- Title
-
Frizzled 8a function is required for oligodendrocyte development in the zebrafish spinal cord
- Authors
- Kim, S., Kim, S.H., Kim, H., Chung, A.Y., Cha, Y.I., Kim, C.H., Huh, T.L., and Park, H.C.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Dyn.
|
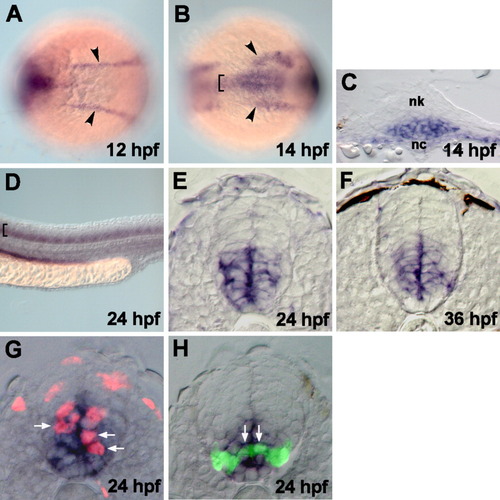
fz8a expression revealed by in situ RNA hybridization. A,B: Dorsal views of the trunk region of whole embryos, anterior to the left. Arrowheads and brackets indicate expressions in the prechordal plate and medial neuroectoderm, respectively. C: Transverse sections, dorsal to the top, through the trunk region. Ventral neural keel (nk) cells, overlying notochord (nc), started to express fz8a at 14 hpf. D: Lateral view of the spinal cord of whole embryos, dorsal to the top and anterior to the left. Brackets indicate the expression of fz8a in the ventral spinal cord cells. E-H: Transverse sections of the spinal cord, dorsal to the top. E, F: fz8a-expressing cells occupy the ventral neural precursor cells. G: fz8a-expressing cells incorporate BrdU, as indicated by anti-BrdU antibody staining (red color), indicating that they are proliferating precursors. Arrows indicate fz8a+, BrdU+ neural precursor cells. H: fz8a-expressing cells confer olig2+ precursors, which are marked by EGFP fluorescence in the Tg(olig2:egfp) embryo. Arrows indicate fz8a+, olig2+ precursor cells in the ventral spinal cord. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
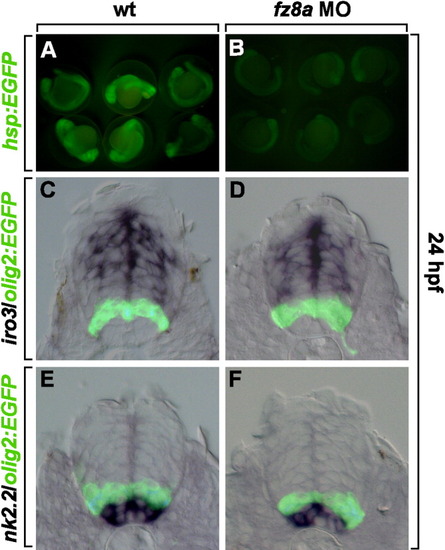
fz8a function is not required for dorso-ventral patterning of the spinal cord. A, B: Tg(hsp70:fz8aCRDTM-egfp) embryos were heat shocked at 18 hpf. A: Control embryos had high levels of EGFP-fluorescence in the whole embryos. B: Embryos injected with fz8a MO had low levels of EGFP fluorescence, suggesting that fz8a MO works specifically to knock-down fz8a expression. C-F: Transverse sections of the spinal cord of Tg(olig2:egfp) embryos. C, E: Control embryos that show olig2-EGFP and iro3 expression (C), or olig2-EGFP and nk2.2 expression (E), revealed by in situ RNA hybridization. D, F: Tg(olig2:egfp) embryos injected with fz8a MO and hybridized by iro2 (D) and nk2.2 (F) RNA probes. |
|
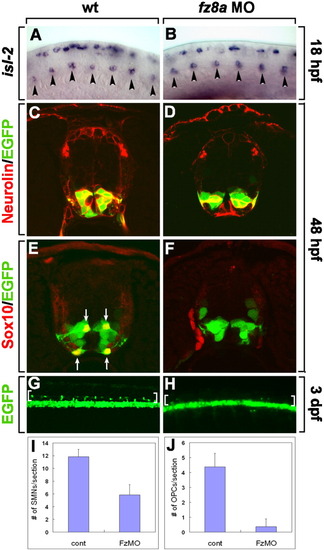
fz8a function is required for motor neuron and oligodendrocyte development. A, B: Lateral views of spinal cords hybridized with an isl-2 RNA probe at 18 hpf, dorsal to the top and anterior to the left. A: Control embryos. B: fz8a MO-injected embryos. Arrowheads indicate primary motor neurons in the ventral spinal cord. C-F: Transverse section of the spinal cord of Tg(olig2:egfp) embryos, dorsal up. C, D: Combined anti-Neurolin (red fluorescence) and olig2:EGFP labeling in control embryos (C), and fz8a MO-injected embryos (D). E, F: Labeling with an anti-Sox10 antibody to mark OPCs (red fluorescence) in control (E) and fz8a MO-injected (F) Tg(olig2:egfp) embryos. G, H: Side views of whole-mount 3-dpf embryos, dorsal up and anterior to the left. G: Control Tg(olig2:egfp) embryo showing numerous olig2:EGFP+ OPCs in the dorsal spinal cord (brackets). H: fz8a MO-injected Tg(olig2:egfp) embryo. Only a few OPCs are evident in the dorsal spinal cord (brackets). I, J: Quantification of Neurolin+ secondary motor neurons (SMNs) (I) and Sox10+ OPCs (J) at 48 hpf in control (cont) and fz8a MO-injected (FzMO) embryos. Bars indicate the average number of cells per transverse section. Data were obtained from 10 sections from each of 5 control and 5 fz8a MO-injected embryos. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
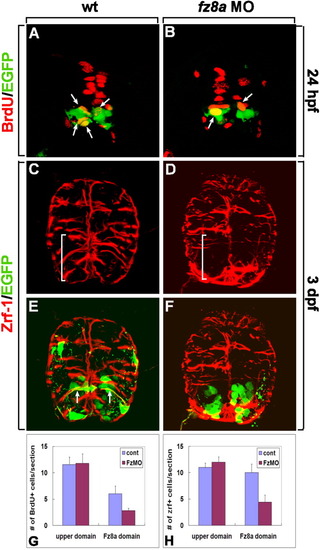
fz8a function is required for the proliferation and spatial organization of radial glia in the ventral spinal cord. A-F: Transverse sections of spinal cords of Tg(olig2:egfp) embryos, dorsal up. A, B: Labeling of control (A) and fz8a MO-injected (B) embryos with an anti-BrdU antibody (red fluorescence) to detect proliferating cells. Arrows indicate olig2-expressing BrdU+ precursors. C-F: Combined anti-Zrf-1 (red fluorescence) and olig2:EGFP labeling of wt control (C, E, same section) and fz8a MO-injected (D, F, same section) embryos. fz8a MO-injected embryo shows disorganized radial glia in the ventral spinal cord (brackets). Arrows indicate processes of olig2+ radial glial cells labeled by olig2:EGFP and anti-Zrf-1 antibody staining (E). G: Quantification of BrdU+ proliferating cells at 24 hpf in control (cont) and fz8a MO-injected (FzMO) embryos. P < 0.0001 by Student's t-test for Fz8a domain. H: Quantification of the number of Zrf-1+ radial glial processes at 3 dpf in control (cont) and fz8a MO-injected (FzMO) embryos. Bars indicate the average number of cells per transverse section. Data were obtained from 10 sections from each of 8 control and 8 fz8a MO-injected embryos. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
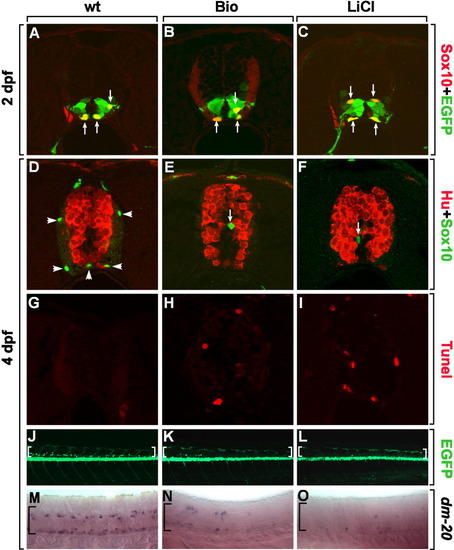
Down-regulation of Wnt signaling is required for the maturation of OPCs. A-I: Transverse sections of spinal cord, dorsal up. A-C: Tg(olig2:egfp) embryos labeled with an anti-Sox10 antibody to detect undifferentiated OPCs at 2 dpf. Arrows indicate Sox10+, olig2:EGFP+ OPCs in control (A), Bio-treated (B), or LiCl-treated (C) embryos from 24-48 hpf. D-F: Combined anti-Hu and anti-Sox10 labeling of control (D), Bio-treated (E), or LiCl-treated (F) embryos from 2-4 dpf. Arrowheads indicate differentiated oligodendrocytes in the white matter (D) and arrows indicate undifferentiated OPCs near the ventricle (E, F). G-I: TUNEL staining of control (G), Bio-treated (H), or LiCl-treated (I) embryos from 2-4 dpf. J-L: Side views of Tg(olig2:egfp) embryos, dorsal to the top and anterior to the left. J: Control embryo has numerous olig2:EGFP+ oligodendrocytes in the dorsal spinal cord (brackets). Bio-treated (K) and LiCl-treated (L) embryos from 2 dpf show only a few olig2:EGFP+ cells in the dorsal spinal cord (brackets) at 4 dpf. M-O: Lateral views of embryos hybridized with dm-20 RNA probes, which label mature oligodendrocytes at 4 dpf. M: Control embryos have many dm-20+ mature oligodendrocytes in the spinal cord (bracket). Bio-treated (N) and LiCl-treated (O) embryos have few cells marked by dm-20, suggesting that OPCs fail to differentiate into mature oligodendrocytes (brackets). |
|
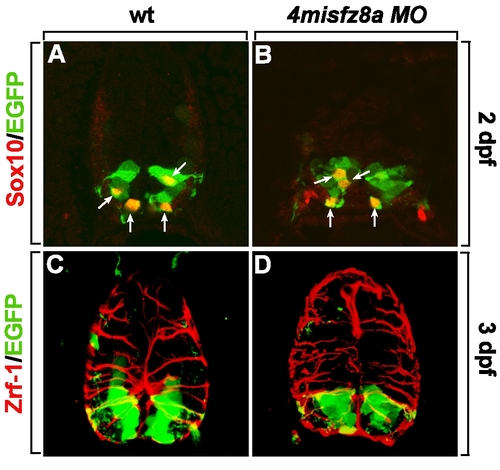
Specificity test of Fz8a MO by injection of 4misfz8a MO. All panels are transverse sections of the spinal cords of Tg(olig2:egfp) embryos, dorsal up. A, C: Wild-type embryos labeled with anti-Sox10 (A) and anti-Zrf-1 (C) antibodies to detect OPCs and radial glial processes. B, D: Embryos injected with the four base pair mismatched control morpholino for fz8a (4misfz8a MO) and labeled with anti-Sox10 (B) and anti-Zrf-1 (D) antibodies. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
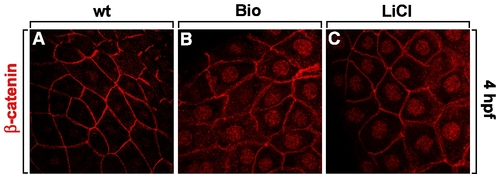
Bio and LiCl activate canonical Wnt signaling. Treatment of Bio- (B) or LiCl (C) at 1-cell-stage embryos shows nuclear translocation of membrane-localized β-catenin at 4 dpf, indicating that Wnt signaling is activated. Control embryo (A) shows membrane-localized β-catenin. |

Unillustrated author statements EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|