- Title
-
Development of the brain vasculature and the blood-brain barrier in zebrafish
- Authors
- Quiñonez-Silvero, C., Hübner, K., Herzog, W.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
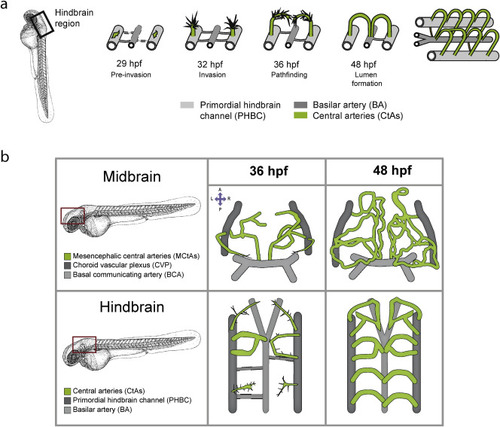
Brain angiogenesis in zebrafish. a) Schematic depiction of hindbrain vascularization in the zebrafish. Localization of the hindbrain is indicated with a black box. Around 29 hpf, the tip cells of the central arteries (CtAs, green) become specified in the dorsal site of the primordial hindbrain channels (PHBCs, light grey). CtA sprouts invade the hindbrain at 32 hpf by migrating dorsally, then turn and around 36 hpf they migrate ventrally towards the basilar artery (BA, dark grey). Between 36 and 48 hpf the CtAs establish connections with the basilar artery or each other to become perfused. At 48 hpf all CtAs have a functional lumen and a characteristic arch architecture (image modified from (Hübner et al., 2018)). b) Illustration of the midbrain and hindbrain vasculature in zebrafish embryos in dorsal views. The red boxes indicate midbrain and hindbrain localization. The upper panels represent the midbrain capillaries (mesencephalic central arteries, MCtAs) at 36 hpf (left), during sprouting and migration from the choroid vascular plexus, and at 48 hpf (right), when they are connected to the basal communicating artery (BCA) and form a complex vascular network. The lower panels represent the hindbrain capillaries during sprouting and migration (36 hpf, left) and after lumenization (48 hpf, right). Anterior to the top. A: anterior, P: posterior, L: left, R: right. The zebrafish embryo overview was taken from (Kimmel et al., 1995). |
|
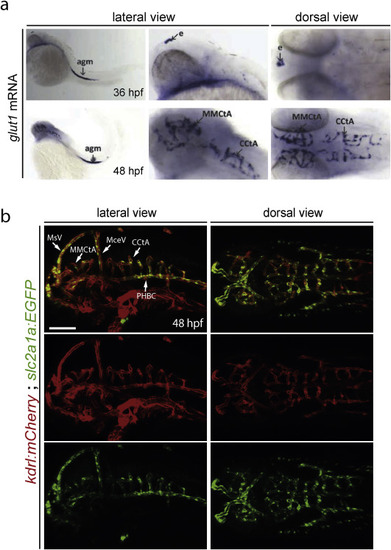
glut1 mRNA expression labels the brain capillaries of the BBB. a) glut1b mRNA expression in zebrafish embryos. At 36 hpf (upper panels) glut1 expression is detected in the epiphysis (e) and in the aorta-gonad-mesonephros (agm). At 48 hpf (lower panels) glut1 expression becomes prominent in the brain capillaries (MCtAs and CtAs). In situ probe synthesis and hybridization was done according to (Thisse and Thisse, 2008) using the following primers: fwd: GCAGGAGGAACTCAATGCTC, rev+T7; AACGTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAAACTGGAAGCACATTCCCACT. b) Tg(slc2a1a:EGFP)mu213 reporter line expression in 48 hpf embryos. At 48 hpf glut1b (slc2a1a) is strongly expressed in brain capillaries (MCtAs and CtAs) of Tg(kdrl:ras-mCherry)s896 and in the extracerebral vessels PHBC, BA, BCA, MCeV, MtA, MsVs, but not in the rest of the vessels in the head (lateral view). 8.7 kb of the slc2a1a genomic region upstream of the ATG were cloned upstream of EGFP via Gateway into a Tol2 destination vector (Villefranc et al., 2007) and used for transgenesis as describe previously (Helker et al., 2015). PHBC, primordial hindbrain channel; BA, basilar artery; BCA, basal communicating artery; MCtAs, mesencephalic central arteries; CtAs, central arteries; MCeV, middle cerebral vein; MtA, metencephalic artery; MsV, mesencephalic vein; Scale bar: 100 μm. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 457(2), Quiñonez-Silvero, C., Hübner, K., Herzog, W., Development of the brain vasculature and the blood-brain barrier in zebrafish, 181-190, Copyright (2019) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.