- Title
-
CDX4 and retinoic acid interact to position the hindbrain-spinal cord transition
- Authors
- Chang, J., Skromne, I., Ho, R.K.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
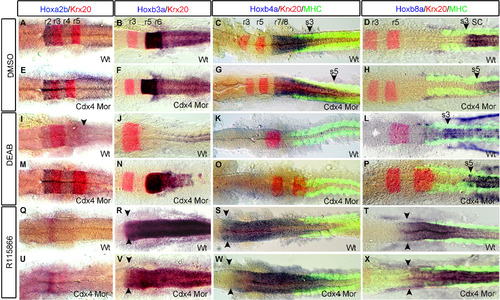
Hindbrain and spinal cord hox gene expression shifts along the AP-axis when Cdx4 or RA functions are perturbed. Expression of hoxa2b in r2-4 and hoxb3a in r5-6 is the same in Cdx4-deficient embryos (E, F) and wild-types (A, B). hoxb4a expression in r7/8 is caudally expanded in Cdx4-deficient embryos (G arrowhead) compared to wildtypes (C arrowhead). In RA-deficient embryos hoxb3a (J) and hoxb4a (K) expression is lost, while hoxa2b expression in r4 is caudally expanded (I arrowhead). In RA/Cdx4 deficient embryos, hoxb3a expression is rescued (N) but not hoxb4a (O). In both wild type and Cdx4 deficient embryos treated with R115866 hoxa2b (Q, U) expression is lost while hoxb3a (R, V) and hoxb4a (S, W) expression are both rostrally expanded. The anterior expression limit of spinal cord hoxb8a is located at somite 3 in wildtypes (D arrowhead) and RA deficient embryos (L arrowhead) but its expression is caudally shifted to somite 5 in Cdx4 deficient embryos (H arrowhead) and RA/Cdx4 deficient embryos (P arrowhead). hoxb8a expression expands into the hindbrain in both wild type (T arrowheads) and Cdx4 deficient embryos (X arrowhead) treated with R115866. (A-X) are co-stained with krx20 (r3,r5). (C, D, G, H, K, L, O, P, S, T, W, X) co-stained with myosin heavy chain antibody (somites). (A-X) flat-mounted embryos at 20 somite stage n=45/45 per condition. |
|
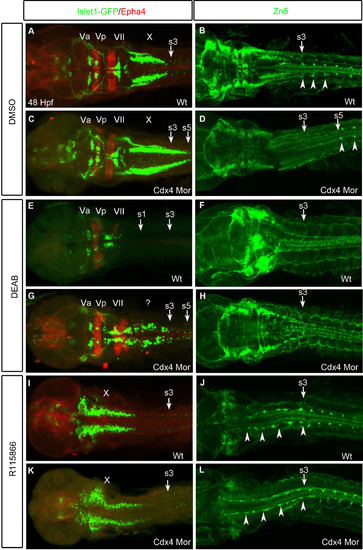
Hindbrain and spinal cord neural populations shift along the AP-axis when Cdx4 or RA functions are perturbed. (A,C,E,G,I,K) Branchial motor neurons marked by Islet1-Gfp and r3,r5 visualized by anti-Epha4. The trigeminals(Va/Vp) in r2-3 and facials(VII) in r6 are unchanged but the vagals(X) in r7/8 are caudally expanded in Cdx4-deficient embryos (C) compared to wildtypes (A). Vagals (r7/8) and Epha4 (r5) are lost in RA-deficient embryos (E). Epha4 in r5 and Islet1-Gfp cells in r5-8 are rescued in RA/Cdx4 deficient embryos (G). Vagals are rostrally shifted while trigeminals and facials are absent in both wildtypes (I) and Cdx4-deficient embryos (K) treated with R115866. (B,D,F,H,J,L) Spinal cord motor neurons marked by Zn5 antibody. The first spinal cord motor neuron arises at the level of somite 3 in wildtypes (B arrow) but at the level of somite 5 in Cdx4-deficient embryos (D arrow). Spinal cord motor neurons are lost in RA-deficient (F) and RA/Cdx4 deficient (H) embryos. Spinal cord motor neurons expand rostrally in both wildtypes (J) and Cdx4-deficient embryos (L) treated with R115866. (A-L) Flat-mounted embryos at 48 hpf. (A,C,E,G,I,K) n=30/30 per condition and (B,D,F,H,J,L) n=15/15 per condition. |
