- Title
-
Mutation in the type IB bone morphogenetic protein receptor alk6b impairs germ-cell differentiation and causes germ-cell tumors in zebrafish
- Authors
- Neumann, J.C., Chandler, G.L., Damoulis, V.A., Fustino, N.J., Lillard, K., Looijenga, L., Margraf, L., Rakheja, D., and Amatruda, J.F.
- Source
- Full text @ Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA
|
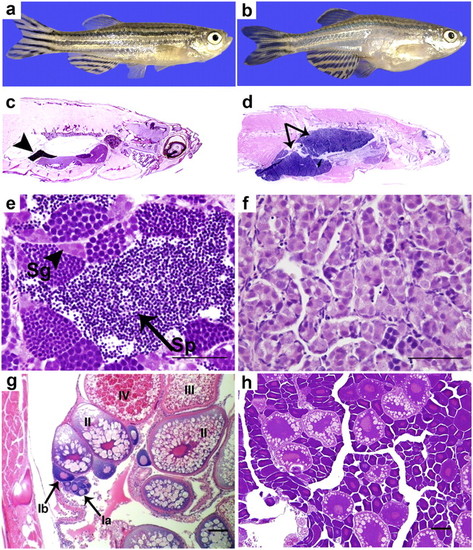
The tgct mutants develop GCTs because of impaired germ-cell differentiation. Compared with adult wild-type males (A and C) (arrowhead: normal testis), adult tgct males display marked testicular enlargement (B and D) (arrow: testicular tumor). Wild-type testis (E) exhibits normal spermatogenesis (arrowhead: spermatogonia; arrow: spermatozoa). The tgct mutant testis (F) accumulates primitive germ cells. Although wild-type ovary (G) shows all stages of oocyte maturation up to mature stage IV oocytes, oocyte maturation is impaired in tgct homozygous females (H). [Scale bars: 100 μm (E and F); 50 μm (G and H).] PHENOTYPE:
|
|
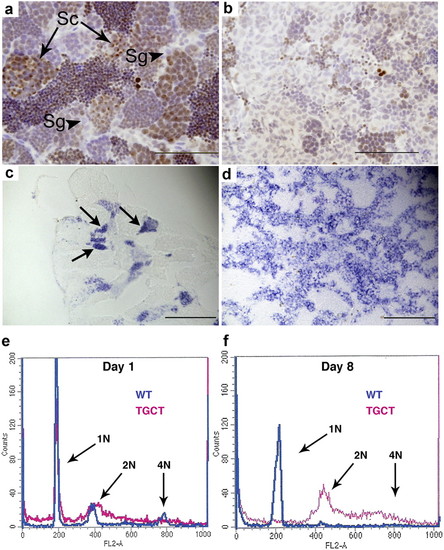
The tgct mutants exhibit impaired differentiation and reduced meiosis in vitro and in vivo. In wild-type testis (A), phosphohistone H2Ax marks clusters of primary spermatocytes undergoing meiosis (arrows). Spermatogonia (arrowheads) are phosphohistone H2AX-negative. The tgct mutant testis (B) exhibits severely reduced clusters of meiotic spermatocytes. The tumor cells are phosphohistone H2AX-negative. (C and D) In situ hybridization for the germ-cell–specific gene ziwi. In wild-type testis (C), ziwi expression is strong in clusters of spermatogonia (arrows) and rapidly declines as cells enter meiosis. The tgct testis tumors (D) show uniformly high expression of ziwi. (E) FACS analysis for DNA content of cultured wild-type and tgct testis on day 1. (F) FACS analysis on day 8 after culturing. Wild-type spermatogonia have completed meiosis to become haploid spermatocytes and spermatozoa (1N), but tgct tumor cells remain diploid (2N) and do not undergo meiosis. [Scale bars: 100 μm (A and B); 200 μm (C and D).] |
|
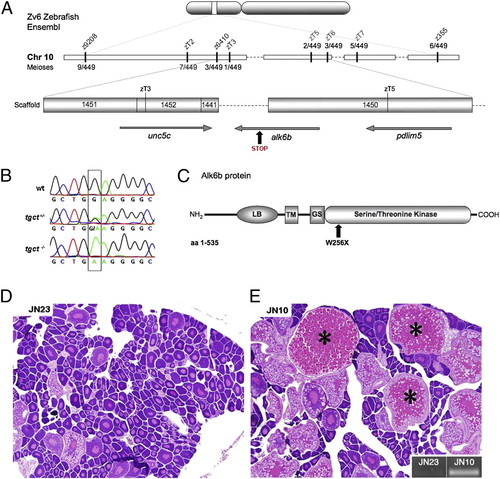
Positional cloning of the tgct mutant locus. (A) Position of the tgct mutation on chromosome 10 between novel SSLP markers zT3 and zT5, located on Zv6 Ensembl scaffolds 1452 and 1450, respectively. (B) Chromatogram showing the G to A transition in alk6bW256X mutants. (C) Schematic of Alk6b protein illustrating the Activin-like receptor (AcvR) ligand binding (LB), transmembrane (TM), GS box (GS), and serine/threonine kinase domains. The tgct mutation is located in the kinase domain at amino acid 256. (D) A β-actin-alk6bwt transgene injected alk6bW256X female showing no rescue of oocyte maturation and no transgene incorporation (E, Inset) into genomic DNA. (E) A β-actin-alk6bwt transgene injected alk6bW256X female with restored oocyte maturation (*) and incorporation of the transgene into genomic DNA (Inset). (D and E: magnification 50×.) |
