- Title
-
Definitive hematopoiesis initiates through a committed erythromyeloid progenitor in the zebrafish embryo
- Authors
- Bertrand, J.Y., Kim, A.D., Violette, E.P., Stachura, D.L., Cisson, J.L., and Traver, D.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
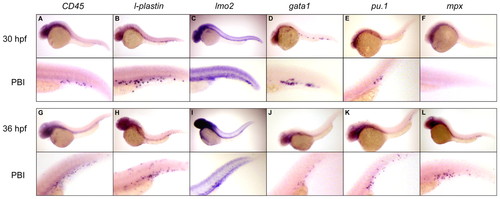
Genes associated with multilineage hematopoiesis are expressed in the posterior blood island as early as 30 hpf. (A,B) By 30 hpf, expression of the pan-leukocyte markers CD45 and l-plastin are observed throughout the PBI. (G,H) By 36 hpf, the number of cells expressing each gene has increased in the PBI, and expressing cells begin to migrate throughout the embryo. Localized expression of lmo2 is observed in the PBI at 30 hpf (C) and 36 hpf (I). (D,J) Expression of gata1 is also observed in cells within the vascular plexus of the PBI at both timepoints. (E,F,K,L) Expression of genes associated with myelopoiesis is also observed within the PBI, including pu.1 and mpx. Rare pu.1+ cells are observed at 30 hpf in the PBI (E) that increase in number by 36 hpf (K), whereas mpx expression is not observed until 36 hpf (F,L), consistent with it being a marker of relatively mature myelomonocytic cell types. Magnification: 100x in whole-embryo images; 300x in PBI images. |
|
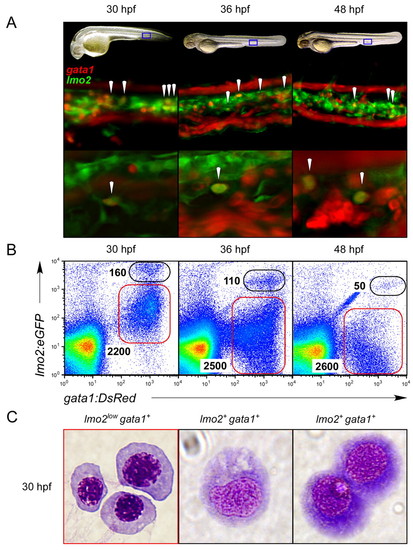
Coexpression of lmo2 and gata1 reveals immature hematopoietic precursors in the PBI. (A) Fluorescence microscopy reveals cells within the vascular plexus of the PBI that expressed both gata1:DsRed and lmo2:eGFP fluorophores (arrowheads) in double transgenic animals. Blue boxes in embryonic images in upper panels denote the regions shown at 200x magnification in middle and 400x magnification in lower panels at 30, 36 and 48 hpf. Lower panels show a single, deconvolved z slice, demonstrating coexpression of each transgene in single cells (arrowheads). (B) Cells coexpressing the gata1:DsRed and lmo2:eGFP transgenes prospectively isolated by flow cytometry. Double-positive cells peak in number at 30 hpf, with approximately 160 cells per embryo (left panel). (C) Compared with purified primitive erythroblasts sorted by low levels of lmo2:eGFP and high levels of gata1:DsRed (red gate in 30 hpf plot in B), cytological staining of purified 30 hpf lmo2+ gata1+ cells (black gate) showed immature morphologies indicative of early hematopoietic progenitors. Magnification, x1000. |
|
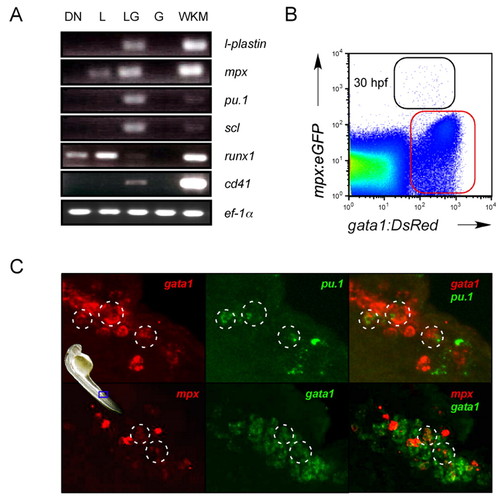
Gene expression profiling of hematopoietic precursors in the PBI suggest multipotency. (A) Cells were purified from 30 hpf embryos by flow cytometry based on expression of gata1:DsRed and lmo2:eGFP transgenes (DN, double negative; L, lmo2:eGFP+, gata1:DsRed-; LG, lmo2:eGFP+, gata1:DsRed+; G, lmo2:eGFPlow, gata1:DsRed+; WKM, whole kidney marrow) and subjected to RT-PCR. (B) FACS analysis shows a population that coexpresses the gata1:DsRed and mpx:eGFP transgenes at 30 hpf (black gate). (C) Two-color FISH demonstrates that cells within the PBI at 30 hpf coexpress gata1 and pu.1 (highlighted circles, upper panels) and gata1 and mpx (highlighted circles, lower panels). Blue frame on embryo denotes regions shown in C at 400x magnification. |
