- Title
-
Rapid identification of kidney cyst mutations by whole exome sequencing in zebrafish
- Authors
- Ryan, S., Willer, J., Marjoram, L., Bagwell, J., Mankiewicz, J., Leshchiner, I., Goessling, W., Bagnat, M., and Katsanis, N.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
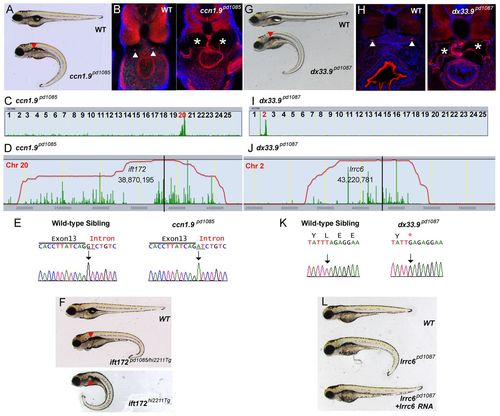
Isolation of new mutant alleles for ift172 and lrrc6 that cause kidney cyst formation. (A) Brightfield image of 5-dpf WT sibling and ccn1.9pd1085 homozygous mutant. Red arrowhead indicates a kidney cyst. (B) Confocal images of transverse sections of 5-dpf WT sibling and ccn1.9pd1085 mutant stained with phalloidin (red) and DAPI (blue). Arrowheads point to the pronephric ducts and asterisks mark kidney cysts. (C) Linkage analysis for ccn1.9pd1085 using SNPtrack. (D) The homozygosity interval for ccn1.9pd1085. (E) Sequencing of genomic DNA of WT and ccn1.9pd1085 mutant larvae. Mutants bear a G-to-A mutation at an essential splice site in exon 13 of ift172 (underlined). (F) Brightfield image of 5-dpf WT sibling, ift172hi2211Tg/pd1085 and ift172hi2211Tg larvae. (G) Brightfield image of 5-dpf WT sibling and dx33.9pd1087 mutant larvae. (H) Confocal images of transverse sections of 5-dpf WT sibling and dx33.9pd1087 mutant larvae stained with phalloidin and DAPI as in B. (I) Linkage analysis for dx33.9pd1087 using SNPtrack. (J) The homozygosity interval for dx33.9pd1087. (K) Sequencing of genomic DNA of WT and dx33.9pd1087 mutant larvae. Mutants are homozygous for a T-to-G nonsense mutation. (L) Rescue of the dx33.9pd1087 phenotype via injection of WT lrrc6 cRNA. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
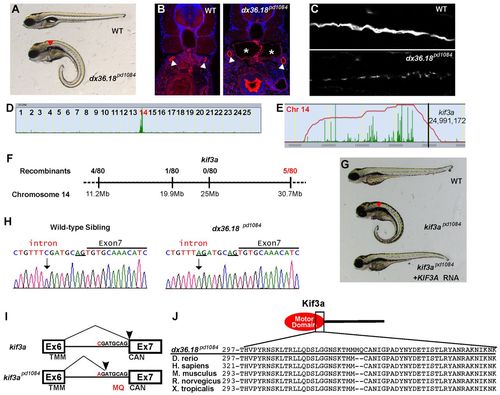
kif3apd1084 mutants present defects in cilia formation and kidney cysts. (A) Brightfield image of 5-dpf WT sibling and dx36.181084 mutant larvae. Red arrowhead indicates a kidney cyst. (B) Confocal images of transverse sections of 5-dpf WT sibling and dx36.181084 mutant larvae stained with phalloidin (red) and DAPI (blue). The arrowheads point to the pronephric ducts and the asterisks mark kidney cysts. (C) Confocal image of 3-dpf WT and dx36.181084 mutant in whole-mount, stained for acetylated tubulin to mark cilia. (D) Linkage analysis for dx36.181084 using SNPtrack. (E) The homozygosity interval for dx36.181084. (F) Linkage analysis of the dx36.181084 locus. (G) Rescue of the dx36.18pd1084 phenotype with WT human KIF3A cRNA. Rescue was confirmed by genotyping (not shown). (H) Sequencing of genomic DNA of WT and kif3apd1084 mutant larvae showing a six nucleotide insertion in kif3a that adds two extra codons between exons 6 and 7 (underlined). (I) Sequencing of cDNA confirms the insertion of codons coding for MQ in kif3apd1084 mutants. TMM, threonine, methionine, methionine; CAN, cysteine, alanine, asparagine. (J) Alignment of Kif3a protein sequences from zebrafish, human, mouse, rat and frog. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
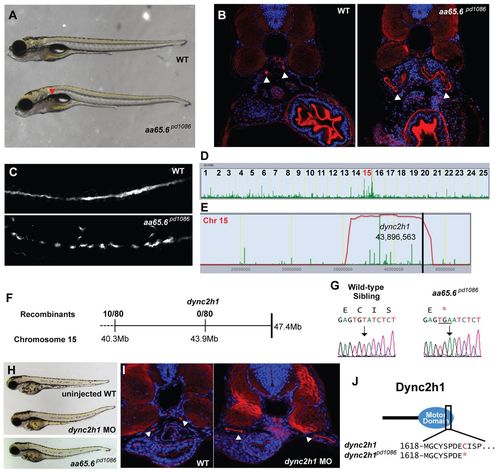
A truncation at the end of the motor domain of Dync2h1 leads to a cystic kidney phenotype. (A) Brightfield image of 5-dpf WT sibling and aa65.6pd1086 mutant larvae. Red arrowhead indicates a kidney cyst. (B) Confocal images of transverse sections of 5-dpf WT sibling and aa65.6pd1086 mutant larvae stained with phalloidin (red) and DAPI (blue). The arrowheads point to pronephric ducts and asterisks mark kidney cysts. (C) Confocal image of 3-dpf WT and aa65.6pd1086 mutant embryos in whole-mount, stained for acetylated tubulin to mark cilia. (D) Linkage analysis for aa65.6pd1086 using SNPtrack. (E) The homozygosity interval for aa65.6pd1086. (F) Linkage analysis using single embryos. (G) Sequencing of genomic DNA of WT and aa65.6pd1086 mutant larvae. (H) Injection of a morpholino directed against a splice site within the motor domain of dync2h1 phenocopies the aa65.6pd1086 mutation. (I) Confocal images of transverse sections 3-dpf WT and dync2h1 morphants stained with phalloidin and DAPI, showing distended pronephric ducts (arrowheads). (J) Schematic of the Dync2h1 protein illustrating that the mutation removes a portion of the motor domain. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
dync2h1 morpholino validation and supplemental characterization of aa65.6pd1086 mutant. (A) RT-PCR from RNA of control and dync2h1 splice-site morpholino-injected EK embryos at the one cell stage and harvested at 3 dpf. (B) Ventral view of cartilage in the jaw of 5 dpf alcian-blue stained larvae. (C) View of chromosome 15 in Ensembl showing the four transcripts that constitute the full length dync2h1 in zebrafish and the corresponding protein domains. |