- Title
-
Zic1 and Zic4 regulate zebrafish roof plate specification and hindbrain ventricle morphogenesis
- Authors
- Elsen, G.E., Choi, L.Y., Millen, K.J., Grinblat, Y., and Prince, V.E.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
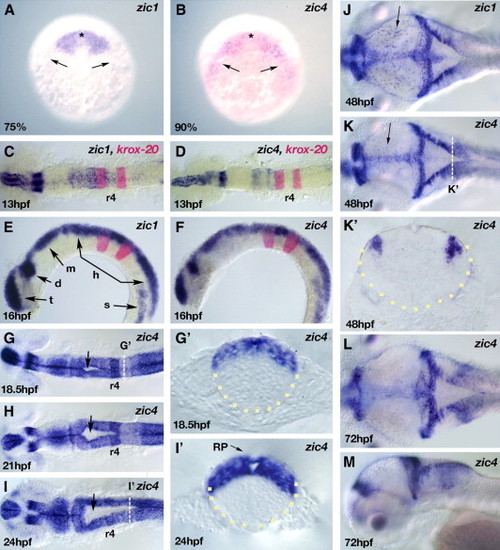
Dorsal neural tube restriction of zic1 and zic4 linked genes during embryonic development. (A, B) Dorsal view (anterior to the top) of RNA in situ hybridization of zic1 (A) and zic4 (B) at their onset of expression at 75% epiboly (zic1) and 90% epiboly (zic4) in the anterior (asterisks) and lateral border (arrows) of the neural plate. (C–M) Developmental stages are as indicated; dorsal (C, D, G–L) and lateral (E, F, M) views, anterior to the left. Transverse sections of the neural tube (outlined with yellow dots) (G′, I′, K′). (C–F) Whole-mount embryos showing modulated zic1 (C, E) and zic4 (D, F) expression along the AP axis (C, D) and dorsal restriction of expression in the neural tube (E, F). (C–F) krox20 is a marker for r3 and r5. (G–I) zic4 RNA in situ hybridization of whole-mount embryos highlighting the progression of hindbrain ventricle opening (arrows) from 18.5 hpf (G) to 21 hpf (H) and 24 hpf (I). Note dorsal restriction of zic4 expression in transverse sections through r5 at 18.5 hpf (G′) and 24 hpf (I′), as indicated by white dotted lines in panels G and I respectively. Note at 18.5 hpf (G′) the absence of a ventricle opening, while at 24 hpf (I′) the opening is clearly defined. zic4 is expressed in the roof plate (RP) indicated by arrow in panel I′. (J–M) zic1 (J) and zic4 (K–M) transcripts continue to be expressed in the dorsal neural tube. Arrow in panels J and K indicates the expression of zic1 and zic4 respectively in an unidentified population of dorsal midbrain neurons. Dorso-lateral expression domain of zic4 is maintained at 48 hpf (K′) in transverse section at level indicated by white dotted line in panel K. t, telencephalon; d, diencephalon; m, midbrain; h, hindbrain, s, somites. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
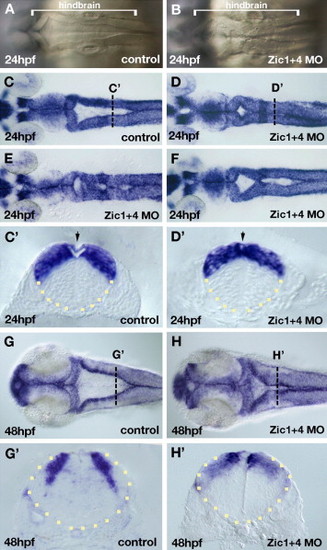
Dorsal hindbrain ventricle morphogenesis is altered in Zic1 and Zic4 morphants. Dorsal view of the hindbrain (A–F, G, H) and cross-sections of the neural tube (outlined by yellow dots) at the level of r5 (C′, D′, G′, H′). (A, B) Bright field live images of hindbrains of 24 hpf control embryos (A) and Zic1 + 4 morphants (B). Dorsal folds that outline the hindbrain ventricle in control hindbrains (A) are aberrantly fused at the dorsal midline in Zic1 + 4 morphants (B). Brackets in panels A and B indicate the length of the hindbrain. (C–F) Dorsal zic1 expression at 24 hpf allows visualization of hindbrain ventricle defects in Zic1 + 4 morphants (D–F; and see Table 1) compared to controls (C). Transverse sections at AP levels indicated by white dotted lines in panels C and D show hindbrain ventricle opening is impaired in 24 hpf Zic1 + 