- Title
-
The Paf1 Complex and P-TEFb have reciprocal and antagonist roles in maintaining multipotent neural crest progenitors
- Authors
- Jurynec, M.J., Bai, X., Bisgrove, B.W., Jackson, H., Nechiporuk, A., Palu, R.A.S., Grunwald, H.A., Su, Y.C., Hoshijima, K., Yost, H.J., Zon, L.I., Grunwald, D.J.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
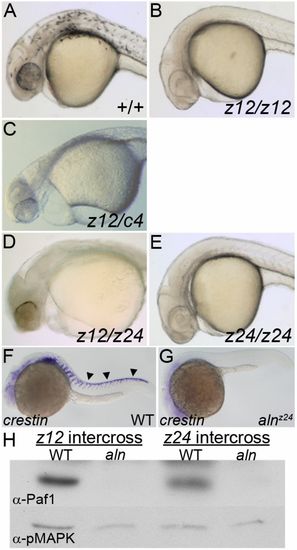
alnz24 is a null mutation that regulates NC formation and encodes RNA polymerase II-associated factor 1 (Paf1). (A-E) 36 hpf wild-type and aln mutant embryos. Wild-type embryos (A) have pigmented melanophores lacking in embryos harboring combinations of aln mutant alleles: (B) homozygous for the alnz12 deletion mutation, (C) transheterozygous for the alnz12 and c4 deletions, (D) transheterozygous for the alnz12 deletion and alnz24 ENU-induced mutations, and (E) homozygous for the alnz24 mutation. (F,G) crestin expression detected by whole-mount in situ hybridization in 24 hpf wild-type sibling (F) and alnz24 mutant (G) embryos, indicating a complete absence of migrating trunk NC in alnz24. Arrowheads indicate premigratory and migrating trunk NC. A-G are lateral views with anterior to the left. (H) Paf1 protein is not detected by immunoblot analysis in 36 hpf alnz12 or alnz24 mutant embryos, but is readily detected in wild-type control siblings. Immunoblot detection of pMAPK serves as a protein-loading control. |
|
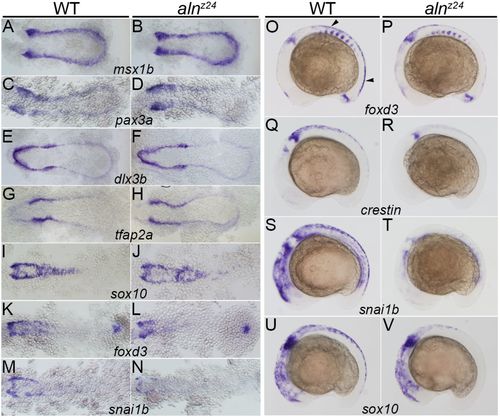
Zygotically supplied Paf1 is not required for the initial induction or specification of the premigratory NC, but is required at later stages for development of the full premigratory and migrating NC population. Gene expression detected by whole-mount in situ hybridization in 11-11.5 hpf (A-D), 11.5-12 hpf (E-J), 12-12.5 hpf (K-N) and 16 hpf (O-V) wild-type sibling and alnz24 mutant embryos. Expression of msx1b (A,B), pax3a (C,D), dlx3b (E,F), tfap2a (G,H) and sox10 (I,J) is similar in alnz24 mutants and wild-type siblings. A slight decrease in foxd3 (K,L) and snai1b (M,N) expression is detected in alnz24 embryos when compared with wild-type siblings. Expression of foxd3 (O,P), crestin (Q,R), snai1b (S,T) and sox10 (U,V) are all reduced or absent in the trunk region of 16 hpf alnz24 mutant embryos. A-N are dorsal views with anterior towards the left. O-V are lateral views with anterior towards the left. Arrowheads indicate premigratory NC. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
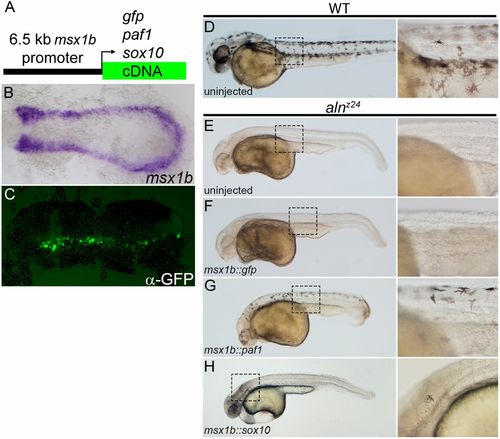
