- Title
-
Context-dependent proangiogenic function of bone morphogenetic protein signaling is mediated by disabled homolog 2
- Authors
- Kim, J.D., Kang, H., Larrivée, B., Lee, M.Y., Mettlen, M., Schmid, S.L., Roman, B.L., Qyang, Y., Eichmann, A., and Jin, S.W.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Cell
|
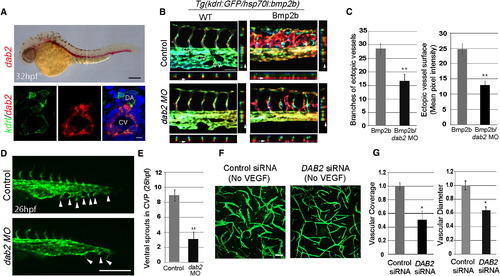
Dab2 Mediates Venous-Specific Proangiogenic Function of Bmp2b (A) Fluorescence in situ for dab2 and immunostaining for kdrl:GFP and DAPI. Lateral view (top) and transverse section (bottom). Scale bar is 200 μm (top) or 10 μm (bottom). DA, dorsal aorta; CV, cardinal vein. See also Figure S1A.(B) Depth-coded images of control or dab2 MO-injected 45 hpf wild-type (WT) and Bmp2b overexpressing (Bmp2) embryos. XZ and YZ axis views of each image are also shown. Arrows point to ectopic vessels in the projection. Images were obtained between the 16th and 20th somite. Scale bar is 100 μm. DA, dorsal aorta; DV, dorsal vein; VV, ventral vein. See also Figures S1B–S1F.(C) Quantification. The number of branches (n = 3, total number of embryos was 19 [Bmp2b] or 17 [Bmp2b/dab2 MO], p < 0.001) and vessel surface as assessed by mean GFP pixel intensity (n = 3, total number of embryos was 21 [Bmp2b] or 19 [Bmp2b/dab2 MO], p < 0.001). Error bars represent standard error of the mean (SEM).(D) Fluorescent images of 26 hpf control (top) or dab2 (bottom) MO-injected embryos. Arrowheads point to ventral sprouts. Scale bar is 100 μm.(E) Quantification of ventral sprouts in the CVP (n = 3, total number of embryos was 25 [Control] or 20 [dab2 MO], p < 0.001). Error bars represent SEM.(F) Fibrin gel assay of control and DAB2 siRNA-treated HUVECs. Scale bar is 10 μm. See also Figures S1G and S1H.(G) Quantification of vascular coverage and diameter. Values were normalized to control siRNA treatment sample by PRISM program. n = 3 and p < 0.05. Error bar is SEM. |
|
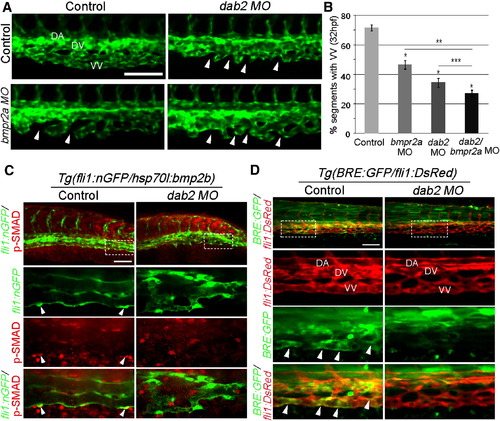
Dab2 Functionally Interacts with Bmp2b Signal to Promote Caudal Vein Plexus Formation (A) Fluorescent images of 32 hpf control, dab2, bmpr2a, and dab2/bmpr2a MO-injected embryos. Arrowheads point to the regions that fail to connect to neighboring sprouts. Scale bar is 100 μm. See also Figure S2A.(B) Quantification of ventral vein (VV) defects. n = 3, and total number of embryos was 54 (control), 32 (bmpr2a MO), 26 (dab2 MO), or 35 (dab2/bmpr2a MO). p < 0.001 in all cases, except p value against dab2 MO-injected embryos, where p = 0.05. comparison with control MO-injected embryos; comparison with bmpr2a MO-injected embryos; and comparison with dab2 MO-injected embryos. Error bars represent SEM.(C) Confocal micrographs of control or dab2 MO-injected 45 hpf Tg(hsp70l:bmp2b) embryos, showing p-Smad-1,5/8 (red) and endothelial cells (green). Arrowheads point to p-Smad-1,5/8 within venous endothelial cells. Scale bar is 100 μm.(D) Confocal micrographs of control or dab2 MO-injected 45 hpf Tg(BRE:GFP);Tg(fli1:DsRed) embryos. Arrowheads point to GFP expression by BRE. Scale bar is 100 μm. DA, dorsal aorta; DV, dorsal vein; VV, ventral vein. |
|
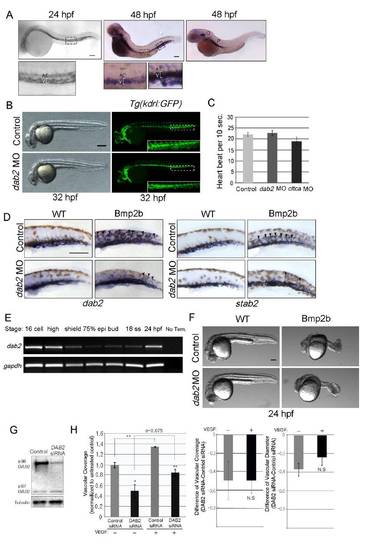
Expression pattern of dab2 in zebrafish embryo and its function in vascular development (related to Figures 1). |
|
CVP formation in wild-type and dab2 deficient embryos. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
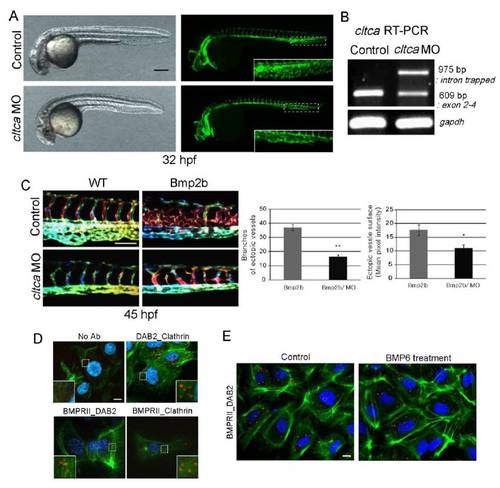
Functional relationship Clathrin with Dab2 in angiogenesis (related to Figure 3). |
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 23(2), Kim, J.D., Kang, H., Larrivée, B., Lee, M.Y., Mettlen, M., Schmid, S.L., Roman, B.L., Qyang, Y., Eichmann, A., and Jin, S.W., Context-dependent proangiogenic function of bone morphogenetic protein signaling is mediated by disabled homolog 2, 441-448, Copyright (2012) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell