- Title
-
An essential role for Radar (Gdf6a) in inducing dorsal fate in the zebrafish retina
- Authors
- Gosse, N.J., and Baier, H.
- Source
- Full text @ Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA
|
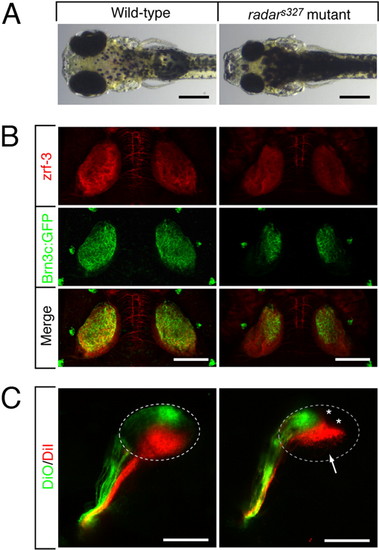
Morphological and retinotectal phenotypes of radars327. (A) Zebrafish radars327 mutants have small eyes and appear dark, because of a VBA defect (see text). Dorsal brightfield views of 7 dpf WT sibling and homozygous radars327 mutant larvae. (B) radars327 mutants lack ventral innervation of the optic tectum. Dorsal confocal projections of 7 dpf larvae show that innervating RGC axons (expressing Brn3c:mGFP) are confined to the dorsal tectum in the mutant. Costaining with a neuropil marker (zrf-3 antibody) reveals that the size of the tectum is similar in WT and mutant. (C) radars327 mutants have a compressed dorsal–ventral retinotectal map. Fixed WT and radars327 eyes (7 dpf) were injected with DiO (ventrally) and DiI (dorsally). Lateral confocal projections are shown. Arrow highlights ventral tectal region not innervated by RGCs in radars327; asterisks show positions of skin melanophores. (Scale bars: 300 μm in A, 100 μm in B and C.) |
|
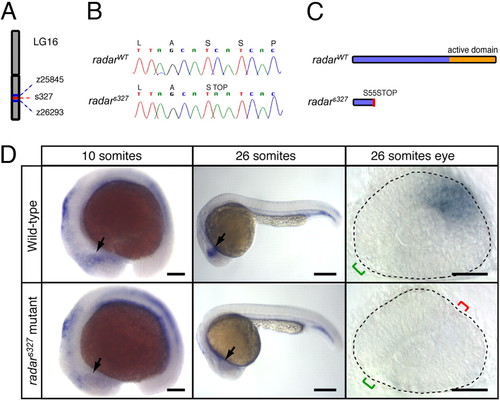
Positional cloning and expression pattern of radar. (A) s327 maps to chromosome 16 between z25845 (2.3 cM) and z26293 (0.7 cM). (B) Sequencing of WT and s327 cDNA reveals a single C-to-A substitution in position 164 of the radar ORF, resulting in a premature stop codon. (C) Predicted translated peptides arising from radarWT and radars327. The mutation is predicted to result in a truncated protein, lacking the mature signaling domain. (D) Whole-mount in situ hybridization shows a restricted pattern of radar expression in WT embryos. radar mRNA is largely absent from the retina of radars327 mutants at all stages. In WT, expression is evident in the distal optic vesicle of WT embryos at 10 somites (arrow). At 26 somites, radar is expressed dorsally, opposite of the optic fissure (green bracket). Note ectopic fissures (red bracket) in radars327 mutants. (Scale bars: 150 μm for 10 somites, 250 μm for 26 somites, 50 μm for dissected 26 somite eyes.) EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
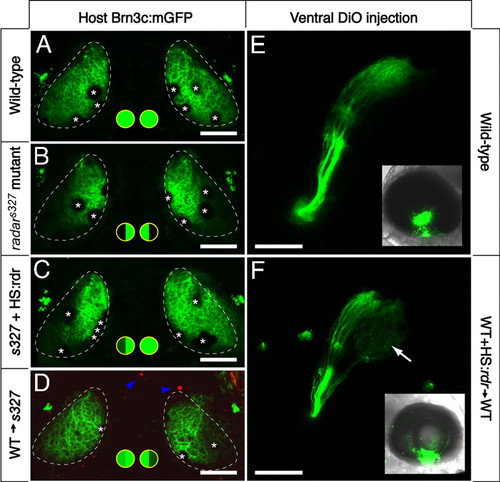
Cell-cell signaling through Radar is sufficient for ventral tectum innervation. (A-D) Rescue experiment. Brn3c:mGFP-labeled retinotectal projections were imaged in vivo at 7 dpf. The tectal neuropil is outlined with a dashed line. Green-filled circles summarize dorsal and ventral tectum innervation results. (A) WT tecta show full innervation. (B) radars327 mutants lack ventral innervation. (C) radarWT expression from heatshock-promoter rescues the retinotectal phenotype of the mutant. In the case shown, only one side was rescued. PCR-based genotyping confirmed that only the rescued eye contained hsp70:radarWT; the other eye had likely not received the injected plasmid because of the mosaicism inherent in transient transgenesis. (D) The radar gene acts cell-nonautonomously in the retina. WT cells transplanted into radars327 host embryos are sufficient to rescue ventral innervation. Only the host carried the Brn3c:mGFP transgene. Donor-derived cells (blue arrowheads) were labeled with rhodamine dextran, and do not contribute to the tectum. (E and F) Gain-of-function experiment. DiO was injected into the ventral retina, and its labeling pattern was imaged from a lateral view. Insets show injected eye. In normal WT larvae (E), ventral RGCs project exclusively to the dorsal tectum. In chimeric WT larvae (F) that have received a transplant of WT cells carrying the hsp70:radarWT construct, some ventral axons ectopically innervate the ventral tectum (arrow). Asterisks (in A-D) show positions of skin melanophores. (Scale bars, 100 μm.) |
|
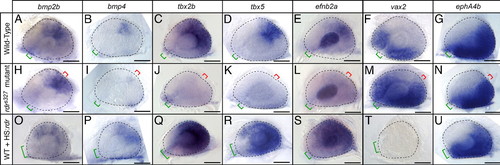
Radar signaling affects known determinants of dorsal-ventral retinal patterning. Expression patterns are visualized by whole-mount in situ hybridization of eyes from 26-somite embryos. Retinal markers in WT (A-G), radars327 mutants (H-N), and WT overexpressing hsp70:radarWT (O-U). In radars327 mutants, retinal bmp2b expression remained normal, bmp4 expression was severely reduced, tbx2b, tbx5, and efnb2a expression was absent, and vax2 expression was expanded dorsally. In radar-overexpressing embryos, bmp2b, bmp4, tbx2b, tbx5 and efnb2a expression were expanded ventrally, and vax2 was lost. ephA4b was unaffected by either loss or gain of radar function. Eyes overexpressing radar were often small and failed to close at the optic fissure. Neural retina is outlined with dashed line; green bracket identifies optic fissure location and size; red bracket indicates location of ectopic fissures in mutants. (Scale bars, 50 μm.) EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