Paf1 is required cell-autonomously in the NC lineage for melanophore development. (A) Schematic representation of a msx1b promoter construct used to express gfp, paf1 or sox10 cDNAs. (B) Endogenous msx1b expression in an 11.5 hpf embryo detected by whole-mount in situ hybridization. (C) GFP (detected by immunohistochemistry) is expressed mosaically, but only within the normal msx1b expression domain of an 11.5 hpf embryo injected at the one-cell stage with 50 pg msx1b::GFP plasmid DNA. (D-H) 48 hpf control and DNA-injected embryos. (D) Wild-type embryo exhibiting normal distribution and morphology of melanophores. Uninjected alnz24 mutant embryos (E) and alnz24 mutants injected with msx1b::GFP plasmid DNA (F) completely lack NC-derived melanophores. (G) alnz24 mutants injected with msx1b::paf1 plasmid DNA have widely distributed melanophores with normal stellate morphology. (H) Expression of sox10 in the msx1b expression domain fails to rescue melanophore development; abnormal pigment cells were occasionally found in the heads of plasmid-injected mutant embryos. (B,C) Dorsal views of flat-mounted embryos, with anterior towards the left. D-H are lateral views of entire embryos (anterior towards the left); boxed regions are shown at higher magnification to the right of each whole-embryo view. |
|
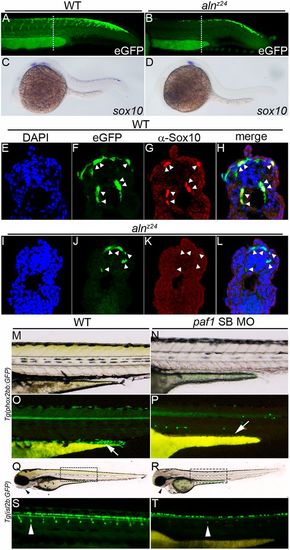
Paf1 is necessary to maintain NC gene expression, identity and the normal complement of multipotent premigratory NC. (A,B) Confocal images of eGFP expression in 26-28 hpf wild-type (A) and alnz24 mutant (B) embryos carrying the Tg(-4.9sox10:egfp)ba2 transgene. Dashed lines indicate approximate plane of section in E-L. (C,D) sox10 gene expression detected by whole-mount in situ hybridization in 24 hpf wild-type (C) and alnz24 mutant (D) embryos. (E-L) Transverse sections through the trunks of 26-28 hpf wild-type (E-H) and alnz24 mutant (I-L) transgenic embryos. In wild-type embryos, eGFP expression colocalizes with Sox10 protein expression (NC cells, indicated by arrowheads) (F-H). In contrast, all migrating GFP+ cells (arrowheads) in the trunk of alnz24 mutant embryos do not express Sox10 (J-L). (M-P) Lateral views with anterior towards the left of 72 hpf wild-type (M,O) and low dose paf1 MO-injected (N,P) Tg(phox2bb:GFP) embryos. GFP-expressing enteric neurons (arrow) are present in the gut of wild-type embryos (M) and are completely absent (arrow) in embryos with reduced paf1 function (P). GFP+ cells in paf1 MO-injected embryos are likely sympathetic neurons. (Q-T) Lateral views with anterior towards the left of 72 hpf wild-type (Q,S) and low dose paf1 MO-injected (R,T) Tg(isl2b:GFP) embryos. Reduction of paf1 function diminishes melanophore formation, and results in cardiac edema and loss of jaw structures (arrowheads) in MO-injected embryos (R) when compared with wild-type embryos (Q). GFP fluorescence marking DRG cells (arrowheads) in wild-type (S) and paf1 MO-injected embryos (T). DRG cell formation in paf1 MO-injected embryos is significantly reduced (T). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
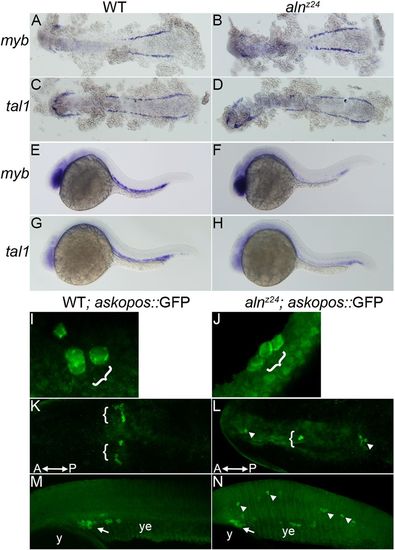