4 morphants (D′) compared to controls (C′). Arrow in panel C′ indicates roof plate (RP) overlying the ventricle, and in panel D′ indicates absence of a well-defined RP. (G–H′) Dorsal view of zic1 expression in 48 hpf controls (G) and Zic1 + 4 morphants (H) showing “dorsal fused” phenotype. (G′, H′) Transverse sections at AP levels indicated by the white dotted lines in panels G and H show ventricle opening is impaired in 48 hpf Zic1 + 4 morphants (H′) compared to controls (G′). |
|
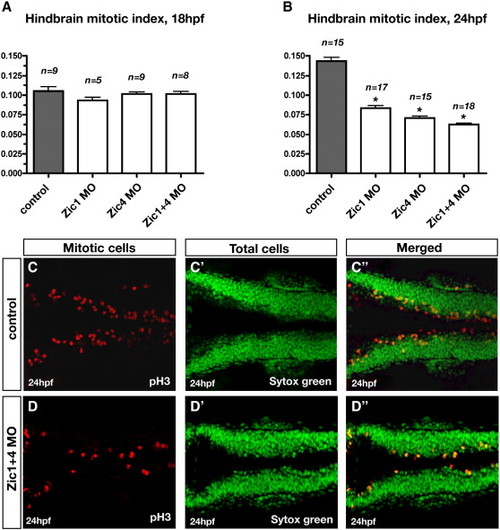
Zic1 and Zic4 function is required after initial ventricle opening for dorsal neural proliferation in the hindbrain. (A, B) Comparison of the quantitative analysis of hindbrain mitotic index at 18 hpf (A) and 24 hpf (B) in controls, Zic1 morphants, Zic4 morphants, and Zic1 + 4 morphants. Mitotic index was calculated in controls and Zic morphants as the ratio of the number of proliferating cells over the total number of cells (as described in Materials and methods). Dorsal neural proliferation at 18 hpf remained unaffected in Zic morphants compared to controls (A), while at 24 hpf the mitotic index was reduced in Zic morphants compared to controls (B). n is the number of embryos assessed per experimental condition. Asterisks in panel B indicate significant differences compared to controls. (C, D) Dorsal confocal sections (3 μm thick; longitudinal view) through hindbrain immunolabeled with the proliferating marker pH3 (C, D), counterstained with the nuclear marker Sytox green (C′, D′), and merged (C″, D″) of 24 hpf controls (C, C′, C″) and Zic1 + 4 morphants (D, D′, D″). PHENOTYPE:
|
|
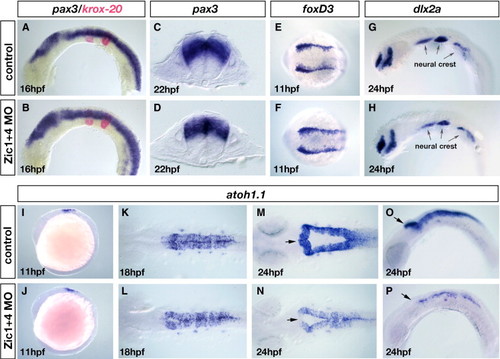
Dorsal fates are selectively altered in Zic1 and Zic4 morphants without affecting early dorsal–ventral (DV) or anterior–posterior (AP) patterning. (A–D) RNA in situ hybridization with a DV marker pax3 (blue in panels A–D) and an AP marker krox20 (red in panels A, B). Lateral view of 16 hpf embryos (A, B) and transverse sections at the level of r5 of 22 hpf embryos (C, D). DV and AP marker distribution and expression are established normally in Zic1 + 4 morphants (B, D) compared to controls (A, C). (E–H) Dorsal view of 11 hpf embryos labeled with the early neural crest induction/specification marker foxD3 (E, F) and lateral view of 24 hpf embryos labeled with a neural crest migration marker dlx2a (G, H). Arrows in panels G and H indicate the expression of dlx2a in the pharyngeal arches. Neural crest induction and migration is unaltered in Zic1 + 4 morphants (F, H) compared to controls (E, G). (I–P) atoh1.1 expression labels dorsal hindbrain progenitors, stages as indicated: lateral views (I, J, O, P), and dorsal views (K–N). At 11 hpf atoh1.1 expression is unaffected in Zic1 + 4 morphants (J) compared to controls (I). At 18 hpf expression is slightly reduced in Zic1 + 4 morphants (L) compared to controls (K). By 24 hpf atoh1.1 expression levels and domain size are dramatically reduced in Zic1 + 4 morphants (N, P) compared to controls (M, O). Arrows in panels M–P indicate the anterior region of r1, where expression of atoh1.1 is lost in Zic1 + 4 morphants. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