|
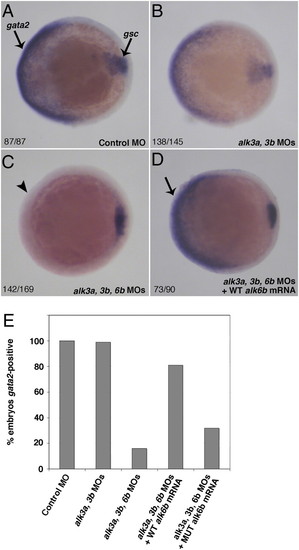
alk6bW256X is a loss-of-function allele. (A–D) Whole-mount in situ hybridization demonstrating ventral expression of the BMP target gene gata2 in control and morpholino knockdown embryos. Goosecoid (gsc) expression in the prechordal plate marks the presumptive dorsal side of the embryo. (A) Control morpholino injected embryos at 75% epiboly showing normal ventral expression of gata2. (B) Morpholino knockdown of the type IA BMP receptors alk3a and alk3b slightly reduces gata2 expression. (C) Triple knockdown of alk3a, alk3b, and alk6b leads to complete loss gata2 expression. (D) Injection of wild-type alk6b mRNA into triple knockdown embryos rescues gata2 expression. (E) Quantification of percentage of embryos expressing gata2 after morpholino knockdown and rescue with wild-type or alk6bW256X mRNA. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
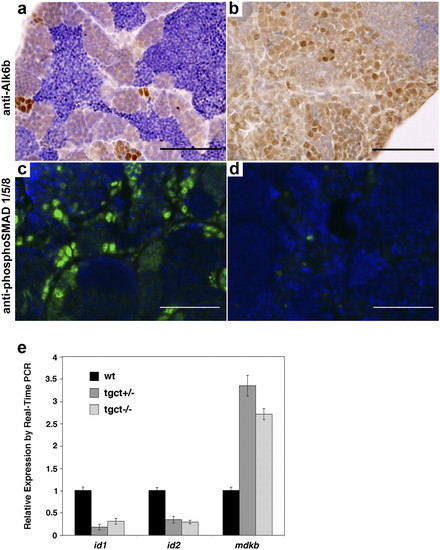
Alk6b is expressed in spermatogonia and is required for BMP signaling activity in the zebrafish testis. (A) Immunohistochemistry for Alk6b shows that protein expression is primarily limited to the spermatogonia in the wild-type testis, with faint staining in some spermatocytes. (B) Alk6b is highly expressed in zebrafish GCTs. (C and D) immunofluorescent detection of phospho-SMAD1/5/8 on cryosections of wild-type and mutant testis. Nuclear p-SMAD1/5/8 is present in wild-type testis (C), indicating active BMP signaling. BMP signaling is absent in alk6bW256X mutant testis (D). (E) Quantitative Real-Time PCR of BMP target genes in wild-type and tumor testis. The BMP targets id1 and id2 are expressed at lower levels in tumors, whereas mdkb expression is derepressed. (Scale bars, 100 μm.) |
|
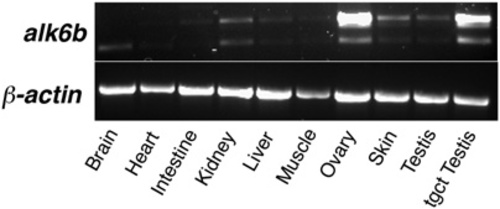
Expression of alk6b in zebrafish tissues organ expression. alk6b is expressed in most organs, with increased expression in the ovary, testis, skin, and kidney. Two splice forms are present. “tgct testis” indicates RNA prepared from a GCT testis arising in an alk6W256X mutant. |
|
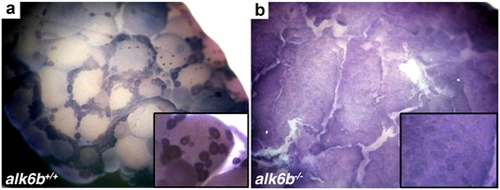
alk6b is expressed in immature oocytes. (A) In situ hybridization indicates that alk6b is predominantly expressed in immature oocytes (stages I and II) in the wild-type ovary. (B) alk6bW256X /W256X mutant ovaries have an accumulation of alk6b expressing immature oocytes with an absence of mature oocytes. (Inset) Higher magnification view. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|