- Title
-
Cloning and spatiotemporal expression of zebrafish neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha 6 and alpha 4 subunit RNAs
- Authors
- Ackerman, K.M., Nakkula, R., Zirger, J.M., Beattie, C.E., and Boyd, R.T.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Dyn.
|
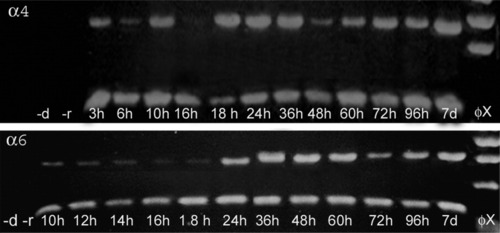
Expression of chrna6 and chrna4 RNA in zebrafish. Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was used to determine when chrna6 and chrna4 nAChR subunit RNAs were expressed in embryos and larvae. Three micrograms of RNA from each age zebrafish (h, hpf; d, dpf) were reverse-transcribed and amplified using subunit-specific primers. The &beta-actin was also amplified for each age. As controls, PCR was performed using zebrafish RNA without reverse transcription (-r) or without cDNA (-d). The size of each PCR product was consistent with the size predicted by the cDNA sequences. The Φx 174 HaeIII DNA (Φχ) was used as a size marker. |
|
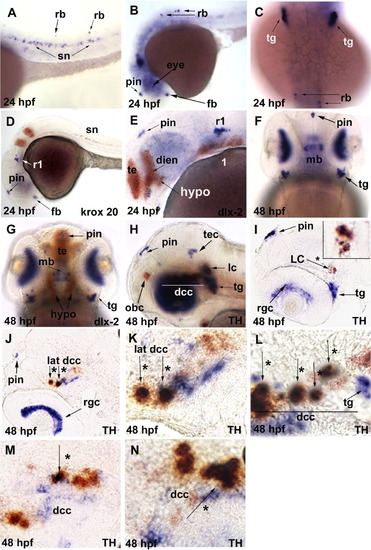
In situ hybridization analysis of chrna6 RNA expression in 24 hours postfertilization (hpf) and 48 hpf zebrafish embryos. The purple stain represents chrna6 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) subunit mRNA in all panels, and the orange labeling is either krox20 in rhombomeres 3 and 5, dlx-2 in telencephalon, diencephalon and pharyngeal arches, or tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) in catecholaminergic neurons. Use of these additional probes is indicated in each panel. All images are lateral views with the anterior to the left unless otherwise noted. Arrows point to specific brain regions and arrows with an asterisk denote co-labeling with TH. A: In 24 hpf embryos, the chrna6 transcript was seen in a subset of spinal neurons and a subset of Rohon-Beard sensory neurons in the trunk. B: 24 hpf, chrna6 expression was present in pineal, ventral forebrain, and Rohon-Beard sensory neurons. C: At 24 hpf, dorsal view, chrna6 expression in trigeminal ganglion and Rohon-Beard sensory neurons. D: At 24 hpf, chrna6 expression was seen in rhombomere 1 as well as forebrain, pineal, and spinal neurons. The Krox20 probe (orange) labeled rhombomeres 3 and 5. E: At 24 hpf, chrna6 expression was identified in diencephalon as shown by the colocalization with dlx2, a marker for telencephalon, diencephalon, and hypothalamus. Additionally, chrna6 is labeled in pineal and rhombomere 1. F: At 48 hpf, dorsal view, chrna6 transcript was heavily expressed in the retina with limited expression in midbrain and continued expression in pineal and trigeminal ganglion. G: At 48 hpf, dorsal view, expression in midbrain is not colocalized with dlx2 and is dorsal to the dlx2 expression domain (orange labeling) in telencephalon, diencephalon, and hypothalamus. Additionally, expression in retina and trigeminal ganglion was present. H: At 48 hpf, chrna6 was expressed in tectum, retina, pineal, and trigeminal ganglion. The diencephalic catecholaminergic cluster and locus coeruleus are detected by the TH probe (orange). As heavy retinal expression is evident in H that impedes with visualizing midbrain, I-N are 8-12-micron sagittal sections though the diencephalic regions marked by a line in H and L. I: At 48 hpf, chrna6 expression was clear in the pineal, retinal ganglion cells, trigeminal ganglion, and colocalization with TH in the locus coeruleus was evident. The insert is a magnification of