Paf1 is necessary for maintenance of blood and germline stem cell populations. (A-D) Expression of myb (A,B) or tal1 (C,D), markers of early blood precursors in the anterior and posterior lateral mesoderm at 12 hpf, is similar in alnz24 mutant and wild-type sibling embryos. (E-H) In contrast, by 26 hpf, expression of myb (E,F) and tal1 (G,H) in the intermediate cell mass is significantly reduced in alnz24 mutant embryos. (I-N) Wild-type sibling and alnz24; askopos::GFP transgenic embryos that express GFP in PGCs. Small clusters of PGCs arise similarly in wild-type and alnz24 mutant 50-60% epiboly embryos (I,J). PGCs are present in two bilateral clusters at 12 hpf (K) and coalesce at the midline above the yolk extension in 32 hpf (M) wild-type sibling embryos. In contrast, PGCs are present in ectopic locations in 12 hpf (L) and 32 hpf (N) alnz24 mutant embryos. Brackets and arrows indicate normal clusters of PGCs, whereas arrowheads indicate ectopic PGCs. y, yolk; ye, yolk extension. A-D,K,L are dorsal views with anterior towards the left; E-H,M,N, are lateral views with anterior towards the left; I,J are dorsolateral views with animal pole upwards. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
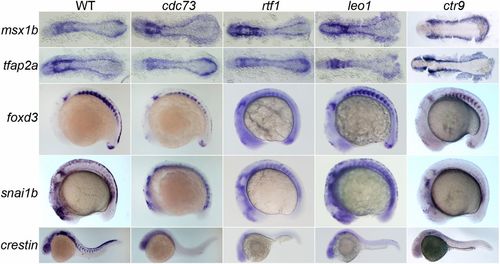
All members of the Paf1C are needed for maintenance of the trunk premigratory NC. Gene expression in 12-12.5 hpf (msx1b and tfap2a), 16-18 hpf (foxd3 and snai1b) and 24 hpf (crestin) wild-type, cdc73/sunrise, rtf1kt641, leo1LA1186 and ctr9zy13 mutant embryos. Expression of msx1b and tfap2a, which mark the NC precursor domain and NC lineage, respectively, is not altered in Paf1C mutant embryos, while expression of foxd3 and snai1b, which mark the premigratory NC, is severely reduced or absent in the trunk of all Paf1C mutant embryos. Paf1C mutant embryos are devoid of crestin-positive cells, except leo1LA1186 mutants, which have a few crestin-positive cells in the trunk. msx1b- and tfap2a-stained embryos are shown as dorsal views with anterior to the left. foxd3-, snai1b- and crestin-stained embryos are lateral views with anterior towards the left. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
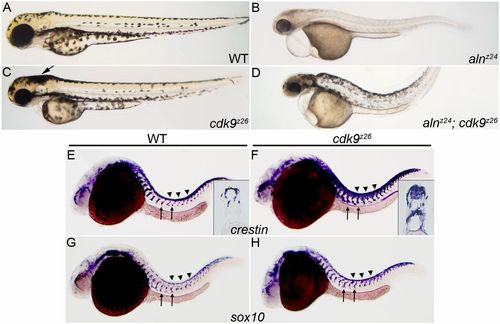
Loss of Cdk9 function expands both the premigratory and migratory NC populations, and suppresses loss of melanophore formation in aln/paf1 mutants. (A-D) Lateral views of 48 hpf wild-type (A), alnz24 mutant (B), cdk9z26 mutant (C) or alnz24; cdk9z26 double mutant embryos (D). (E-H) NC expression of crestin (E,F) and sox10 (G,H) in 26 hpf wild-type and cdk9z26 mutant embryos. Arrow in C indicates an increase in the number of melanophores in the head of cdk9z26 mutant embryos. Insets in E and F are cross-sections through the trunk of crestin-expressing embryos. Arrows indicate migrating NC and arrowheads indicate premigratory NC. |