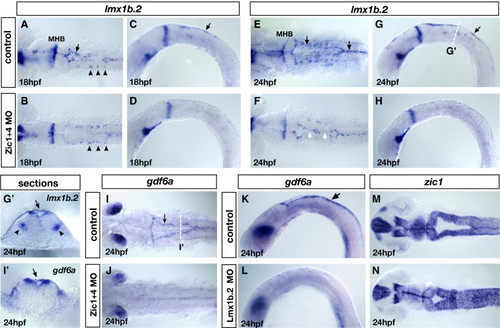
Loss of lmx1b expression in Zic morphants underlies loss of roof plate development and is linked to ventricle morphogenesis. (A–H) Expression of lmx1b.2 at 18 hpf (A–D) and 24 hpf (E–H). Dorsal view (A, B and E, F) and lateral view (C, D and G, H) of controls (A, C and E, G) and Zic1 + 4 morphants (B, D and F, H). In Zic1 + 4 morphants, the expression of lmx1b.2 in hindbrain roof plate (RP) is missing or down-regulated in 18 hpf (B, D) and 24 hpf embryos (F, H) compared to controls at 18 hpf (A, C) and 24 hpf (E, G). The expression of lmx1b.2 in roof plate is indicated in controls (A, C and E, G) by black arrows. The expression of lmx1b.2 in ventral serotonergic neurons is unaffected in Zic1 + 4 morphants (arrowheads in panels A, B). In 24 hpf Zic1 + 4 morphants, loss of lmx1b.2 expression in the roof plate correlates with points of dorsal fusion (white arrows in panel F). (G′, I′) Cross-sections at the levels indicated in panels G and I of 24 hpf embryos labeled with lmx1b.2 probes (G′) and gdf6a probes (I′) to illustrate their expression in roof plate cells (indicated by black arrows). The expression of lmx1b.2 in ventral serotonergic neurons is indicated by black arrowheads. (I, J) gdf6a expression in dorsal view of 24 hpf controls (I) and Zic1 + 4 morphants (J). In control embryos, gdf6a is expressed in the roof plate (arrow in panel I). In Zic1 + 4 morphants (J), the expression of gdf6a expression is missing or down-regulated in roof plate compared to controls (I). (K, L) gdf6a expression in 24 hpf lateral view control embryos (arrow in panel K indicates expression in the RP) and Lmx1b.2 morphants (L), shows that gdf6a expression in roof plate is missing or down-regulated (L). (M, N) zic1 expression, dorsal view of 24 hpf controls (M) and Lmx1b.2 morphants (N) shows that Lmx1b.2 knockdown causes a dorsal ventricle fusion phenotype. MHB, midbrain–hindbrain boundary. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
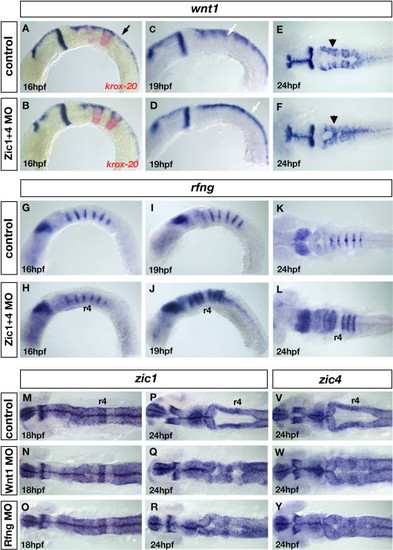
Loss of wnt signaling centers at the rhombomere boundaries in Zic1 and Zic4 morphants affects ventricle morphogenesis. (A–F) wnt1 expression in controls (A, C, E) and Zic1 + 4 morphants (B, D, F) at 16 hpf (A, B), 19 hpf (C, D) and 24 hpf (E, F), lateral view (A–D) and dorsal view (E, F). krox20 (red in panels A, B), provides a marker for r3 and r5. In hindbrain, wnt1 is expressed in roof plate (RP) (black arrow in panel A) at elevated levels in rhombomere boundaries (white arrow in panel C) and in dorsal hindbrain regions (black arrowhead in panel E). We detected no change in wnt1 expression in 16 hpf Zic1 + 4 morphants (B) compared to controls (A). By 19 