locus coeruleus. J: At 48 hpf, indicates chrna6 expression in the most lateral regions of the diencephalic catecholaminergic cluster colocalizing with TH. Additionally, chrna6 expression in the pineal and retinal ganglion cells was present. K: At 48 hpf, higher magnification of K, colocalization of TH and chrna6 transcript in the lateral most region of the diencephalic catecholaminergic cluster in the midbrain. L: At 48 hpf, a midsagittal section through the diencephalic catecholaminergic cluster indicates chrna6 colocalization with TH. M,N: At 48 hpf, medial sagittal sections, indicate areas of colocalization with TH and areas solely expressing chrna6 RNA. dien, diencephalon; dcc, diencephalic catecholaminergic cluster; fb, forebrain; hypo, hypothalamus; lat, lateral; lc, locus coeruleus; 1, mandibular pharyngeal arch; mb, midbrain; obc, olfactory cluster in olfactory bulbs; pin, pineal; rgc, retinal ganglion cells; r1, rhombomere 1; rb, Rohon-Beard sensory neurons; sn, spinal neurons; tec, tectum; tg, trigeminal ganglion. |
|
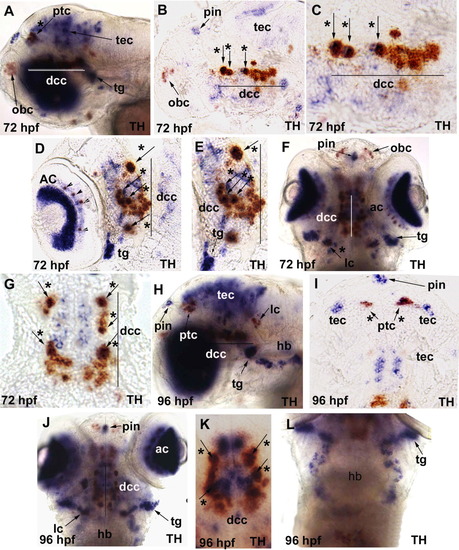
In situ hybridization analysis of chrna6 RNA expression in 72 hours postfertilization (hpf) and 96 hpf zebrafish embryos. The purple stain represents chrna6 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) subunit mRNA in all panels, and the orange labeling is tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) mRNA. All images are lateral views with the anterior to the left unless otherwise noted. Arrows point to specific brain regions, arrowheads point to amacrine cells in the retina, and arrows with an asterisk denote co-labeling with TH. Line denotes diencephalic catecholaminergic cluster in A-G. A: At 72 hpf, chrna6 was now localized heavily to the eye and tectum, pineal, trigeminal ganglion, and colocalization with TH in the diencephalic catecholaminergic cluster and pretectal catecholaminergic cluster. B: At 72 hpf, midsagittal section, showed chrna6 expression in pineal, tectum, and colocalization with TH in a subset of cells in the diencephalic catecholaminergic cluster, and no expression in the olfactory bulb catecholaminergic cluster. C: At 72 hpf, midsagittal section, higher magnification of B, colocalization of chrna6 with TH in the diencephalic catecholaminergic cluster. D: At 72 hpf, sagittal section, chrna6 expression in amacrine cells of the retina, retinal ganglion cells, trigeminal ganglion, and colocalization with TH in a subset of cells in the diencephalic catecholaminergic cluster. E: At 72 hpf, sagittal section higher magnification of D, colocalization of chrna6 with TH in the diencephalic catecholaminergic cluster and expression in trigeminal ganglion. F: At 72 hpf, dorsal view of whole animal, showed chrna6 expression in retina, trigeminal ganglion, pineal, and colocalization with TH in the diencephalic catecholaminergic cluster and locus coeruleus. G: At 72 hpf, longitudinal section, showed chrna6 expression in a subset of TH+ cells in the diencephalic catecholaminergic cluster. H: At 96 hpf, expression was evident in retina, pineal, tectum, trigeminal ganglion, a subset of cells in the hindbrain consistent with cranial sensory neurons, and colocalization with TH in the diencephalic catecholaminergic cluster, locus coeruleus, and pretectal catecholaminergic cluster. I: At 96 hpf, longitudinal section, demonstrated colocalization of TH and chrna6 expression in the pretectal area, with