- Title
-
The Usher gene cadherin 23 is expressed in the zebrafish brain and a subset of retinal amacrine cells
- Authors
- Glover, G., Mueller, K.P., Söllner, C., Neuhauss, S.C., and Nicolson, T.
- Source
|
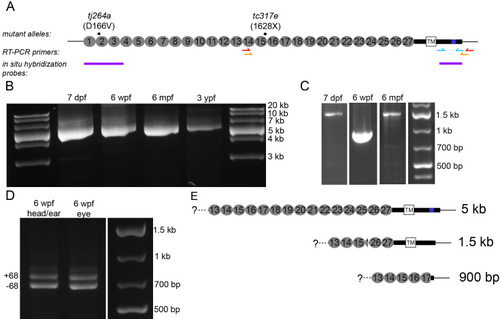
Presence of full-length and splice variants of cdh23 mRNA in zebrafish larval and adult retina. A: Schematic illustrating the locations of the mutations in the two cdh23 mutant fish lines, reverse transcriptase (RT)–PCR primers, and the 52 and 32 in situ hybridization probes used in this study. For the RT–PCR primers, the red and orange arrows indicate the location of the nested primer set used to amplify cdh23 in panels B and C, while the cyan arrows indicate the primer set used in D. B: Developmental time-course showing the full-length cdh23 RT–PCR product isolated from eyes of various ages (n=3). C: Smaller RT–PCR products were also present. A shorter variant containing the transmembrane (TM) segment was amplified from 7 days postfertilization (dpf) and 6 months postfertilization (mpf) retinal transcripts (n=2). A short, soluble variant was amplified from 6 weeks postfertilization (wpf) eyes (n=2). Neither shorter variant was isolated from 3 years postfertilization (ypf) eyes (n=2). D: Using primers directed against sequence encoding the entire C-terminus, both the full-length version (containing exon 68) and the version present in the shorter variant containing the TM segment were isolated from eye or enucleated head (n=2). E: Schematics depicting the sequence and expected size of the full-length and two short forms of cdh23 isolated in (B) and (C). |
|
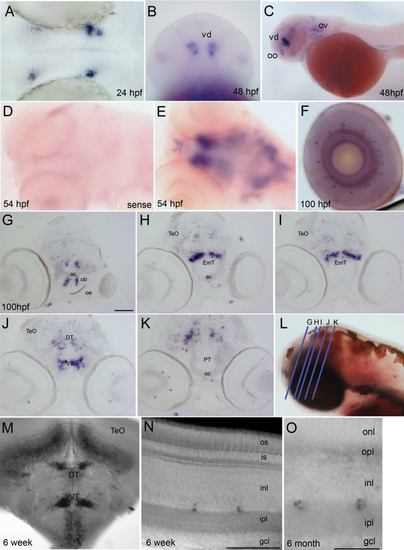
Cdh23 transcripts are expressed in the zebrafish brain and retina. In situ hybridization showing cadherin 23 mRNA (mRNA) expression in the developing and mature zebrafish nervous system. A: Dorsal view of a zebrafish brain at 24 h postfertilization (hpf); the blue/purple signal shows the first detectable expression of cdh23 mRNA in two paired nuclei in the diencephalon, adjacent to the eye. B: Ventral view of intensely stained deep nuclei in the ventral diencephalon (vd) at 48 hpf. C: Lateral view of 48 hpf larva. The two most prominent nuclei labeled are located in the olfactory organ (oo) and the ventral diencephalon. Additional brain labeling is also observed, as is labeling of hair cells in the otic vesicle (ov). D: Sense control shows absence of nonspecific labeling. E: Dorsal view of the brain at 54 hpf, showing telencephalic and ventral diencephalic paired nuclei from a different angle, as well as additional dispersed cells in the mesencephalon and rhombencephalon. F: In the eye, a very small subset of inner layer cells is labeled. G-K: Post–in situ hybridization cryosectioning allowed the more accurate identification of labeled brain nuclei. Paired telencephalic nuclei were located just medial to the olfactory bulb (ob), in the subpallium (G). Caudal to the anterior commissure (ac), very intense labeling was found in bilateral bar-shaped structures in the eminentia thalami (EmT). H, I: Continuing caudally (J), bar-shaped nuclei became more globular in the ventral thalamus. Scattered labeling was also observed in the dorsal thalamus and points caudal in J-K. L: Blue lines represent planes of cryosections made in G-K. M: Cdh23 in situ hybridization in 6 weeks postfertilization (wpf) zebrafish shows ventral and dorsal thalamic labeling similar to that seen in larval stages, but is expanded to even more ventral areas, and to cells lying just ventral to the optic tectum (TeO). N, O: At 6 wpf and 6 months postfertilization (mpf), retinal labeling is still restricted to a very small subpopulation of amacrine cells. gcl, ganglion cell layer; inl, inner nuclear layer; ipl, inner plexiform layer; is, inner segment; onl, outer nuclear layer; opl, outer plexiform layer; os, outer segment. Scale bars=100 μm (G-K, M), 50 μm (N), 20 μm (O). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