hpf elevated expression of wnt1 in rhombomere boundaries (white arrow in panel C) is lost in Zic1 + 4 morphants (white arrow in panel D indicates uniform expression in dorsal hindbrain). Reduced wnt1 expression in rhombomere boundaries persists at 24 hpf in Zic1 + 4 morphants (F, black arrowhead) compared to controls (E). Note that altered wnt1 expression (F) is accompanied by a dorsal fused ventricle phenotype. (G–L) rfng expression in controls (G, I, K) and Zic morphants (H, J, L), lateral view (G–J) and dorsal view (K, L). Expression is not changed in 16 hpf Zic1 + 4 morphants (H) compared to controls (G). At 19 hpf and 24 hpf, down-regulation of wnt1 expression in rhombomere boundaries in Zic1 + 4 morphants is accompanied by expansion of rfng, expression into the rhombomere territory (J, L) compared to controls (I, K). No expansion is observed into r4 (J, L). (M–R) zic1 expression in 18 hpf and 24 hpf controls (M, P), Wnt1 morphants (N, Q) and Rfng morphants (O, R), dorsal view, and (V, Y) zic4 expression in 24 hpf controls (V), Wnt1 morphants (W), and Rfng morphants (Y), dorsal view. The expression of zic1 and zic4 is not altered in the hindbrains of Wnt1 morphants (N, Q, W) and Rfng morphants (O, R, Y) compared to controls (M, P, V). Wnt1 knockdown (Q, W) and Rfng knockdown (R, Y) cause dorsal fused phenotypes similar to Zic and Lmx morphants. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
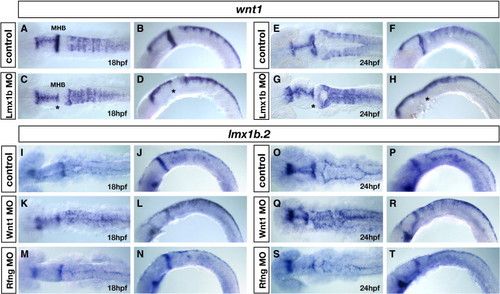
Roof-plate dependent regulation of rhombomere boundary signals. (A–H) wnt1 expression in controls (A, B and E, F) and Lmx1b double morphants (C, D and G, H) at 18 hpf (A, B) and 24 hpf (E, F), dorsal view (A, C and E, G) and lateral view (B, D and F, H). The wnt1 expression pattern is not changed in Lmx1b morphants at 18 hpf compared to controls (A–D), whereas in 24 hpf Lmx1b morphants, wnt1 expression is specifically down-regulated in rhombomere boundaries (F, H) compared to 24 hpf controls (E, G). Notice the uniform expression of wnt1 in the dorsal hindbrain of Lmx morphants (G, H), indicating that elevated levels of wnt1 in rhombomere boundaries are not maintained in the absence of lmx1b-dependent roof plate development. Asterisks in panels C, D, G, H denote loss of wnt1 expression in MHB (midbrain–hindbrain boundary) of Lmx1b morphants. (I–T) lmx1b.2 expression in controls (I, J, O, P), Wnt1 morphants (K, L, Q, R), and Rfng morphants (M, N, S, T) at 18 hpf (I–N) and 24 hpf (O–T), dorsal view (I, K, M, O, Q, S) and lateral view (J, L, N, P, R, T). In control embryos, dorsal hindbrain lmx1b.2expression is restricted to the roof plate cells (I, J, O, P), while in Wnt1 morphants, lmx1b.2 expression is expanded throughout the dorsal hindbrain (K, L, Q, R), indicating that dorsal hindbrain Wnt1 signals are required for the restriction of lmx1b.2 expression to the roof plate. By contrast, in Rfng morphants, in which wnt1 signals are down-regulated exclusively in rhombomere boundaries (M, N, S, T), lmx1b.2 expression is not altered compared to controls (I, J, O, P), indicating that rhombomere boundary-derived signals do not control the expression of lmx1b.2 expression in the dorsal hindbrain. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
