|
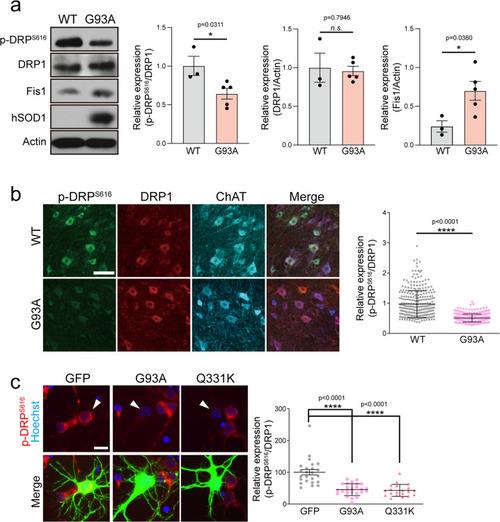
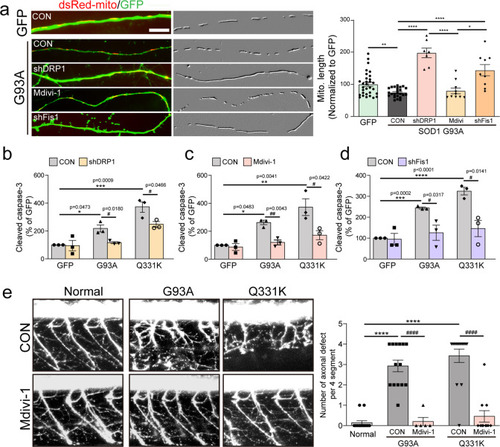
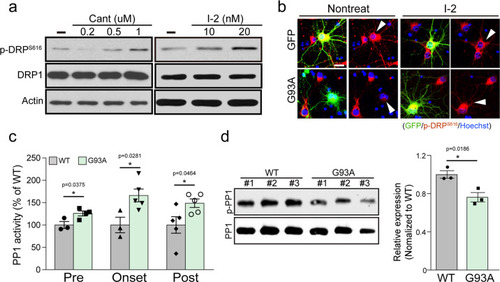
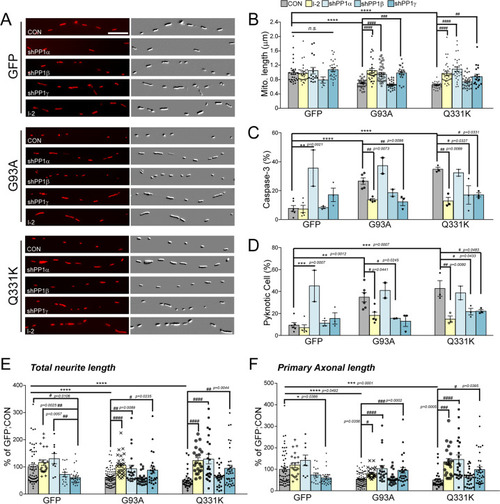
Effects of the blockade of PP1 on G93A and Q331-induced neurodegeneration.a The representative image of mitochondria in the neurite of GFP+ primary cortical neuron with 40 nM I-2 treatment or shRNA lenti-viral infection after transfection of dsRed-mito and mALS genes, over 72 h. The mitochondrial image has been embossed using Photoshop and measured on the GFP+ cortical neuron. Scale bar, 5 μm. b Analysis of mitochondrial length in (a). GFP:CON = 1.00 ± 0.06 (n = 29 GFP+ neurons), GFP:shPP1α = 1.1 ± 0.09 (n = 17 GFP+ neurons) GFP:shPP1β=0.79 ± 0.87 (n = 7 GFP+ neurons), GFP:shPP1γ = 1.08 ± 0.05 (n = 27 GFP+ neurons), GFP:I-2 = 0.96 ± 0.05 (n = 30 GFP+ neurons), G93A:CON = 0.7 ± 0.02 (n = 30 GFP+ neurons), G93A:shPP1α = 1.00 ± 0.4 (n = 33 GFP+ neurons), G93A:shPP1β = 0.66 ± 0.02 (n = 30 GFP+ neurons), G93A:shPP1γ = 0.99 ± 0.05 (n = 20 GFP+ neurons), G93A:I-2 = 1.04 ± 0.06 (n = 30 GFP+ neurons), Q331K:CON = 0.65 ± 0.02 (n = 30 GFP+ neurons), Q331K:shPP1α = 1.1 ± 0.06 (n = 31 GFP+ neurons), Q331K:shPP1β = 0.74 ± 0.03 (n = 30 GFP+ neurons), Q331K:shPP1γ = 0.89 ± 0.6 (n = 19 GFP+ neurons), Q331K:I-2 = 0.98 ± 0.05 (n = 35 GFP+ neurons). Values are mean ± S.E.M. F(2,86) = 26.64, ****P < 0.0001 for CON groups; F(4,105) = 1.710, n.s.: not significant for GFP groups; F(4,138) = 20.02, ###P = 0.0001, ####P < 0.0001 for G93A groups; F(4,138) = 20.02, ##P = 0.0089, ####P < 0.0001 for Q331K groups by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc analysis for multiple comparisons. c Quantification of cleaved caspase-3-positive neurons in GFP+ neurons with 40 nM I-2 treatment or shRNA lenti-viral infection following transfection of mALS genes, over 72 h. GFP:CON = 7.67 ± 2.06 (n = 6 independent primary culture), GFP:shPP1α = 35.61 ± 12.54 (n = 2 independent primary culture), GFP:shPP1β=8.28 ± 0.75 (n = 3 independent primary culture), GFP:shPP1γ = 17.11 ± 4.65 (n = 3 independent primary culture), GFP:I-2 = 7.5 ± 2.51 (n = 5 independent primary culture), G93A:CON = 26.59 ± 2.31 (n = 5 independent primary culture), G93A:shPP1α = 37.09 ± 5.51 (n = 2 independent primary culture), G93A:shPP1β = 18.39 ± 2.45 (n = 2 independent primary