- Title
-
Identification of a distant cis-regulatory element controlling pharyngeal arch-specific expression of zebrafish gdf6a/radar
- Authors
- Reed, N.P., and Mortlock, D.P.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Dyn.
|
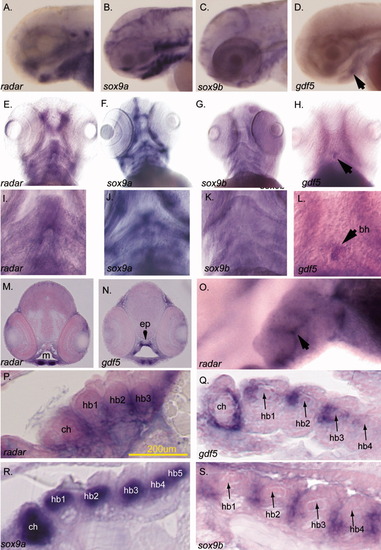
AL,O: Expression of radar in the pharyngeal arch cartilages. (A-D,O lateral; E-L ventral). The expression of radar, sox9a, sox9b, and gdf5 in ventral arches is evident by in situ hybridization at 77 hours postfertilization (hpf). B,C,F,G,J,K: sox9a (B,F,J) is detected in cartilage while sox9b (C,G,K) is localized to the epithelial sheath surrounding cartilages (K). D,H,L: gdf5 is expressed in the jaw joint (white arrow, H) and medially in posterior arches, and at the basihyal (black arrows; Chiang et al.,[2001]; Yan et al.,[2005]). radar expression is detected in the jaw and along the ventral midline (E and arrows in I). M,N: Transverse sections detecting radar and gdf5 transcript. Both are expressed in the jaw joint (paired ventral staining in M and N) while only gdf5 is expressed dorsally in the pharynx (N). O: High resolution whole-mount imaging shows radar is detectable between posterior arch pharyngeal cartilages (arrow; lateral view; left = anterior). P: Sagittal section shows that radar is expressed surrounding medial hypobranchial cartilages. Q-S: Sagittal sections showing sox9a, sox9b, and gdf5 transcripts. gdf5 and radar are coexpressed near the midline around ceratohyals and hypobranchials though radar extends more ventrally below hypobranchials. bh, basihyal; ch, ceratohyal; hb1, hypobranchial 1; hb2, hypobranchial 2; hb3, hypobranchial 3; ep, ethmoid plate; e, eye; m, mouth opening. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
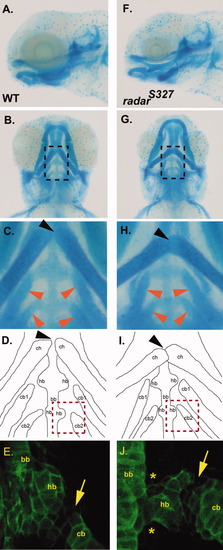
Analysis of pharyngeal arch organization in wild-type and radar mutant larvae. A,B: Lateral and ventral view of Alcian blue stained 5 days postfertilization (dpf) wild-type larvae. C: High magnification of dotted box area in A noting normal articulation of ceratohyals (at joint indicated by black arrow) and normal positions of ceratobranchials (red arrows) D: Camera lucida image outlining the Alcian blue stained cartilages in B. E: Collagen-2α1 staining of the third arch in 5 dpf wild-type larvae to visualize ceratobranchial, basibranchial, and hypobranchial. F,G: Lateral and ventral view of Alcian blue radars327 mutant. H: High magnification of region in panel F demarcated by dotted box showing abnormal articulation of ceratohyals (black arrow) and more sharply angled ceratobranchials (red arrows). I: Camera lucida image of the Alcian blue stained cartilages in E. J: Collagen-2α1 staining of third arch in 5 dpf mutant larvae reveals morphological abnormalities of the hypobranchial (asterix) and hypobranchial/ceratobranchial joint (arrow). ch, ceratohyals; cb, ceratobranchials; bb, basibranchial; hb, hypobranchials. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
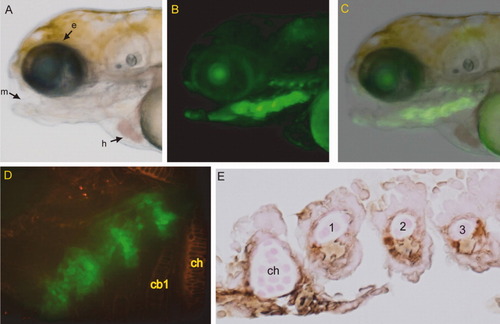
ECR5 drives transgene expression in a subset of the pharyngeal arches in context of the minimal cFOS promoter. A: Lateral brightfield image of ECR5 transgenic zebrafish larva at 4 days postfertilization (dpf). B: Fluorescent image of ECR5 transgenic at 4 dpf showing transgene expression in a subset of the pharyngeal arches. The faint line of signal dorsal to the arches was due to autofluorescence and not transgene expression, as revealed by staining with anti-GFP antibody (not shown). C: Overlay of brightfield and fluorescent ECR5 transgene expression. D: Ventral view of ECR5 transgene expression (green). Anterior is at top right. Wheat germ agglutinin labeling of cartilage (red) shows that transgene expression does not overlap with mature cartilage of the flanking ceratohyals. E: Immunohistochemistry for GFP on a ECR5 transgenic 4 dpf embryo sagittal section shows that transgene (brown) is not expressed in internal chondrocytes within cartilage elements but is restricted to perichondrium and cells between elements. e, eye; m, mouth; h, heart; ch, ceratohyal cb1, ceratobranchial 1. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|

Unillustrated author statements |