- Title
-
Deletion of a dehydratase important for intracellular growth and cording renders rough Mycobacterium abscessus avirulent
- Authors
- Halloum, I., Carrère-Kremer, S., Blaise, M., Viljoen, A., Bernut, A., Le Moigne, V., Vilchèze, C., Guérardel, Y., Lutfalla, G., Herrmann, J.L., Jacobs, W.R., Kremer, L.
- Source
- Full text @ Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA
|
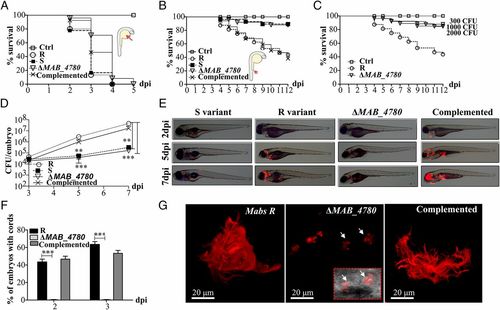
The ΔMAB_4780 mutant is extremely attenuated in infected zebrafish embryos. (A) Survival curves of embryos injected in the yolk sac (~100-200 cfu) of tdTomato-expressing Mabs S, Mabs R, ΔMAB_4780 mutant, or the complemented strain (n = 20). There are no significant differences between the different infected strains. Data are representative of three independent experiments. The Inset represents an embryo at 30 hpf, and the arrow indicates the injection site in the yolk. Ctrl, noninfected control embryos. (B) Survival curve for zebrafish embryos (n = 20) injected i.v. at 30 hpf with 100-200 cfu of the different Mabs strains compared with control embryos. Larvae infected with the ΔMAB_4780 mutant showed a significant increase in survival compared with larvae infected with the parental strain (P = 0.0008, log-rank test), whereas the complemented strain behaved like the wild-type R variant and restored virulence (no statistically significant differences were seen in the survival of embryos infected with the R or complemented strains; log-rank test). Shown are representative data of three independent experiments. The Inset represents an embryo at 30 hpf, and the arrow indicates the caudal vein injection site. (C) Survival curve of embryos infected with increasing doses of the ΔMAB_4780 mutant. Embryos injected with the ΔMAB_4780 mutant showed no statistically significant difference with the control group in terms of survival, regardless of the dose. Data shown are representative of two independent experiments (n = 20). (D) In vivo growth of the ΔMAB_4780 mutant. Enumeration was performed by plating homogenates of whole individual larvae at different time points on selective agar plates and subsequent counting of bacterial colonies. A significant reduction in bacterial burden was observed with the ΔMAB_4780 mutant (Kruskal-Wallis with Dunn’s multiple test; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001). Data are representative of three independent experiments. (E) Bright field/fluorescence overlay images of tdTomato-labeled Mabs (<150 cfu). Each larva was followed and imaged at 2, 5, and 7 dpi. (F) Cords were recorded in i.v.-infected embryos with either tdTomato-expressing Mabs R, ΔMAB_4780 mutant, or complemented strains at 2 and 3 dpi. Cords were never observed in ΔMAB_4780-infected embryos. Histograms represent means calculated from three independent experiments (n = 10 per experiment), and the statistical test used was Fisher’s exact test; ***P < 0.001. Error bars represent the SEM. (G) Maximum intensity projection of confocal images showing representative pathological events in 3 dpi embryos i.v.-infected with Mabs R, ΔMAB_4780, or complemented strains expressing tdTomato (100-200 cfu). Arrows indicate infected cells containing the tdTomato-labeled ΔMAB_4780 mutant. Only Mabs R and complemented strains formed cords. |
|
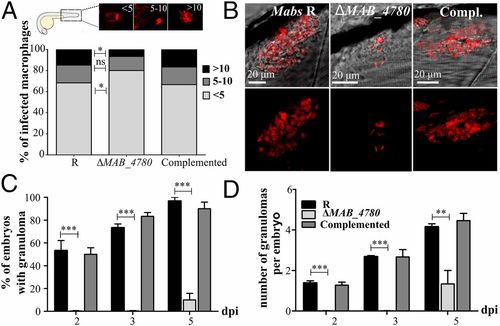
The intracellular growth defect of ΔMAB_4780 is associated with impaired granuloma formation in zebrafish. (A) Average proportion of infected macrophages classified as mildly, moderately, or highly infected (containing <5, 5-10, and >10 bacteria, respectively) at 24 hpi. Significance was assessed by a Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple posttest (*P < 0.05). Top enclosed panel shows representative infected macrophage of each class. (B) Maximum intensity projection of confocal images showing representative granuloma-like structures in 3 dpi larvae i.v.-infected with Mabs R, ΔMAB_4780, or the complemented strain expressing tdTomato. (C) Kinetics of granuloma formation in intravenously-infected embryos (~150 cfu; n = 30). Histograms represent means calculated from three independent experiments. Overall, ΔMAB_4780 mutant-infected embryos developed significantly less granuloma compared with the R and complemented strains. (n = 30; Fisher’s exact test; ***P < 0.001). Error bars represent the SEM. (D) Number of granulomas per embryo harboring granuloma. A significant reduction in the number of granulomas per embryo is found in embryos infected with ΔMAB_4780 compared with R-infected embryos. The statistical test used was the Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple posttest (n = 30); **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. Error bars represent the SEM. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