|
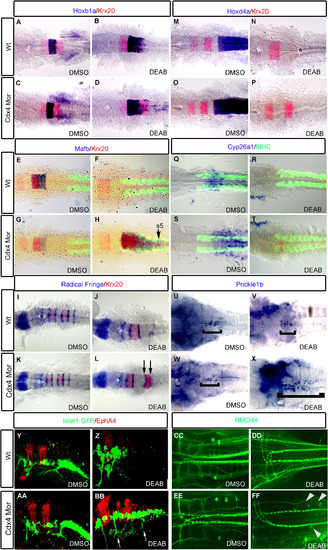
Knockdown of Cdx4 in RA-deficient embryos rescues the posterior hindbrain. hoxb1a expression in r4 is slightly expanded in RA-deficient embryos (B) compared to wildtypes (A) and Cdx4-deficient embryos (C). Expression of krx20 in r5; mafb in r5,r6; hoxd4a and cyp26a1 in r7/8 are lost in RA-deficient embryos (F, N, R) compared to wildtypes (E, M, Q) and Cdx4-deficient embryos (G, O, S). In RA/Cdx4 deficient embryos hoxb1a (D) expression is reduced, krx20 in r5 (D, H, L, P), mafb in r5,r6 (H) is rescued but hoxd4a (P) and cyp26a1 (T) expression in r7/8 is still absent. Six radical fringe (rf) bands marking rhombomere boundaries are found in wildtypes (I) and Cdx4-deficient embryos (K). Three rf bands are detected in RA-deficient embryos (J), while two additional bands, flanking krx20 expression in r5, return in RA/Cdx4 deficient embryos (L arrows). Prickle1b expression is in facial motor neurons of r4-6 in wildtypes (U bracket), cdx4 morphants (W bracket) and RA deficient embryos (V bracket). Prickle1b expression is expanded into the r7/8 position in Cdx4/RA double deficient embryos (X bracket). (Y-Z, AA, BB) Lateral view of hindbrain motor neurons marked by Islet:gfp and r3,5 marked with epha4. Branchal motor neurons in cdx4 morphants (AA) appear similar to wildtypes (Y). Vagal motor neurons of r7/8 are absent in RA deficient embryos (Z). Islet:gfp neurons return to r7/8 in Cdx4/RA double deficient embryos (BB arrows). RMO44 antibody marks reticulospinal neurons in wild-types (CC) and Cdx4-deficient embryos (EE). Mi and CaD are absent in RA-deficient embryos (DD) but return in Cdx4/RA deficient embryos (FF arrowheads). (A-P) are co-stained with krx20 (r3,r5) and (E-dH, Q-T) are co-stained with myosin heavy chain antibody (somites). All embryos are flat-mounted, (A-T) at 20 somite stage and (U-Z, AA-FF) at 48 hpf. (A-D) n=30/30, (E-H) n=15/15, (I-T) n=15/15, (U-X) n=20/20, (Y-Z, AA-BB) n=15/15, (CC-FF) n=13/15 per condition. |
|
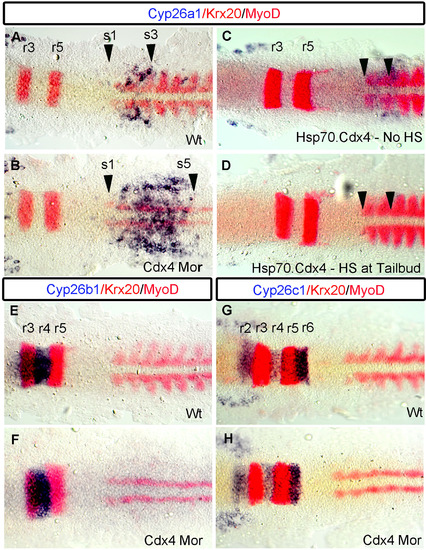
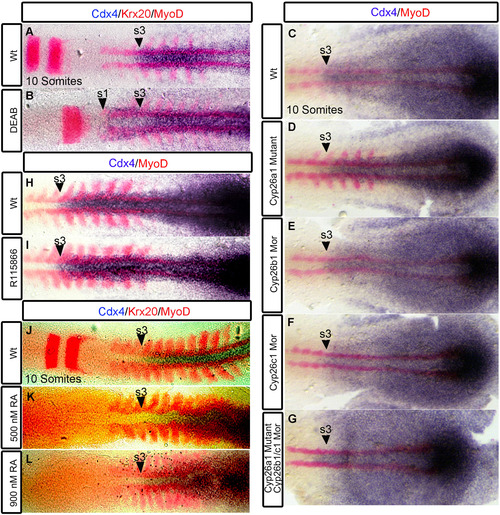