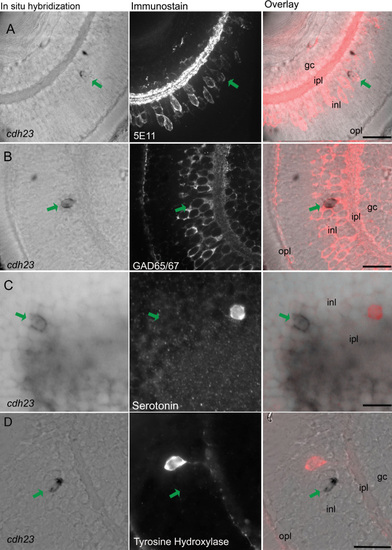
Cdh23 is expressed in GABAergic amacrine cells. In situ hybridization of cdh23 was combined with immunocytochemistry for various amacrine cell markers. In each row of images, the left panel shows retinal slices labeled with the cdh23 mRNA (mRNA) probe, the center panel shows fluorescent immunostaining, and the right panel shows an overlay of the in situ hybridization and the immunofluorescence images. A: cdh23-positive retinal cells colabel with the pan-amacrine cell antibody 5E11. B: cdh23-positive amacrine cells also colocalize with an antibody to the GABAergic cell marker glutamate decarboxylase 65/67 (GAD65/67). C, D: Neither serotonin-positive nor tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)-positive amacrine cells colabel with cdh23 mRNA. Scale bar, 20 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
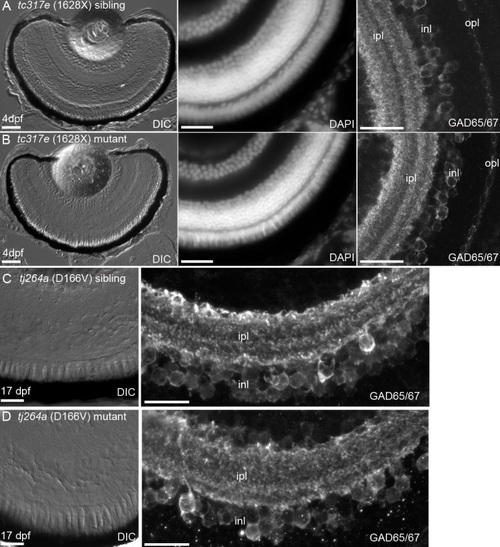
Retinal morphology is normal in cdh23 mutants. Zebrafish lines carrying one of two different severe cdh23 mutant alleles, which each cause profound deafness/balance defects, were examined for retinal defects. A, B: Examination of 4 days postfertilization (dpf) retinal cryosections by differential interference contrast microscopy (left panel), by staining with the nuclear dye DAPI (middle panel), or by examining GABAergic amacrine cell morphology and the inner nuclear layer banding pattern with anti-GAD65/67 (right panel) showed that cdh23tc317e siblings (A) and homozygous mutants (B) had morphologically identical retinas. C, D: Siblings and mutants of the cdh23tj264a allele were raised to 17 dpf and their retinas were examined as in A, B. No differences in morphology between siblings and mutants were observed at this later stage of development. Scale bar=50 µm in A, left panel (applies to A and B left panels). Scale bar=20 µm for middle, right panels in A, C (also applies to image directly below). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
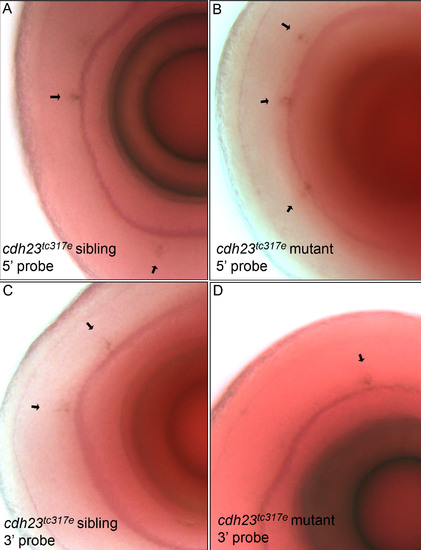
In situ hybridization using a probe directed against either the 52- or 32 region of cdh23 showed that cdh23 mRNA (mRNA) is expressed in a subset of amacrine cells of both cdh23tc317e siblings (left panels) and homozygous mutants (right panels). The 52 RNA probe used in (A, B) was complementary to nucleotides 448–1,566 from cdh23 cDNA. C, D: The same amacrine cell staining of cdh23tc317e siblings (C) and mutants (D) was observed using a 32 RNA probe complementary to nucleotides 9730–10,515. |
|
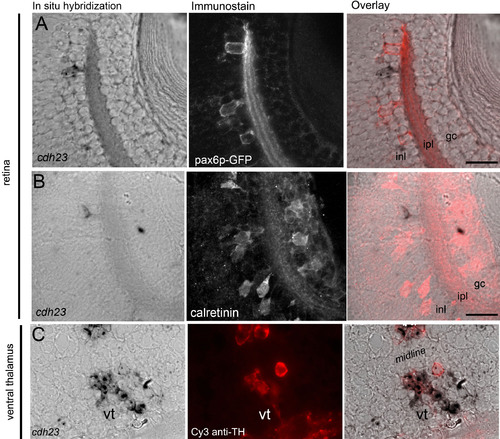
Partial colocalization between tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and cdh23 was observed in the ventral tegmentum. A: Combined cdh23 in situ hybridization (left panel) and anti-GFP antibody labeling (middle panel) shows that cdh23 is not expressed in pax6p-GFP-positive amacrine cells (overlay, right panel). B: Cdh23 is also not expressed in calretinin-positive amacrine cells. C: In the ventral thalamus, a subset of the bilateral deep diencephalic cdh23-positive cells (corresponding to the area shown in Figure 2J) label with anti-TH, which marks the dopaminergic neurons of the ventral tegmentum. |