- Title
-
Gene-specific differential response to anti-apoptotic therapies in zebrafish models of ocular coloboma
- Authors
- Gregory-Evans, C.Y., Moosajee, M., Shan, X., and Gregory-Evans, K.
- Source
|
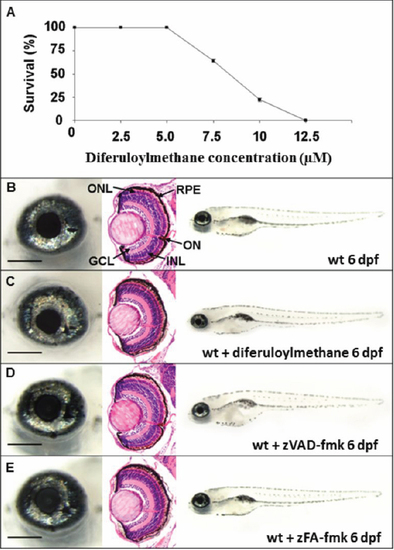
Effect of drug treatment on wildtype zebrafish. A: Wildtype embryos were dosed continuously from 10 hpf with diferuloylmethane. Percentage survival of embryos at 6 dpf was determined for each treatment group (30 embryos/group), n=3, mean±SEM. Error bars smaller than the symbol are not visible. B-E: Left panels, wholemount eye; center panels, coronal retinal section; right panels, wholemount larvae. B: Wildtype phenotype untreated at 6 dpf. C: Wildtype phenotype at 6 dpf treated with 5 μM diferuloylmethane from 10 hpf. D: Wildtype phenotype at 6 dpf following 300 μM zVAD-fmk treatment. E: Wildtype phenotype at 6 dpf following 300 μM zFA-fmk treatment. Scale bar left panel=200 μm. GCL, ganglion cell layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium, ON, optic nerve. |
|
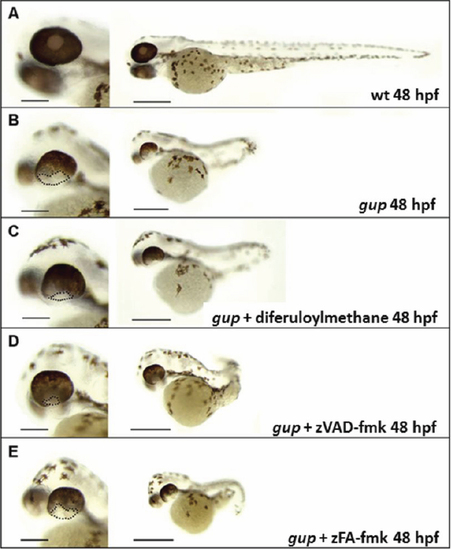
Representative morphology of gup mutants at 48 hpf following drug treatment. Left panel, enlarged image of wholemount eye, scale bar=200 μm. Right panel, whole embryo morphology, scale bar=500 μm. A: Wildtype control, complete closure of optic fissure. B: Untreated gup mutant, displaying large open optic fissure at ventral aspect of eye. C: gup mutant treated with 5 μM diferuloylmethane, displaying open optic fissure which is smaller in size compared to untreated mutants. D: gup mutant treated with 300 μM zVAD-fmk, displaying a smaller open optic fissure than untreated mutants. E: gup mutant treated with 300 μM zFA-fmk, displaying a large open optic fissure as in untreated mutants. Optic fissure closure defect delineated by black dotted line. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Representative images of drug treatment in gup mutants at 6 dpf. A, C, E, G, I: Enlarged wholemount of the eye, scale=200 μm, and wholemount larvae, scale=500 μm. B, D, F, H, J: corresponding TUNEL stained wholemount of PTU-treated eye and larvae. A, B: Wildtype zebrafish showing normal morphology and minimal apoptosis in the eye and wholemount. C, D: Untreated gup mutants displaying large coloboma in ventral aspect of the eye, TUNEL-positive labeled tissue at the site of the unfused optic fissure and throughout the whole fish. E, F: gup mutants treated with 5 μM