- Title
-
Intraovarian transplantation of stage I-II follicles results in viable zebrafish embryos
- Authors
- Csenki, Z., Zaucker, A., Kovacs, B., Hadzhiev, Y., Hegyi, R., Lefler, K.K., Muller, T., Kovacs, R., Urbanyi, B., Varadi, L., and Muller, F.
- Source
- Full text @ Int. J. Dev. Biol.
|
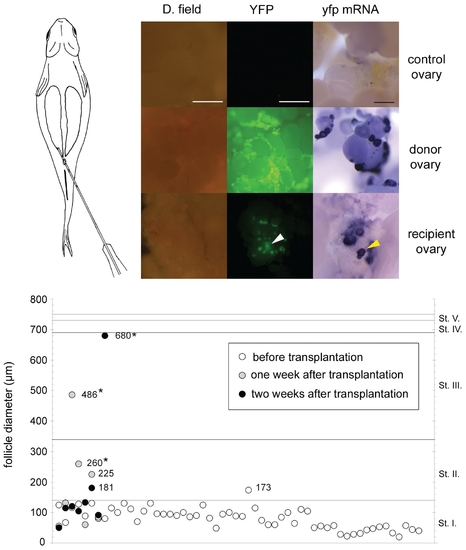
Transplanted follicles invade the recipient ovary and continue oocyte development. (A), Schematic picture of the process of transplantation. (B-D), Intrauterine injection of stage I follicles results in the appearance of transplanted donor oocytes/follicles in the non-transgenic host ovary. dark field (left), YFP filter view (middle) and whole mount in situ hybridisation analysis (right) of ovaries. Transgenic donor follicles are yellowish green in GFP filter view (C) and purple in the whole mount hybridisation analysis, while no YFP signal is detected in wild type recipient ovaries without transplantation (B). (D), transplanted follicles are indicated by arrowheads among non-transgenic host follicles in a recipient ovary. (E), Size distribution of follicles (in μm) before transplantation and after recovery from recipient ovaries. Asterisks indicate values of donor follicles recovered from recipient ovaries that are significantly different from the donor follicles measured before transplantation (Kruskal-Walis test, P≤0,05). Scale bar indicates 300 μm. |
|
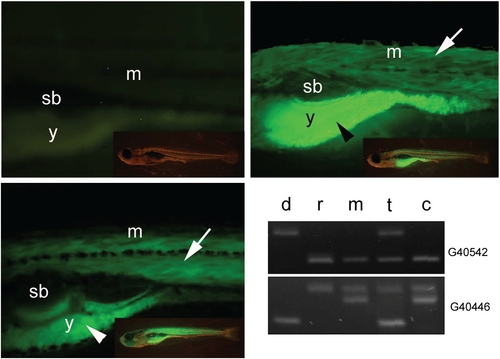
Transplanted follicles develop to fertilizable eggs and produce viable offspring. (A) Non-transgenic offspring from recipient female mated with wild type male. (B) Transgenic offspring of a sibling of the donor female mated with a wild type male. (C) Transgenic offspring developing from a recipient female, which was injected with transgenic donor follicles and mated with wild type male 3 weeks after transplantation. All larvae are shown at 10 days after fertilization. Transgenic and non transgenic offspring of recipient female were analysed at 10 days post fertilization. Side view onto the trunk above the yolk ball and part of tail are shown. Fluorescence signal of the β-actin:yfp reporter construct activity is detected in the skeletal muscle and the yolk ball (arrow and arrowhead respectively). Inserts show the full view of larvae respectively. (D) Microsatellite analysis of genetic composition of donor female (d), recipient female (r), male used for crossing with recipient female (m), offspring developing from transplanted follicle (t) and sibling from recipient female (c). The identification number of microsatellite markers are indicated on the right (for details see Table 2). Abbreviations, (sb) swim bladder, (m), muscle, (y) yolk. |
|
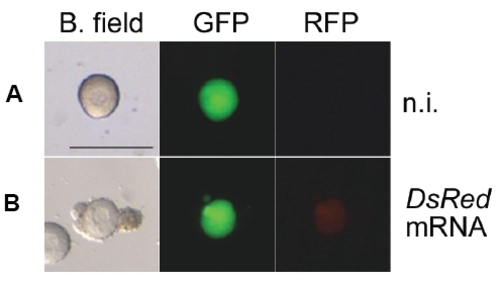
Microinjected stage I and stage II follicles express reporter proteins. Transgenic YFP positive non-injected (A) and DsRed mRNA injected (B) follicles recovered from recipient mothers 1 day after transplantation in bright field, GFP and RFP filter views. Scale bar indicates 400 μm. |