|
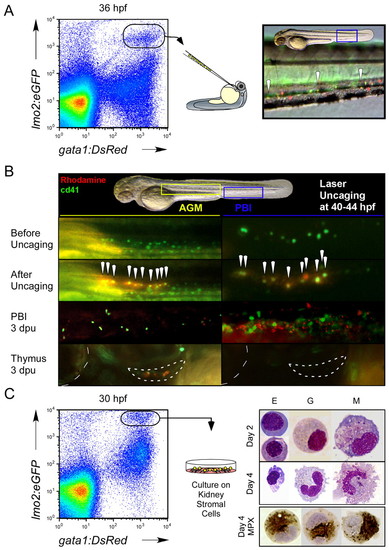
Functional studies demonstrate that gata1+ lmo2+ CD41+ cells are committed erythromyeloid progenitors. (A) Dissociated gata1:DsRed+ lmo2:eGFP+ cells were purified from 36 hpf embryos by flow cytometry and transplanted into wild-type embryonic recipients. Transplanted cells were observed to home back to the PBI in host animals (right panel, 200x magnification). Arrowheads denote gata1:DsRed+ lmo2:eGFP+ cells. (B) In vivo fate-mapping studies were performed by laser activation of caged rhodamine in CD41+cells in the 44 hpf AGM or 40 hpf PBI. Presumptive AGM HSCs were targeted as positive controls for thymus colonization (lower panels; outlined crescent-shaped structure). Boxed yellow and blue regions in upper panel denote close-up areas shown below in left panels for the AGM and right panels for the PBI, respectively. All animals are shown in lateral view, with head oriented to the left and dorsal side up. Dotted line at the left edge of lower boxes denotes outline of the eye for orientation. White arrowheads indicate uncaged, GFP+ cells. (C) Short-term culture of lmo2+ gata1+ cells atop kidney stromal cells demonstrates erythroid (E), granulocytic (G) and monocytic/macrophage (M) differentiation potentials. Cultured cells were stained for myeloperoxidase (MPX) activity after 4 days (bottom panel). |
|
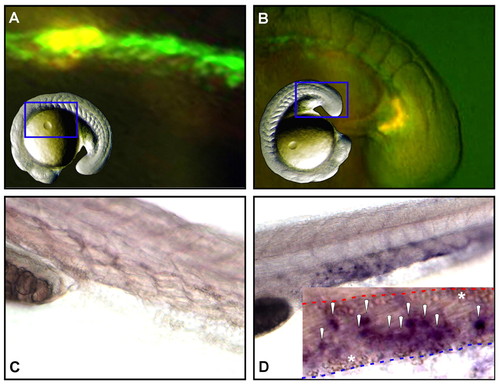
Erythromyeloid progenitors arise autonomously within the PBI. (A-D) Cells expressing GFP under control of the lmo2 promoter were lineage traced by uncaging a combination of caged rhodamine and FITC. GFP+ cells were targeted, either in the medial (bounded by somites 1-10; panel A) or most posterior (panel B) regions of the lmo2 expression domain between 13- and 15-somite stages. (C,D) Analysis of targeted progeny at 30 hpf showed no medially derived cells in the PBI (C), whereas posterior-derived daughter cells were observed throughout the venous plexus of the PBI (D). Inset in (D) shows a close-up of the PBI in a second animal, with marked progeny found within the vascular plexus between the aorta (dashed red line) and caudal vein (dashed blue line). Primitive erythrocytes within each vessel are indicated with asterisks and the daughters of posterior lmo2+ cells are indicated by white arrowheads. Blue framed areas in inset images of whole animals indicate the regions shown in close-up in A and B. |
|
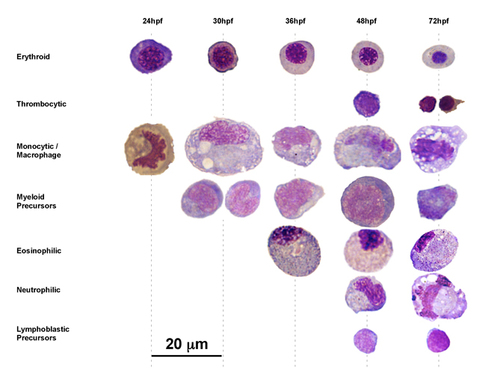
Temporal appearance of definitive blood cell types in the embryonic tail. Hematopoietic cells identified from tail preparations at noted timepoints were assigned to presumptive lineage affiliations by morphological criteria. |