diferuloylmethane (+D) showing small colobomatous defect, minimal TUNEL-positive staining in the eye, and reduced levels in the whole larvae compared to untreated mutants. G, H: gup mutants treated with 300 μM zVAD-fmk (+V) showing small colobomatous defect, minimal TUNEL-positive staining in the eye, and reduced levels in the whole larvae compared to untreated mutants. I, J: gup mutants treated with 300 μM zFA-fmk (+F) showing large colobomatous defect and TUNEL-positive staining at the site of the unfused fissure. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
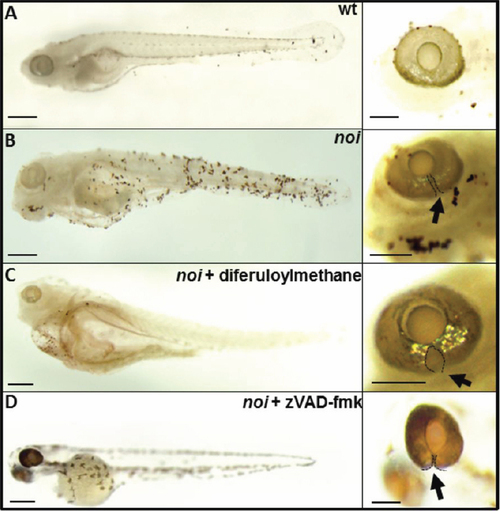
Representative images of the effect of diferuloylmethane on TUNEL-labeling in noi mutant larvae at 6 dpf. A: TUNEL-labeling in wholemount larvae (left) and wholemount eye (right) of wildtype zebrafish (wt). B: Extensive TUNEL labeling in larvae and eye of untreated noi mutant zebrafish. C: noi mutant larvae treated with 5 μM diferuloylmethane. D: noi larvae treated with 300 μM zVAD-fmk. Arrow points to optic fissure closure defect delineated by black dotted line. Scale bar whole eye=200 μm; scale bar larval fish=500 μm. |
|
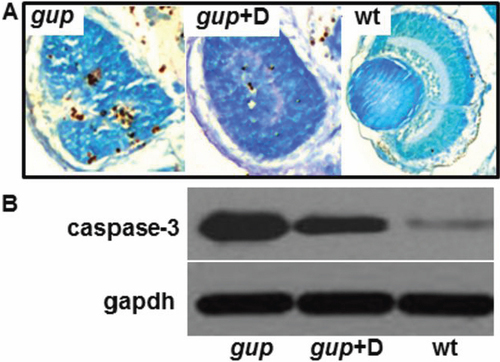
Effect of diferuloylmethane on cell death in gup mutant larvae. A: Comparison of TUNEL-positive cells in coronal cryosections of the eye from mutant gup embryos (left), mutant gup embryos treated with 5 μM diferuloylmethane (center) and wildtype embryos (right) at 6 dpf. Histological sections counterstained with methyl green. B: Representative western blot of lysates from untreated mutant larvae (gup), mutant larvae treated with 5 μM diferuloylmethane (gup+D) and wildtype larvae (wt). Upper lanes, correspond to cleaved caspase-3; lower lanes, corresponding gapdh loading controls. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
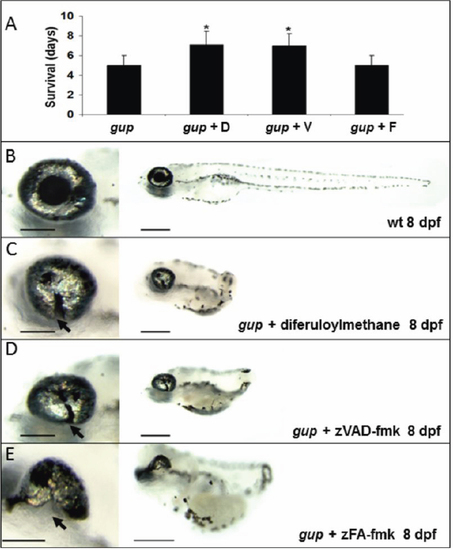
Effect of caspase inhibition on survival and optic fissure closure. A: Mean survival of gup mutant embryos with no treatment or with either diferuloylmethane, zVAD-fmk or control inhibitor zFA-fmk. n=30 for each group, mean±SEM (*p<0.001). B: Wildtype (wt) larval phenotype at 8 dpf. C: Phenotype of gup mutants treated with 5 μM diferuloylmethane. D: Phenotype of gup mutant embryos treated with 300 μM zVAD-fmk. E: Phenotype of gup mutants treated with 300 μM zFA-fmk. Arrows indicate the position of the coloboma. Size bar in left panels=200 μm; size bar in right panels=500 μm. |