culture), G93A:shPP1γ = 12.09 ± 2.63 (n = 3 independent primary culture), G93A:I-2 = 13.79 ± 0.84 (n = 4 independent primary culture), Q331K:CON = 34.83 ± 1.370 (n = 3 independent primary culture), Q331K:shPP1α = 32.39 ± 2.39 (n = 2 independent primary culture), Q331K:shPP1β = 17.03 ± 6.39 (n = 3 independent primary culture), Q331K:shPP1γ=17.07 ± 1.44 (n = 3 independent primary culture), Q331K:I-2 = 12.57 ± 2.60 (n = 3 independent primary culture). Values are mean ± S.E.M. F(2,11) = 41.29, ****P < 0.0001 for CON groups; F(4,14) = 7.230, ***P = 0.0007 for GFP groups; F(4,11) = 14.03, ##P = 0.0096 for G93A:CON versus G93A: shPP1γ, ##P = 0.0073 for G93A:CON versus G93A: I-2; F(4,9) = 7.887, #P = 0.0327 for Q331K:CON versus Q331K: shPP1β, #P = 0.0327 for Q331K:CON versus Q331K: shPP1γ, ##P = 0.0089 by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. d Quantification of pyknotic cell in GFP+ neurons with 40 nM I-2 treatment or shRNA lenti-viral infection following transfection of mALS genes, over 72 h. GFP:CON = 9.39 ± 2.33 (n = 6 independent primary culture), GFP:shPP1α = 45.01 ± 14.25 (n = 2 independent primary culture), GFP:shPP1β = 11.08 ± 2.31 (n = 3 independent primary culture), GFP:shPP1γ = 15.40 ± 5.19 (n = 3 independent primary culture), GFP:I-2 = 6.64 ± 2.67 (n = 5 independent primary culture), G93A:CON = 34.85 ± 4.25 (n = 6 independent primary culture), G93A:shPP1α=41.18 ± 6.97 (n = 2 independent primary culture), G93A:shPP1β = 15.78 ± 0.16 (n = 2 independent primary culture), G93A:shPP1γ = 13.13 ± 4.84 (n = 3 independent primary culture), G93A:I-2 = 17.98 ± 3.12 (n = 5 independent primary culture), Q331K:CON = 42.76 ± 7.15 (n = 3 independent primary culture), Q331K:shPP1α = 38.71 ± 6.21 (n = 2 independent primary culture), Q331K:shPP1β = 21.69 ± 2.95 (n = 3 independent primary culture), Q331K:shPP1γ = 22.14 ± 1.44 (n = 3 independent primary culture), Q331K:I-2 = 14.45 ± 2.93 (n = 3 independent primary culture). Values are mean ± S.E.M. F(2,12) = 17.58, **P = 0.0012, ***P = 0.0007 for each CON group; F(4,14) = .101, ***P = 0.0007 for each GFP group; F(4,13) = 6.49, #P = 0.0245 for G93A:CON versus G93A:shPP1γ, #P = 0.0441 for G93A:CON versus G93A:I-2; F(4,9) = 7.405, #P = 0.0433 for Q331K:CON versus Q331K: shPP1β, #P = 0.0483 for Q331K:CON versus Q331K: shPP1γ, ##P = 0.0080 