- Title
-
Inhibition of the mitochondrial calcium uniporter rescues dopaminergic neurons in pink1-/- zebrafish.
- Authors
- Soman, S., Keatinge, M., Moein, M., DaCosta, M., Mortiboys, H., Skupin, A., Sugunan, S., Bazala, M., Kuznicki, J., Bandmann, O.
- Source
- Full text @ Eur. J. Neurosci.
|
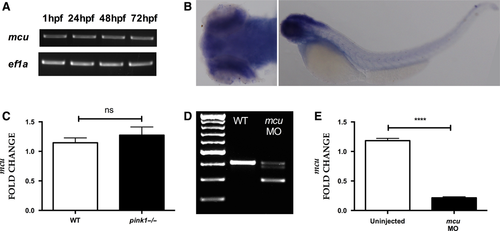
mcu expression. (A) RT-PCR analysis showing consistent expression of mcu throughout development (1, 24, 48 and 72 hpf). (B) In situ hybridization with dorsal (left) and lateral (right) views of mcu expression in 3 dpf zebrafish larvae, demonstrating strong expression in the brain. (C) Quantification of mcu mRNA at 3 dpf, demonstrating similar expression levels in wt and pink1−/−. (D) RT-PCR analysis of mcu knockdown using antisense morpholino (MO) at 3 dpf, demonstrating the marked effect of MO mediated mcu k/d on mcu wild type transcript levels. (E) Q-PCR based confirmation of marked effect of MO-mediated mcu k/d on mcu mRNA transcript levels (****P < 0.0001). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
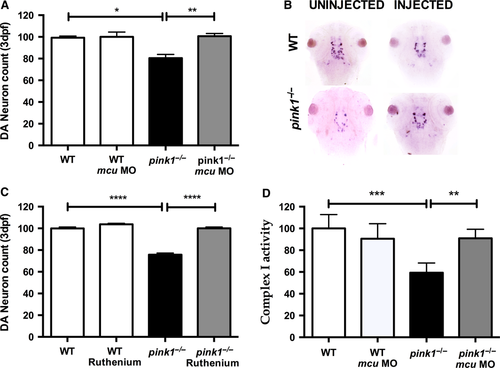
Knockdown of mcu leads to rescue of dopaminergic neurons. (A) Dopaminergic (DA) neuronal cell count in wt, wt MCU (wt microinjected with MO against mcu), pink1−/−, pink1−/− MCU (pink1−/− microinjected with MO against mcu) zebrafish larvae at 3 dpf. DA neuronal cell count is reduced in pink1−/− (*P = 0.012) but completely rescued after MCU inactivation (**P = 0.0085). The scale on the y axis reflects % of DA neurons compared to wt controls. (B) Representative image showing dopaminergic neurons in the diencephalon [using tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) whole mount in situ (WISH) staining] in wt controls and pink1−/− zebrafish injected with and without mcu MO. (C) Dopaminergic (DA) neuronal cell count in wt, wt embryos treated with Ruthenium red (RR) (wt RR), pink1−/− and pink1−/− embryos treated with RR (pink1−/− RR) with complete rescue of DA neurons in pink1−/− larvae after RR treatment (****P < 0.0001). The scale on the y axis reflects % of DA neurons compared to wt controls. (D) WT vs pink1−/− (***P = 0.0007). Mitochondrial complex I activity is restored in 5 dpf pink1−/− following mcu k/d (**P = 0.0071). Complex I activity is measured in μmol oxidized NADH per 1 unit of citrate synthase activity and set to 100% for the complex I activity in WT controls. The scale on the y axis reflects % of complex I activity compared to wt controls. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
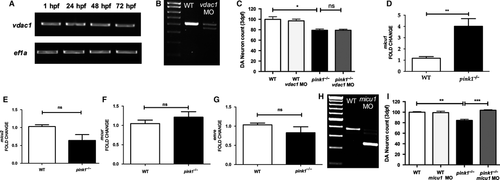
VDAC1 and MICU1 analysis. (A) RT-PCR analysis demonstrating expression of vdac1 at 1, 24, 48 and 72 hpf. (B) RT-PCR analysis of vdac1 in wt controls and after MO mediated vdac1 k/d, demonstrating a marked effect of the vdac1 MO on vdac1 wt transcript levels. (C) Dopaminergic (DA) neuronal cell count in wt, wt vdac1 (wt injected with MO against vdac1), pink1−/−, pink1−/− vdac1 (pink1−/− injected with MO against vdac1) at 3 dpf, reflecting the lack of an effect of VDAC1 inactivation on DA neuronal cell count in pink1−/− (P > 0.99) (*P = 0.0105). (D) qPCR analysis of micu1, showing significant upregulation of micu1 in pink1−/− larvae at 3 dpf compared to wt (**P = 0.0066). (E) qPCR analysis of micu2, showing a non-significant down regulation of micu2 in pink1−/− larvae at 3 dpf compared to wt (nsP = 0.0902). (F) qPCR analysis of mcur, showing a non-significant upregulation of mcur in pink1−/− larvae at 3 dpf compared to wt (nsP = 0.2088). (G) qPCR analysis of emre, showing a non-significant down regulation of emre in pink1−/− larvae at 3 dpf compared to wt (nsP = 0.2712). (H) RT-PCR analysis of micu1 at 3 dpf in uninjected larvae (WT) and after MO mediated k/d (micu MO), demonstrating the marked effect of micu1 MO injection on micu1 mRNA transcript levels. (I) Dopaminergic (DA) neuronal cell count in wt, wt micu1 (wt injected with MO against micu1), pink1−/−, and pink1−/− micu1 (pink1−/− injected with MO against micu1) zebrafish larvae at 3 dpf, demonstrating the rescue effect of MICU1 inactivation on DA neurons in PINK1 deficiency (***P = 0.0004). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|