- Title
-
BAC transgenic zebrafish reveal hypothalamic enhancer activity around obesity associated SNP rs9939609 within the human FTO gene
- Authors
- Rinkwitz, S., Geng, F., Manning, E., Suster, M., Kawakami, K., Becker, T.S.
- Source
- Full text @ Genesis
|
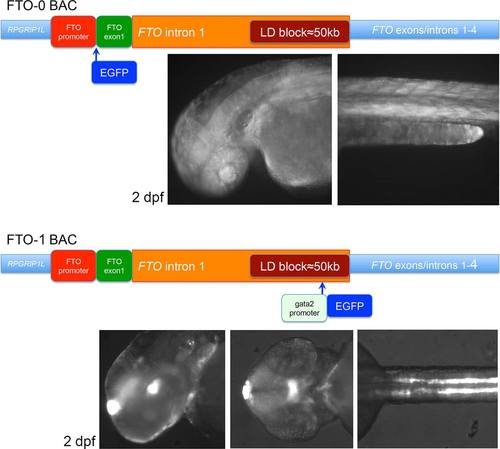
Schematics of the homologous recombinations into the FTO locus. FTO-0: EGFP was inserted in frame with FTO ATG. The transgenic embryos and larvae had weak ubiquitous expression. FTO-1 uses enhancer detection as shown in Figure 1c. The transgenic embryos and larvae had expression in the epiphysis, in the posterior tuberculum and in the hypothalamus, in the inner ear, notochord, and in the kidneys. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
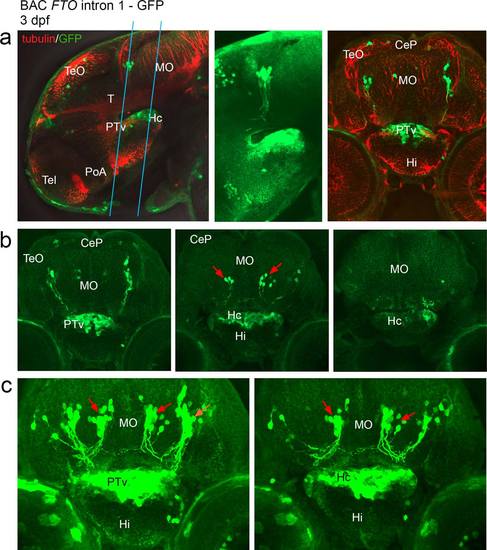
Confocal scan of transgenic larvae at 3 dpf having a promoter-GFP cassette inserted upstream of SNP rs9939609 in FTO intron 1 (a–c). Expression is detected in the ventral part of posterior tuberculum, in the caudal hypothalamus and in the anterior brainstem. (a) Representative optical sections through 3 dpf larvae that were stained for GFP and tubulin, in lateral and transverse views. The blue lines indicate the range of sections shown in b,c. (b) A row of optical sections through the GFP expression domain as indicated in "a." (c) Z-stack images. The first z-stack image includes hypothalamus and PTv, "b" is further posterior and includes the caudal hypothalamus only. Red arrows: Neurons in the hindbrain are strongly labeled and project ventrally as well as contralaterally. Abbreviations: (CeP) Cerebellar plate, (Hc) caudal hypothalamus, (Hi) intermediate hypothalamus, (MO) Medulla oblongata, (PoA) preoptic area, (PTv) ventral part of posterior tuberculum, (T) midbrain tegmentum, (Tel) Telencephalon, (TeO) Tectum opticum. From Mueller and Wullimann, Atlas of early Zebrafish brain development, 2005, Elsevier. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
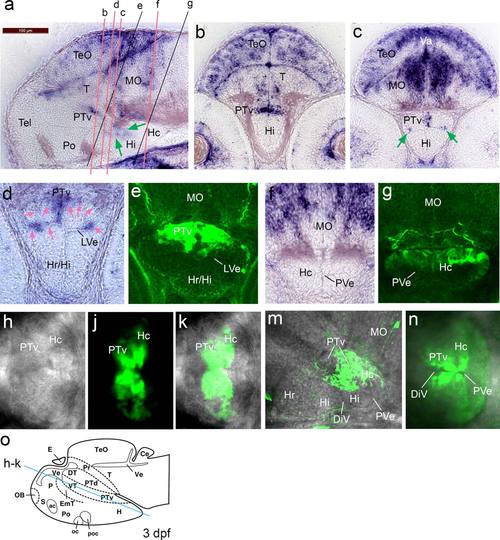
Irx3a in situ hybridization signals in 3 dpf embryos compared to GFP distribution in anti-GFP stained FTO-1 specimen that were analyzed by confocal microscopy. Emphasis is on the hypothalamus. (a–c) irx3a in situ hybridization in 3 dpf embryos, lateral (a) and transverse (b, c) sections. Expression of irx3a in the brain is within the optic tectum, tegmentum, cerebellum, hindbrain, posterior tuberculum, and hypothalamus. The signal in the hypothalamus is localized around the ventricular zone. The green arrows in “a” point to hybridization signal around the ventricular zone of the intermediate and caudal hypothalamus. Arrows in “c” point to irx3a activity in the lateral ventricular recess of the hypothalamus (LVe). (d and e) Sections with focus on the ventral posterior tuberculum and the hypothalamus in high magnification. The hybridization signal is strongest in the lateral ventricular recess of the hypothalamus and the medial region of the PTv, only very faint staining was detected dorsolaterally of the PTv (pink arrows). In the transgenic line the GFP appears more widely distributed. (f and g) The caudal hypothalamus appears free of irx3a transcripts, but GFP can be detected in this region. (h to k) Optical section of a scan performed horizontally through a live embryo (dorsal view) with focus on the posterior tuberculum and hypothalamus. The blue line in “o” indicates the approximate level of the section. (h) Bright field image. (j) The GFP is stronger around the ventricular zone. (k) Maximal intensity projection of the composite image shows that the posterior part of the caudal hypothalamus is free of GFP. (m) Lateral confocal scan. Maximal intensity projection of the medial expression domain. The GFP appears dorsal of the LVe. (n) Horizontally performed scan with ventral view. Maximal intensity projection of the GFP expression domain. The GFP is strongest around the ventricular zone. Abbreviations: DiV, diencephalic ventricle, LVe lateral recess ventricle of hypothalamus, (Hc) caudal hypothalamus, (Hi) intermediate hypothalamus, (Hr) rostral hypothalamus, (MO) medulla oblongata, (Po) preoptic region, (PTv) ventral part of posterior tuberculum, (PVe) posterior ventricular recess of H, (T) midbrain tegmentum, (Tel) telencephalon, (TeO) tectum opticum, (Va) valvula cerebelli. From Mueller and Wullimann, Atlas of early Zebrafish brain development, 2005, Elsevier. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
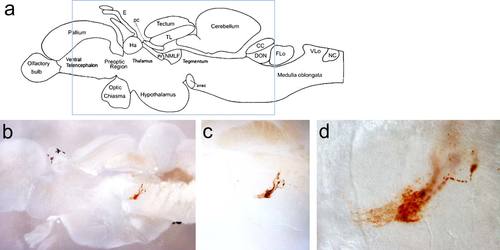
DAB anti-GFP immunostain of FTO-1 BAC adult brain sagittal sections. (a) Schematics of the adult zebrafish telencephalon (From Wullimann et al., Neuroanatomy of the Zebrafish Brain, 2004, Birkhaeuser Verlag). The blue rectangle indicates the area shown in the section in “b.” (b–d) Light microscopic images of FTO-1 BAC transgenic brain with magnifications focusing on DAB-stained neurons in the brainstem projecting ventrally. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|