by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. e Analysis of total neurite length in (a). GFP:CON = 100 ± 8.70 (n = 57 GFP+ neurons), GFP:I-2 = 115.90 ± 9.90 (n = 22 GFP+ neuron), GFP: shPP1α=130.3 ± 18.51 (n = 9 GFP+ neuron), GFP:shPP1β=72.12 ± 8.25 (n = 16 GFP+ neuron), GFP:shPP1γ=60.66 ± 5.05 (n = 29 GFP+ neuron), G93A:CON = 61.61 ± 3.10 (n = 91 GFP+ neuron), G93A:I-2 = 106.3 ± 7.51 (n = 27 GFP+ neuron), G93A:shPP1α = 93.39 ± 13.05 (n = 21 GFP+ neuron), G93A:shPP1β = 57.56 ± 4.52 (n = 23 GFP+ neuron), G93A:shPP1γ = 88.06 ± 11.45 (n = 26 GFP+ neuron), Q331K:CON = 42.39 ± 3.47 (n = 25 GFP+ neuron), Q331K:I-2 = 122.2 ± 10.61 (n = 21 GFP+ neuron), Q331K:shPP1α=128.8 ± 17.3 (n = 23 GFP+ neuron), Q331K:shPP1β = 60.97 ± 6.15 (n = 27 GFP+ neuron), Q331K:shPP1γ = 94.81 ± 11.55 (n = 37 GFP+ neuron),. Values are mean ± S.E.M. F(2,170) = 19.98, ****P < 0.0001 for each CON group;F(4,128) = 7.415, #P = 0.0106, ##P = 0.0025 for GFP:I-2 versus GFP:shPP1γ, ##P = 0.0057 for GFP:shPP1α versus GFP:shPP1γ; F(4,183)=9.91, #P = 0.0235, #P = 0.0089, ###P = 0.0008 for each G93A group; F(4,128) = 10.63, ##P = 0.0044, ####P < 0.0001 for each Q331K group by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. f Analysis of total axonal length in (a). GFP:CON = 100 ± 10.33 (n = 56 GFP+ neuron), GFP:I-2 = 119.4 ± 11.51 (n = 22 GFP+ neuron), GFP: shPP1α = 141.4 ± 24.44 (n = 9 GFP+ neuron), GFP:shPP1β = 73.71 ± 9.06 (n = 16 GFP+ neuron), GFP:shPP1γ = 59.58 ± 6.13 (n = 29 GFP+ neuron), G93A:CON = 54.08 ± 3.02 (n = 86 GFP+ neuron), G93A:I-2 = 80.63 ± 4.57 (n = 27 GFP+ neuron), G93A:shPP1α = 02.8 ± 15.10 (n = 21 GFP+ neuron), G93A:shPP1β = 58.73 ± 6.10 (n = 23 GFP+ neuron), G93A:shPP1γ = 95.06 ± 13.3 (n = 26 GFP+ neuron), Q331K:CON = 49.70 ± 7.46 (n = 28 GFP+ neuron), Q331K:I-2 = 131.7 ± 15.21 (n = 21 GFP+ neuron), Q331K:shPP1α = 145.8 ± 20.67 (n = 23 GFP+ neuron), Q331K:shPP1β = 60.02 ± 7.01 (n = 27 GFP+ neuron), Q331K:shPP1γ = 98.4 ± 12.79 (n = 37 GFP+ neuron). Values are mean ± S.E.M. F(2, 167) = 15.91, ***P = 0.0001, ****P < 0.0001 for each CON group; F(4,127) = 5.083, #P = 0.0386 for each GFP group;F(4,178) = 9.565, #P = 0.0356, ###P = 0.0002, ####P < 0.0001 for each G93A group;F(4,131) = 4.236, #P = 0.0395, ###P = 0.0005, ####P < 0.0001 for each Q331K group by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test.
|