- Title
-
Identification and expression analysis of the zebrafish homologs of the ceramide synthase gene family
- Authors
- Brondolin, M., Berger, S., Reinke, M., Tanaka, H., Ohshima, T., Fuss, B., and Hoch, M.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Dyn.
|
Spatial expression patterns of zebrafish cers1, cers2a and cers2b in gastrula (8 hours postfertilization [hpf]), 6-somite stage (12 hpf), 18-somite stage (18 hpf), 24 hpf, and 48 hpf embryos. A: cers1 is present in the trigeminal placode (tp), Rohon-Beard sensory neurons (RB), the hematopoietic intermediate cell mass (ICM), brain (b), and pectoral fin (pf). B: At 12 hpf, cers2a is expressed in rhombomere 5 (R5) and the developing notochord (nc), whereas at 18 hpf and 24 hpf, the gene is expressed in paraxial mesoderm (pam) and cloaca (cl), eye (e), including the lens (le), midbrain–hindbrain boundary (mh), and pronephric duct (pd). At 48 hpf, it is found in brain (b), otic vesicle (ov), pectoral fin (pf), myotomes (mt), and pronephric duct (pd). C: cers2b shows an expression in the anterior polster (ap) and paraxial mesoderm (pam), the lens of the eye (le), branchial arches (ba), and posterior somites (ps). The latter is reduced to the posterior mesoderm (pm) at 24 hpf. At 48 hpf, the expression is ubiquitous, brain (b), otic vesicle (ov), pectoral fin (pf), myotomes (mt), and the pronephric duct (pd) indicated by arrows. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
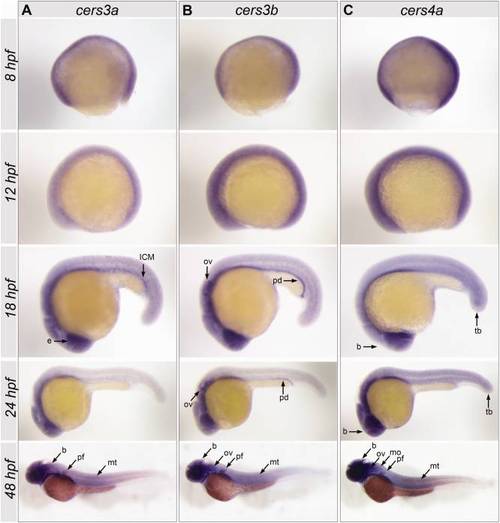
Spatial expression patterns of zebrafish cers3a, cers3b, and cers4a in gastrula (8 hours postfertilization [hpf]), 6-somite stage (12 hpf), 18-somite stage (18 hpf), 24 hpf, and 48 hpf embryos. A: The cers3a pattern at 18 hpf includes the eye (e) and intermediate cell mass (ICM) and a subset of putatively neuronal cells. At 48 hpf, an expression is found in the brain (b), pectoral fin (pf), and myotomes (mt). B: cers3b expression is found in the otic vesicle (ov) and pronephric duct (pd) at 18 hpf and 24hpf. At 48 hpf, cers3b is detected in the brain (b), otic vesicle (ov), pectoral fin (pf), and myotome (mt). C: cers4a shows an ubiquitous pattern in all stages analyzed, most pronounced in the brain (b) and tail bud (tb). At 48 hpf, the expression is particularly localized in brain (b), otic vesicle (ov), medulla oblongata (mo), pectoral fin (pf), and myotomes (mt). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
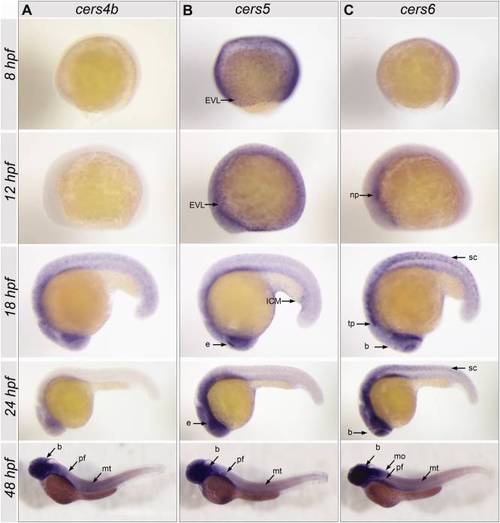