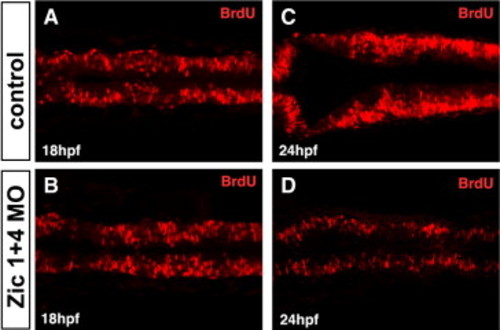
Zic1 and Zic4 function is required after 18 hpf for dorsal neural proliferation in the hindbrain. (A–D) Dorsal confocal sections (3 μm thick; longitudinal view) through hindbrain immunolabeled with BrdU, marking cells in the S-phase of the cell cycle, at 18 hpf (A,B) and 24 hpf (C,D) in control (A,C) and Zic1 + 4 morphants (B,D). No change in hindbrain proliferation is detected at 18 hpf in Zic1 + 4 morphants (B, n = 11) compared to control embryos (A, n = 10), whereas at 24 hpf, proliferation is markedly reduced in Zic1 + 4 morphants (D, n = 8) compared to control embryos (C, n = 13). PHENOTYPE:
|
|
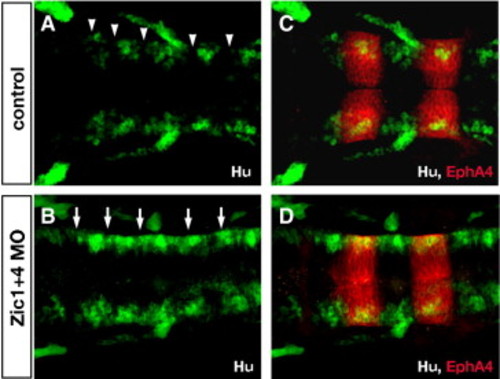
Zic1 and Zic4-deficient embryos lack normal segmental patterns of neuronal differentiation in the hindbrain. (A,B) Longitudinal confocal sections through the dorsal hindbrain of Hu immunolabeling (green, labels post-mitotic neurons), and (C,D) of double labeling with antibodies to Hu (green) and EphA4 (red, labels r3 and r5). In 24 hpf control embryos (A,C) post-mitotic neurons are clustered in the center of rhombomeres and absent from rhombomere boundaries (white arrowheads in A), while in Zic1 + 4 morphants (B,D) segmental pattern of Hu labeling is disrupted with ectopic differentiation of Hu-positive neurons in boundary regions (white arrows in B). PHENOTYPE:
|
|
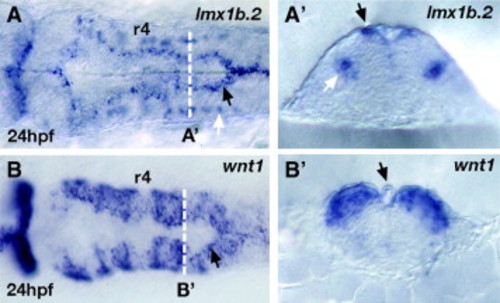
lmx1b.2 and wnt1 expression in overlapping and non-overlapping domains in the hindbrain. (A,A′) lmx1b.2 mRNA and (B,B′) wnt1mRNA in situ hybridization of 24 hpf whole mount hindbrains in dorsal view (A,B) and cross-sections (A′,B′) at the level indicated by the white dotted line in A and B. In the hindbrain, lmx1b.2 is expressed dorsally in the roof plate cells (including the membrane covering the ventricle as well as the “shoulder” region indicated by black arrow in A and A′) and ventrally in the serotonergic neurons (white arrows in A and A′). In the hindbrain, wnt1 expression overlaps with lmx1b.2 expression in the roof plate cells (black arrows in B and B′). wnt1 expression also occurs at elevated levels in the dorsal part of rhombomere boundaries, as well as at lower levels throughout the dorsal hindbrain. The cross-section in B′ indicates the elevated levels of expression of wnt1 at the boundary between r5 and r6. r4, rhombomere 4. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 314(2), Elsen, G.E., Choi, L.Y., Millen, K.J., Grinblat, Y., and Prince, V.E., Zic1 and Zic4 regulate zebrafish roof plate specification and hindbrain ventricle morphogenesis, 376-392, Copyright (2008) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.