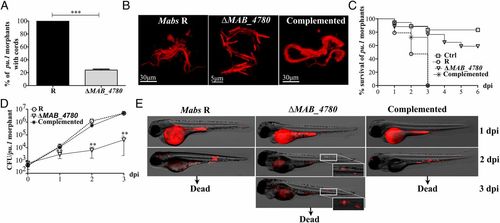
MABS_4780 is required for acute and lethal zebrafish infection. (A) Cords were recorded in pu.1 embryos infected i.v. with ~100-200 cfu of either tdTomato-expressing Mabs R, ΔMAB_4780, or the complemented strain at 2 and 3 dpi (n = 20). Percentage of pu.1 morphants harboring mycobacterial cords after infection with either the R variant or the ΔMAB_4780 mutant (n = 20) at 3 dpi. Data are expressed as means calculated from three independent experiments (n = 10 per experiment). The statistical test was Fisher’s exact test; ***P < 0.001. Error bars represent the SEM. (B) Maximum intensity projection of confocal images showing representative cords in pu.1 morphants i.v. infected with the Mabs R, ΔMAB_4780, and complemented strains expressing tdTomato at 2 dpi (<150 cfu). Only Mabs R and the complemented strain exhibited cords made of structured networks of multiple tight bundles, consisting of end-to-end and side-to-side parallel-aligned bacilli along the long axis of the cord, whereas extracellular growth of ΔMAB_4780 resulted essentially in size-limited and very thin structures. (C) Survival of macrophage-depleted embryos infected with 150 cfu at 30 hpf. Embryos are significantly more susceptible to R infection (P < 0.0001, log-rank test) than to ΔMAB_4780 infection (statistically not different from pu.1 morphant control). Shown are representative data of three independent experiments. (D) Growth kinetic of ΔMAB_4780 in pu.1 morphants (~100-200 cfu). The cfu enumeration showed reduced ΔMAB_4780 loads compared with R loads (**P < 0.01; Mann–Whitney test). Symbols represent means calculated from three independent experiments. Error bars represent the SEM. (E) Real-time imaging of pu.1 morphants infected as in B, with special emphasis on cording. Autofluorescence of the yolk is seen at 1 dpi. |
|
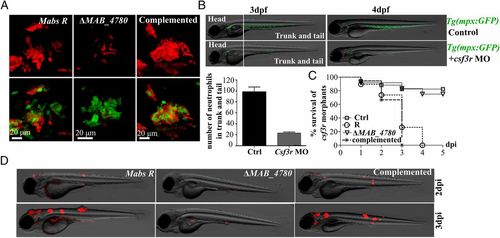
Virulence of ΔMAB_4780 is attenuated in a neutrophil-depleted host. (A) Maximum intensity projection of confocal images showing representative neutrophil activity (at 2 dpi) in pu.1 Tg(mpx:egpf) morphants i.v.-infected with Mabs R, ΔMAB_4780, or complemented strain expressing tdTomato. (B) Csf3r Tg(mpx:egpf) morphants showed highly reduced neutrophil numbers at 3 and 4 dpf, confirming the proper activity of the morpholino. The numbers of mpx-positive neutrophils counted in the trunk and tail at 3 dpf are depicted in the graph. (C) Survival curve of neutrophil-depleted larvae i.v.-infected with the Mabs R, ΔMAB_4780, and complemented strains (~150 cfu, n = 20 per group). These larvae were hypersusceptible to Mabs R and to the complemented strain (P < 0.001, log-rank test) but not to ΔMAB_4780 (statistically not different from PBS-injected controls). Shown are representative data from two independent experiments. (D) Representative fluorescence and DIC overlays of infected csf3r morphants at 2 and 3 dpi. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
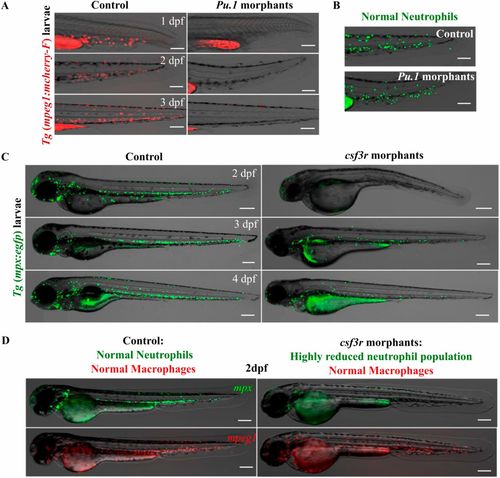
Efficacy of the macrophage and neutrophil depletion strategy. (A) The double transgenic zebrafish line [tg(mpx:egfp)/(mpeg1:mCherry-F)] was injected at the one-cell stage with the pu.1 morpholino to specifically deplete macrophages. Representative overlays of transmission and red fluorescence stereomicroscope time-lapse images showing the pu.1 morpholino effect on the macrophage population in the tail region. (Scale bars, 200 µm.) (B) Representative overlays of transmission and green fluorescence stereomicroscope images showing the absence of effect of the pu.1 morpholino on the neutrophil population in the tail region at 48 hpf. (Scale bars, 200 µm.) This resulted in a total depletion of macrophages, whereas neutrophils remained unaffected. The first macrophages start to renew at 4 dpf. (C) The double transgenic zebrafish line [tg(mpx:egfp)/(mpeg1:mCherry-F)] exhibiting green neutrophils and red macrophages was injected at the one-cell stage with the csf3r morpholino to specifically deplete neutrophils. Representative overlays of transmission and green fluorescence stereomicroscope time-lapse images show the csf3r morpholino effect in neutrophil population in whole embryo. (Scale bars, 200 µm.) This resulted in a highly reduced neutrophil population. (D) Shown are the overlays of transmission and green/red fluorescence stereomicroscope images of representative 2 dpf larvae showing that the macrophage population remained unaffected in the csf3r morphants. |