pineal and tectum labeled. J: At 96 hpf, dorsal view whole-mount, chrna6 expression shown in retina, pineal, trigeminal ganglion, diencephalic catecholaminergic cluster, and locus coeruleus. K: At 96 hpf, dorsal view whole embryo, chrna6 colocalization with TH in the diencephalic catecholaminergic cluster. L: At 96 hpf, dorsal view whole embryo, chrna6 expression in hindbrain neurons consistent with the localization of cranial sensory neurons. ac, amacrine cells in the retina; dcc, diencephalic catecholaminergic cluster; hb, hindbrain nuclei; lc, locus coereuleus; obc, olfactory bulb catecholaminergic cluster; ptc, pretectal catecholaminergic cluster; pin, pineal; tec, tectum; tg, trigeminal ganglion. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
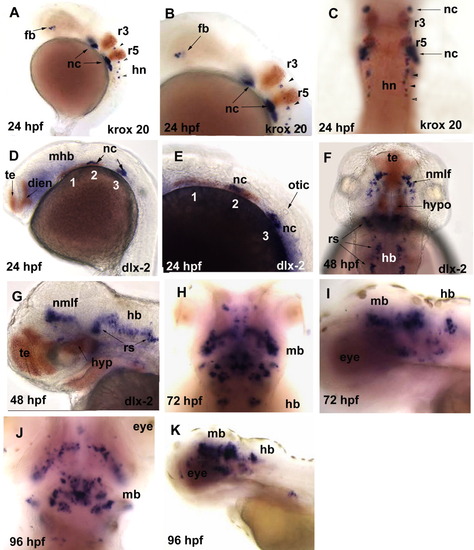
Whole-mount in situ hybridization analysis of chrna4 RNA expression in 24-96 hours postfertilization (hpf) zebrafish embryos. The purple stain represents chrna4 neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) subunit mRNA in all panels, and orange labeling denotes either krox20 RNA in rhombomeres 3 and 5 or dlx2 RNA in telencephalon, diencephalon, and the pharyngeal arches. All images are lateral views with the anterior to the left unless otherwise noted. Arrows point to specific brain regions and arrowheads point to spinal neurons. A: At 24 hpf, chrna4 expression was localized to a limited area of forebrain, a subset of cells along the yolk sac consistent with neural crest cells, and in a subset of hindbrain neurons with expression beginning in rhombomere 4. B: At 24 hpf, magnification of A, expression in forebrain, hindbrain neurons, and in dlx2-expressing areas likely to be neural crest. C: At 24 hpf, dorsal view whole embryo, possible neural crest expression at the level of, but outside of the rhombomeres, with expression also evident in spinal neurons. D: At 24hpf, chrna4 likely localization in neural crest cells in the dlx2-expressing domain of the mandibular (1), hyoid (2), and brachial (3) pharyngeal arches. E: At 24 hpf, higher magnification of D, chrna4 expression was evident in the dlx2 expression domain of the hyoid (2) pharyngeal arch and brachial (3) arch. F: At 48 hpf, dorsal view, localization consistent with the nucleus of the medial longitudinal fascicle and reticulospinal neurons of the hindbrain. G: At 48 hpf, chrna4 expression was not present in the telencephalon or hypothalamus as evident by using dlx2 expression to localize these structures. There was midbrain and hindbrain expression consistent with the localization pattern of the nucleus of the medial longitudinal fascicle and reticulospinal neurons. H: At 72 hpf, dorsal view and I: At 72 hpf, chrna4 expression was extensive in midbrain and limited in hindbrain. J: At 96 hpf, dorsal view and K: At 96 hpf, chrna4 expression was extensive in midbrain and limited in hindbrain similar to the pattern that seen in 72 hpf embryos (I). dien, diencephalon; fb, forebrain; hb, hindbrain; hn, hindbrain neurons; mb, midbrain; mhb, midbrain hindbrain boundary; nc, neural crest; otic, otic vesicle; pharyngeal arches: (1) mandibular, (2) hyoid, and (3) brachial arch; nmlf, nucleus of the medial longitudinal fascicle; rs, reticulospinal neurons; rhombomeres 3 (r3) and 5 (r5), telencephalon (te). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|

Unillustrated author statements EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|