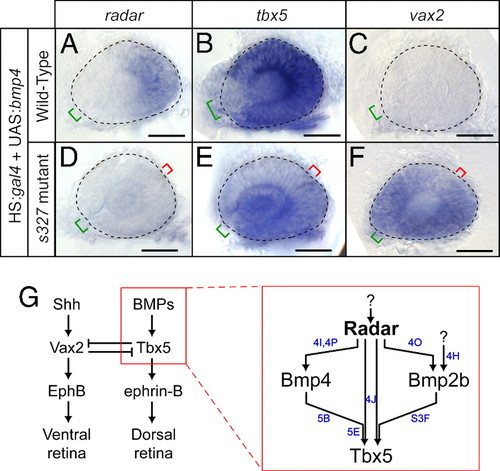
Overexpression of bmp4 requires radar to alter dorsal–ventral patterning. (A--F) Expression patterns visualized by whole-mount in situ hybridization of eyes from 26-somite embryos. Neural retina is outlined with dashed line; green bracket identifies optic fissure location and size; red bracket indicates location of ectopic fissures in mutants. (Scale bars, 50 μm.) radar expression is mildly expanded (A), tbx5 expression dramatically increases (B), and vax2 expression is eliminated (C) in WT; hsp70:gal4; UAS:bmp4 embryos. radar expression remains absent (D), tbx5 is expressed at low levels in ectopic locations (E), and vax2 expression is dorsally expanded (F) in radars327 mutant; hsp70:gal4; UAS:bmp4 embryos. (G) Summary model for retinal patterning, synthesizing roles for Radar with known dorsal–ventral patterning genes. Radar is the critical determinant of dorsal identity and is required for normal expression of Bmp4, Tbx transcription factors, and ephrin-B. Blue letters indicate which panels in this figure and in Fig. 4 and Fig. S3F provide evidence for the relationships shown. |
|
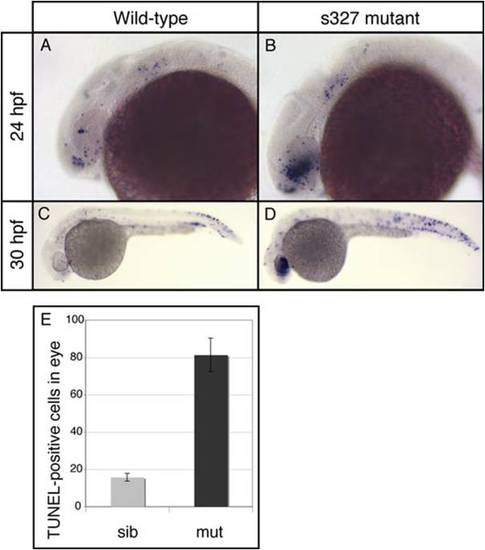
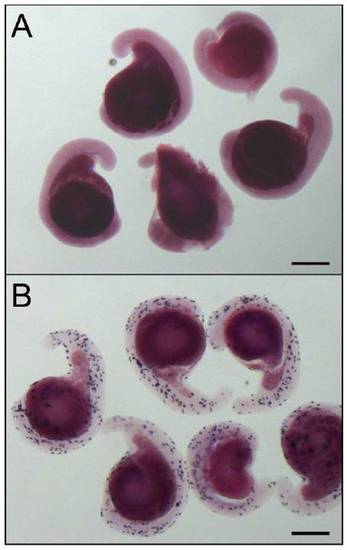
Increased cell death in the eyes of radars327 mutants. Lateral views of whole-mount TUNEL-stained embryos. (A) 24 hours post-fertilization (hpf) WT embryos have small numbers of TUNEL-positive cells throughout the head and trunk. (B) 24hpf radars327 mutant embryos have a large increase in TUNEL reactivity in the developing eye. (C and D) 30 hpf radars327 mutant embryos have significantly more TUNEL-positive cells in the eyes than WT. The difference is less dramatic in the trunk. (E) Quantification of TUNEL staining in 30 hpf embryos. radars327 mutants (n = 6) have significantly more TUNEL-positive cells in the eye than WT embryos (n = 8, t test, P < 0.000001). |
|
In situ hybridzation reveals transient overexpression of radar. (A) Uninjected 18 somite embryos, heatshocked at 12-14 somites show no specific pattern of expression after 30 min of color reaction. (B) Embryos injected with 25 ng/ μl hsp70:radarWT, heat-shocked at 12-14 somites show intense staining after 10 min of color reaction, with broad mosaic expression, often, but not always, including the eye. (Scale bars, 100 μm.) |