Spatial expression patterns of zebrafish cers4b, cers5, and cers6 in gastrula (8 hours postfertilization [hpf]), 6-somite stage (12 hpf), 18-somite stage (18 hpf), 24 hpf, and 48 hpf embryos. A: For cers4b no expression was detected in early stages, whereas at the 48 hpf stage an expression is found in the brain (b), pectoral fins (pf), and myotomes (mt). B: At gastrula and 6-somites stages, cers5 is expressed in the enveloping layer (EVL), and later at the 18 hpf stage, its expression is pronounced in the periderm and eye (e), particularly the dorsal posterior eye margin. At 24 hpf, cers5 is present in the periderm and eye (e), particularly in a spot in the dorsal posterior region. At 48 hpf, expression is pronounced in the brain (b) pectoral fin (pf) and myotomes (mt). C: At 12 hpf cers6 shows a weak expression in the neural plate (np). At 18 hpf and 24 hpf, cers6 is expressed in spinal cord (sc), trigeminal placodes (tp), and in parts of the developing brain (b). At 48 hpf, cers6 expression is most pronounced in brain (b), medulla oblongata (mo), pectoral fin (pf), and myotomes (mt). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
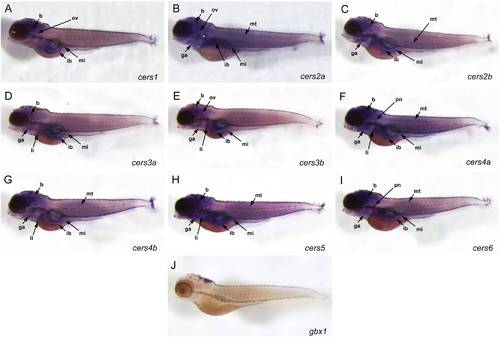
Spatial expression patterns of zebrafish cers in 5 dpf embryos. A: At this stage, cers1 is localized in brain (b), otic vesicle (ov), intestinal bulb (ib), and mid intestine (mi). B:cers2a is expressed ubiquitously, but its expression is pronounced in the brain, otic vesicle, gill arches (ga), intestinal bulb, mid intestine, and myotomes (mt). C:cers2b shows a strong expression in brain, gill arches, intestinal bulb, mid intestine and myotomes. D: At 5dpf, cers3a can be detected in brain, gill arches, liver (li), intestinal bulb, and mid intestine. E:cers3b is expressed prominently in brain, otic vesicle, gill arches, liver, intestinal bulb, and mid intestine. F:cers4a is remarkably expressed in brain, gill arches, pronephros (pn), liver, intestinal bulb, mid intestine, and myotomes. G:cers4b shows an expression which is similar to the one of its paralogue cers4a, localized in brain, gill arches, liver, intestinal bulb, mid intestine, and myotomes. H:cers5 is strongly expressed in brain, gill arches, liver, intestinal bulb, mid intestine, and myotomes. I:cers6 expression is localized in brain, gill arches, pronephros, intestinal bulb, mid intestine, and myotomes. J: A riboprobe specific for the gbx1 gene, expressed in midbrain and hindbrain, was used as a positive control. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
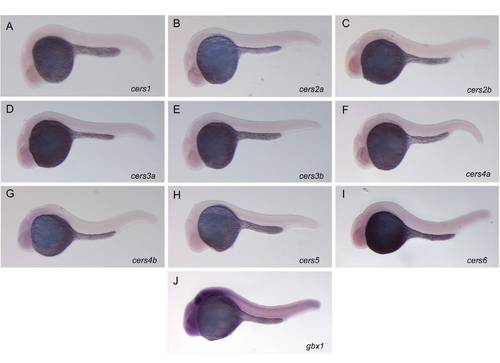
A–I: Whole-mount in situ hybridization with sense RNA probes for the nine ceramide synthases in zebrafish embryos at 24 hpf (negative controls). J: Whole-mount in situ hybridization with an antisense RNA probe for the zebrafish gbx1 gene (Rhinn et al., 2009). Lateral views, anterior to the left. Whereas the in situ hybridization for gbx1 gives a strong signal in the hindbrain and the spinal cord (positive control), in situ hybridization with zebrafish cers sense probes demonstrated no expression, confirming the specificity of the stainings. |