (Basel)
|
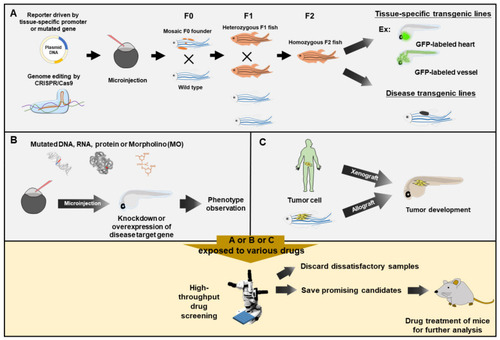
Zebrafish served as a rapid means for phenotype-based high-throughput drug screening. Zebrafish embryos exposed to various drugs for drug screening would be obtained from three approaches. (A) Embryos from tissue-specific transgenic lines and disease-like transgenic lines. The DNA constructs, as indicated, are microinjected into one-cell fertilized eggs, followed by selection and breeding to heterozygous or homozygous transgenic strains. (B) Embryos with knockdown or overexpression of a specific gene. The mutated DNA, mRNA, protein or antisense oligonucleotide Morpholino (MO) is injected into the zebrafish embryos for knockdown or overexpression of disease target gene, followed by transient phenotypic observation. (C) Embryos after transplantation. Cancer cells from human (Xenograft) or zebrafish (allograft) are transplanted into zebrafish embryos, resulting in tumor development. Zebrafish embryos obtained from (A), (B) or (C) are employed to perform high-throughput drug screening via exposure to various tested drugs by using automated quantitative analysis and phenotypic scoring in multiple plates. After preliminary high-throughput rapidly screening, researchers could rule out most negative candidates and only save the most promising candidates for further validation on the mammalian system. |
|
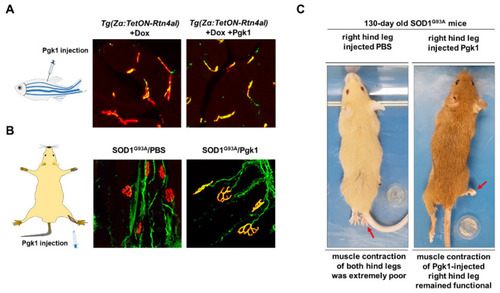
Intramuscular injection of Pgk1 could reduce the NMJ denervation occurring in the ALS animal models of zebrafish and mouse. (A) ALS-like adult zebrafish model. Left: diagram illustrates the muscle injection of Pgk1 into adult zebrafish; middle: after Doxycycline (Dox) was treated for one week, a few number of axonal motor neurons (MNs; labeled with green fluorescence signal) co-localized with motor end plate (labeled with red fluorescent signal) presented in yellow fluorescent signal was observed in the ALS-like zebrafish strain Tg(Zα:TetON-Rtn4al), indicating that NMJ denervation, a pathogenesis indicator at early stage of ALS, seriously occurred in the Rtn4al/NogoA-overexpressed zebrafish; right: Pgk1 was injected into the muscle of Dox-treated adult zebrafish, and the number of axonalMNs (labeled with green fluorescence signal) co-localized with motor end plate (labeled with red fluorescent signal) presented in yellow fluorescent signal was increased, indicating extracellular injection of Pgk1 could reduce the denervation and maintain the complete NMJ structure in the Rtn4al/NogoA-overexpressed zebrafish. (B) ALS (SOD1G93A) mice model. Left: diagram illustrates that the solution was injected into the gastrocnemius of right hind leg of ALS mice; middle: phosphate buffer saline (PBS) served as control was injected into the gastrocnemius of right hind leg of ALS mice, and the denervation of axonal MNs was examined. A few numbers of axonal MNs (labeled with green fluorescence signal) co-localized with motor end plate (labeled with red fluorescent signal) presented in yellow fluorescent signal was observed in the 75-day-old ALS mice; right: Pgk1 was injected into the gastrocnemius of right hind leg of ALS mice at 60 days old, and the denervation of axonal MNs was examined at 75 days old. The number of NMJ with complete structure presented a yellow fluorescent signal was increased compared to that of control group. (C) The first shot of Pgk1 was injected into the gastrocnemius of right hind leg of SOD1G93A ALS-mice at 60 days old, followed by the other shot for every 15 days until 120s days old. The treated ALS-mice were observed at 130 days old. Left: both hind legs of ALS-mice injected with PBS (control) were completely paralyzed. Right: the right hind leg injected with Pgk1 could keep contraction and movable, while the left hind leg was paralyzed. Figure modified from [106]. |
|
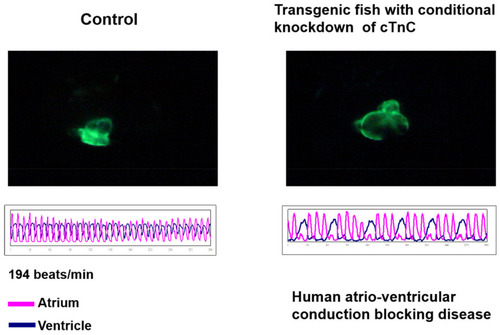
Dilated Cardiomyopathy could be conditionally induced to occur in the transgenic zebrafish. Zebrafish transgenic line Tg(cmlc2:tetON-cTnc-antisence) was generated by Tsai’s lab, in which the antisense RNA strand of cardiac Troponin C (cTnC) gene and myocardium-specific GFP mRNA were conditionally induced to synthesize simultaneously in the myocardial cells of the heart; due to this, both directional transcriptions were driven by the promoter of cardiac myosin light chain 2 gene (cmlc2) under the Tet-On control system [114]. The heart shape (upper panel of left figures) and heartbeat (lower panel of left figures) were apparent normally in the embryos derived from this transgenic line without treatment of Doxycline (DOX) (control). However, when these embryos were treated with DOX, the dilated cardiomyopathy of heart shape occurred (upper panel of right figures), which was able to be observed under confocal microscope, and arrhythmic heart-beating was also detected (lower panel of right figures). These symptoms shown on zebrafish caused by knocking down of cTnC were similar to those of human incomplete atrio-ventricular conduction blocking disease. |
|
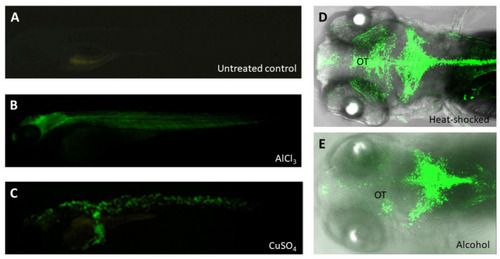
The GFP reporter was expressed in the embryos from zebrafish transgenic line huORFZ exposed to various stresses. (A) The huORFZ embryos without any treatment displayed no GFP signal during 96 hpf served as negative control. (B,C) The heavy metal-containing chemicals, including AlCl3 and CuSO4, were used individually to treat huORFZ embryos at 72 hpf and observed at 96 hpf [118]. (B) For AlCl3-treated huORFZ embryos, GFP signals were observed in the brain and muscles. (C) For CuSO4-treated huORFZ embryos, GFP signal was observed in the skin cells. (D,E) The huORFZ embryos at 72 hpf were individually treated with heat shock or 1.5% alcohol and then observed the GFP signal during 96 hpf. Although GFP was induced to express by both stresses at the CNS, the expression patterns of them were distinct. (E) Alcohol-treated huORFZ embryos displayed weak GFP signal at the optic tectum (OT). |