|
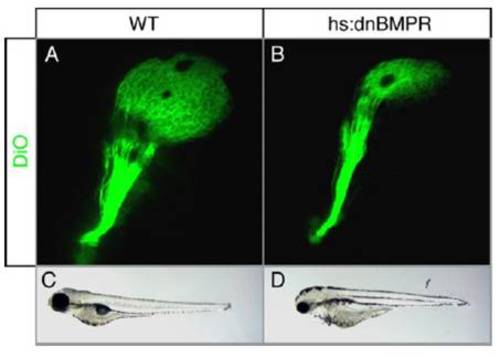
Dominant-negative inhibition of Bmp/Gdf signaling in the eye. (A and B) Lateral view of DiO-filled retinotectal projections in 5 days post-fertilization (dpf) larvae heatshocked at 12 somites. In controls (A), the entire tectum is innervated. In hs:dnBMPR transgenic animals (B) only dorsal tectum is innervated, similar to radars327. (C and D) Brightfield lateral view of 4 dpf larvae. Control larvae (C) show normal eye size, whereas hs:dnBMPR larvae (D) have smaller eyes similar to radars327. |
|
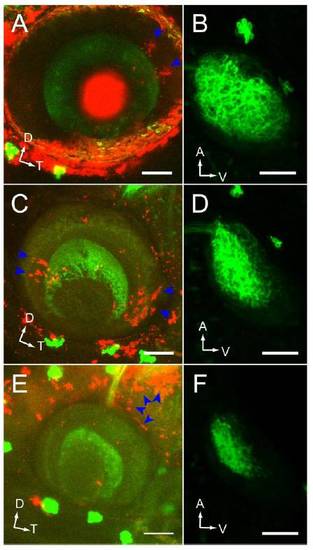
Donor-derived clone location and position-dependent rescue of the retinotectal projection in WT-> radars327 chimeras. (A, C, and E) Lateral confocal projection of the eye. Donor-derived clones were labeled with rhodamine-dextran (blue arrowheads). GFP was only expressed in RGCs of the host. Dorsal up, temporal to the right. (Scale bars, 50μm.) (B, D, and F) Corresponding dorsal confocal projections of tectum. Anterior up, ventral to the right. (Scale bars, 50μm.) (A and B) Donor-derived clones in dorsal eye drive substantial rescue of ventral tectum innervation. (C and D) Donor-derived clones in the ventral eye fail to rescue ventral tectum innervation. (E and F) Donor-derived clones outside of the eye do not rescue ventral tectum innervation. |
|
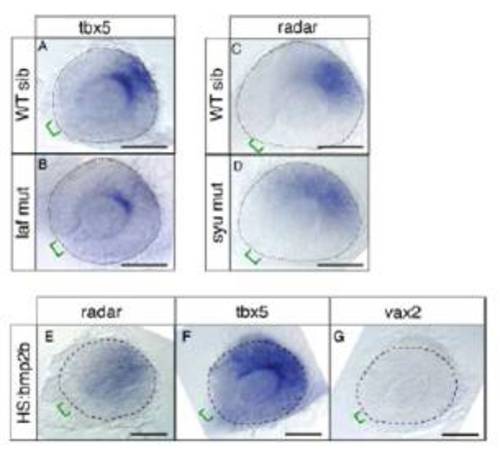
Additional analysis of Radar signaling and regulation. (A-G) Dissected eyes following whole-mount in situ hybridizations on 26-somite embryos with the antisense probes indicated. (Scale bars, 50 μm.) (A) WT eyes express tbx5 in the dorsal retina, opposite of the optic fissure. (B) lost-a-fin (laf ) mutants, lacking functional Alk8 receptor, have reduced expression of tbx5. (C) In WT eyes radar expression is restricted to a narrow patch opposite of the optic fissure. (D) In sonic you (syu) mutants, in which Shh is disrupted, radar expression is slightly expanded to the ventral retina. (E-G) bmp2b overexpression mirrors the effects of bmp4 overexpression. hsp70:bmp2b transgenic fish were induced at 12-14 somites to overexpress bmp2b. radar expression is weakly expanded, tbx5 expression is strongly up-regulated, vax2 expression is absent from the retina. |

Unillustrated author statements PHENOTYPE:
|