Cyp26a1 expression at the Hb-Sc transition is under the regulation of Cdx4. In wild-types, cyp26a1 is expressed in r7/8, and in the adjacent somites 1-3 (A arrowhead). In Cdx4-deficient embryos (B), cyp26a1 expression is expanded into the spinal cord domain and terminates at the level of somite 5 (B arrowhead). Overexpression of cdx4 using Tg(hsp70:cdx4) line (C) leads to abrogation of cyp26a1 expression (D arrowheads). cyp26b1 expression (E) in r3-4 and cyp26c1 expression (G) in r2,r4,r6 remain unaffected in Cdx4-deficient embryos (F, H). (A-H) Embryos are co-stained with krx20 (r3,r5), myoD (somites) and flat-mounted at the 10 somite stage. (A, B) n=30/30 (C, D) n=15/15, (E, H) n=30/30, (I, J) n=10/10 per condition. |
|
Tissue specific regulation of cdx4 expression by RA signaling. In wildtypes, cdx4 anterior expression limit corresponds to the beginning of the spinal cord located at the level of somite 3 (A, C, H, J, arrowheads). cdx4 expression is rostrally expanded to the level of somite 1 (B arrowhead) in RA-deficient embryos. Expression of cdx4 is unchanged in R115866 treated embryos (I arrowhead), in embryos treated with 500 nM RA (K arrowhead) and 900 nM RA (L arrowhead). cdx4 expression remains unchanged in cyp26a1 mutants (D), cyp26b1 morphants (E), cyp26c1 morphants (F), and cyp26a1 mutants injected with cyp26b1 and cyp26c1 morpholinos (G). (A-G, J-L) Embryos are co-stained with myoD (somites) and krx20 (r3,r5). (H-J) Embryos co-stained with myoD. (A-L) Embryos are at 10 somite stage and flat-mounted. (A-B, H-I) n=30/30, (C-G) n>12, (J-L) n=20/20 per condition. |
|
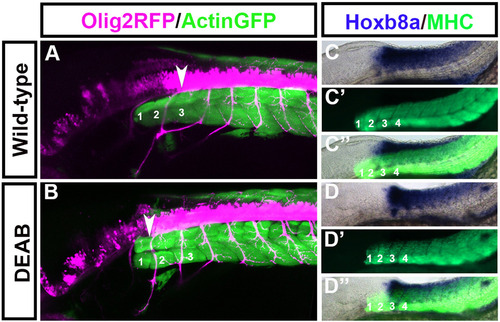
Spinal cord motor neurons shift rostrally while hox gene expression remains unchanged in embryos treated with DEAB between 50% epiboly and tailbud stage. Olig2-Rfp:Actin-Gfp double transgenic embryos were treated with DEAB between 50% Epiboly to tailbud stage. Olig2-Rfp marks spinal cord motor neurons (pink) and Actin-Gfp marks somites (green). In wildtypes the first motor neuron (A arrowhead) projects out at the level of somite 3. In DEAB treated embryos the first spinal cord motorneuron (B arrowhead) arises at the level of somite 1. At 48 hpf the anterior expression limit of hoxb8a is at the level of somite 3 in wild-types (C) and this expression limit remains unchanged in embryos treated with DEAB between 50% epiboly to tailbud stage (D). (C, D) Hoxb8a expression, (C′D′) MHC, (C′′,D′′) merge. (A-D) Embryos at 48 hpf with the anterior located to the left. (A) n=6/6, (B) n=10/10, (C, D) n=15/15. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 410(2), Chang, J., Skromne, I., Ho, R.K., CDX4 and retinoic acid interact to position the hindbrain-spinal cord transition, 178-89, Copyright (2016) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.