- Title
-
Fbxw7 controls angiogenesis by regulating endothelial notch activity
- Authors
- Izumi, N., Helker, C., Ehling, M., Behrens, A., Herzog, W., and Adams, R.H.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS One
|
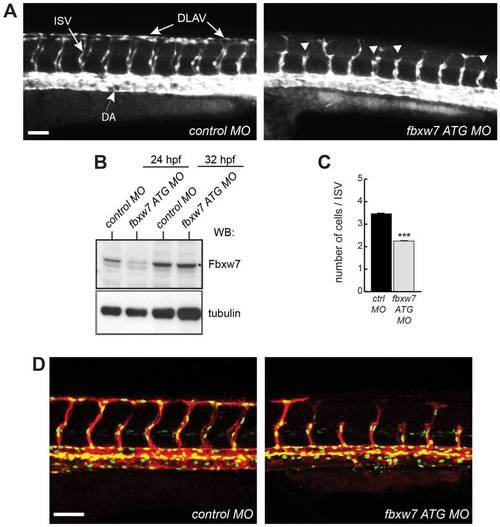
Impaired ISV growth after knockdown of zebrafish fbxw7 expression. Following injection with control morpholino (control MO) or fbxw7 transcription blocking morpholino (fbxw7 ATG MO), the fluorescent vasculature of Tg(kdrl:EGFP)s843 transgenic embryos was examined by live microscopy. Outgrowth of ISVs from the dorsal aorta (DA) and formation of the DLAV (as indicated in the left image) were impaired in fbxw7 morphant embryos (arrowheads) at 32 hpf (A). Scale bar is 70 μm. Protein extracts from control and fbxw7 ATG MO embryos at 24 hpf and 32 hpf were analyzed by Western blotting (B). Note transient reduction of the Fbxw7 band (asterisk). Tubulin was used as loading control. Quantification of the number of ECs per ISV in control MO and fbxw7 ATG MO injected embryos at 32 hpf (based on 3 independent experiments) (C). Proliferation of endothelial cells at 32 hpf in ISVs of Tg(fli1a:nEGFP)y7 x Tg(kdrl:HsHRAS-mCherry)s896 double transgenic embryos injected with control MO or Fbxw7 ATG MO (D). Error bars indicate SEM. P value (*) in (C) is <0.05. |
|
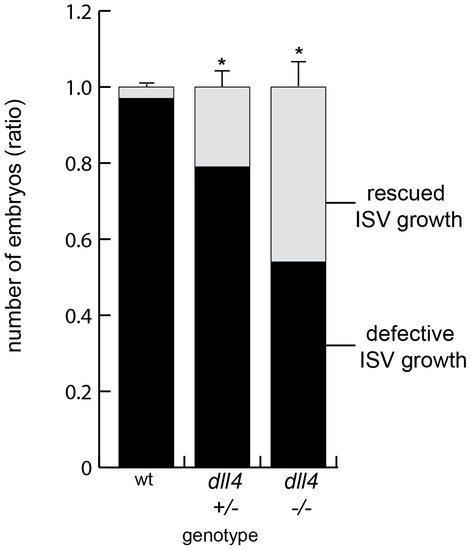
Impaired Notch signaling alleviates the fbxw7 morphant phenotype in zebrafish. Offspring resulting from an intercross of heterozyogous dll4j16e1 mutants were injected with fbxw7 ATG MO and the ISV morphology was analyzed at 32 hpf. The fraction of embryos showing normal ISV growth (light grey) was highest in a dll4 homozygous background. In contrast, fbxw7 silencing led to defective ISV growth (black) in almost all dll4 wild-type embryos. The ratio of ISV phenotypes within each genotype group was calculated (based on 3 independent experiments). Error bars reflect SEM. P value (*) is <0.05. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
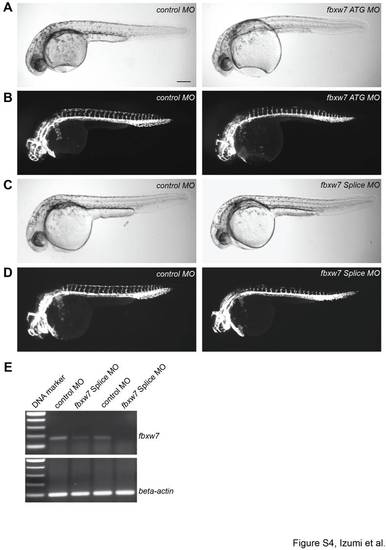
Vascular defects caused by the knockdown of zebrafish fbxw7. Bright-field images (A, C) and endothelial fluorescence (B, D) of Tg(kdrl:EGFP)s843 zebrafish embryos at 32 hpf injected with control (control MO), fbxw7 translation-blocking (ATG MO) or fbxw7 splicing-blocking (Splice MO) morpholinos, as indicated. The knockdown of fbxw7 impaired ISV outgrowth and prevented the formation of the DLAV, while the size and general growth of the morphant embryos were unaffected. Scale bar is 200 μm. PCR analysis (E) showing the reduction of fbxw7 transcripts in zebrafish embryos injected with Splice MO in two independent experiments. Beta-actin PCR products were used as loading control. PHENOTYPE:
|