- Title
-
Biphasic Hoxd gene expression in shark paired fins reveals an ancient origin of the distal limb domain
- Authors
- Freitas, R., Zhang, G., and Cohn, M.J.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS One
|
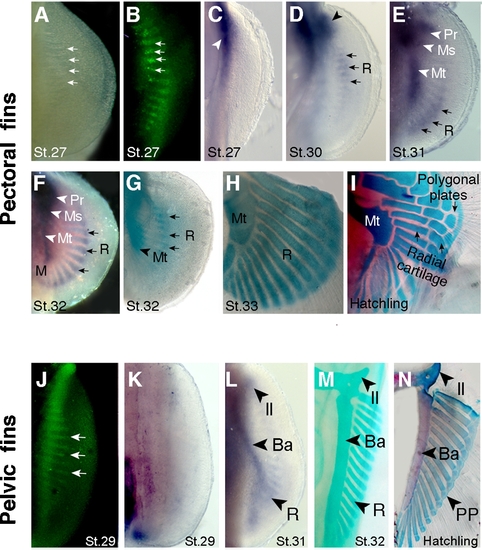
Endoskeletal development in catshark pectoral and pelvic fins. Ventral views of pectoral (A–I) and pelvic (J–N) fins. Stages (St.) of development indicated at bottom of each panel. (A) Light micrograph of pectoral fin showing gaps in the pectoral fin plate. (B) Acridine orange staining (green fluorescence) shows apoptotic cells in the gaps observed in panel A. Arrows in A and B mark four examples. (C) Sox8 expression marks initiation of chondrogenesis in the pectoral girdle region (arrowhead). Note absence of chondrogenesis in the fin plate at this stage. (D) Sox8 expression marks initiation of chondrogenesis in anterior part of the fin plate, in basal cartilages (arrowhead) and radials (arrows). (E) Sox8 domain prefigures development of the basal cartilages along the anteroposterior axis of the fin: Pr, propterygium; Ms, mesopterygium; Mt, metapterygium; R, radials. Arrows mark expression in the most posterior radials. (F) Sox8 expression in basal cartilages (arrowheads) and in all radials along the anteroposterior axis (subset of radials marked with arrows). (G, H) Alcian green staining of pectoral fins. Note that radials chondrify in domains pre-established by Sox8 expression domains (compare with panels F and G). Chondrified, unsegmented radials are seen in H. (I) Alcian blue and alizarin red stained pectoral fin showing a fully developed cartilaginous endoskeleton at the time of hatching. Note segmentation of proximal radials, intermediate radials and distal polygonal plates (compare panels H and I). (J) Acridine orange-positive cells in gaps of the pelvic fin plate. (K) Sox8 expression marks initiation of chondrogenesis proximal, posterior region of fin. Note absence of chondrogenesis in the fin plate at this stage. (L) Sox8 expression prefigures development of endoskeletal elements in the pelvic fin. Il, iliac process; Ba, basipterygium; R, radials. (M) Alcian green staining of the pelvic fin showing chondrified unsegmented radials. (N) Alcian blue and alizarin red staining of the pelvic fin showing fully developed cartilaginous endoskeleton at hatching. Note segmentation of the radials into distal polygonal plates (PP) and proximal radials (compare panels M and N). |
|
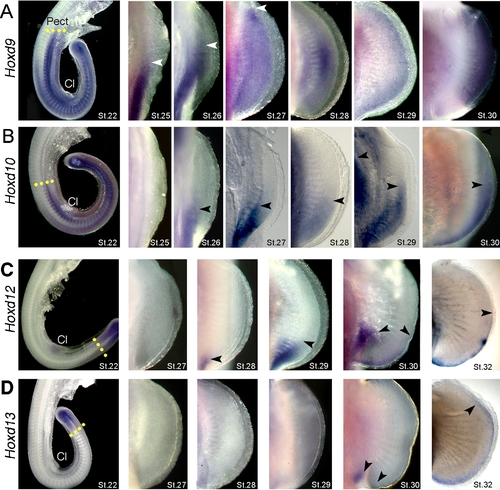
Expression of Hoxd genes in catshark pectoral fins. Stages of development indicated in lower right corners of each panel. (A–D) Whole mount in situ hybridizations showing expression of Hoxd9 (A), Hoxd10 (B), Hoxd12 (C) and Hoxd13 (D). Pect, Pectoral fin bud; Cl, cloaca. Note anterior expansion of Hoxd12 and Hoxd13 in distal fin at stage 32. Arrows mark anterior limits of expression. Yellow dotted lines in the left column mark the anterior boundaries of expression at stage 22. |
|
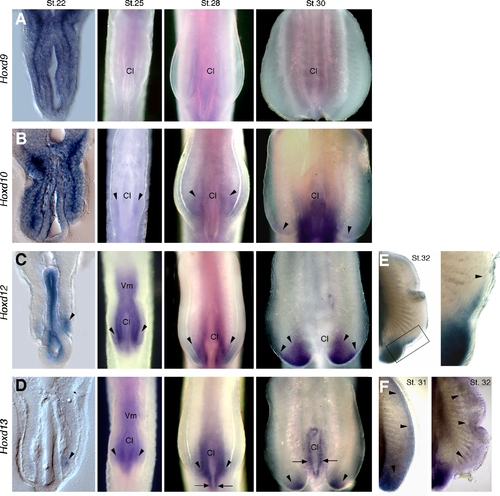
Expression of Hoxd genes in catshark pelvic fins. Stages of development indicated in the top of each column in A–D and in upper right corner in E and F. Left column shows transverse histological sections at level of cloaca (Cl) and pelvic fins. All other panels show whole mounts in ventral view. (A–D) Whole mount in situ hybridizations showing expression of Hoxd9 (A), Hoxd10 (B), Hoxd12 (C) and Hoxd13 (D). Arrowheads mark expression in pelvic fin buds. Arrows in D mark expression in cloacal epithelium. (E, F) Pelvic fins showing expression of Hoxd12 at stage 32 (E) and Hoxd13 at stages 31 and 32 (F). Boxed area in E is shown in high magnification at right. Arrowheads in E mark anterior limits of expression, and in F they outline the extent of the distal Hoxd13 domain. |
|
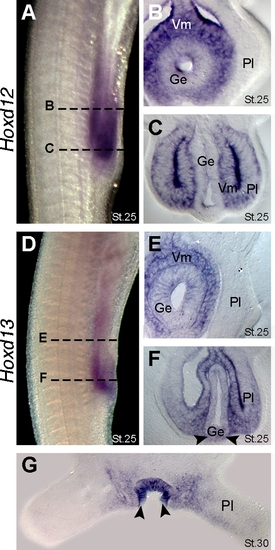
Expression of Hoxd13 in the cloacal region of catsharks. (A) Lateral view of pelvic fin region showing Hoxd12 expression at stage 25. Dashed lines mark the approximate planes of section showed in panels B and C. (B) Transverse section showing Hoxd12 expression in visceral mesoderm (Vm) and gut endoderm (Ge). Note absence of Hoxd12 expression in anterior part of the pelvic fin (Pl). (C) Transverse section showing Hoxd12 expression in the posterior part of pelvic fin and adjacent visceral mesoderm. Note absence of Hoxd12 expression in the gut endoderm. (D) Lateral view of the pelvic fin region showing Hoxd13 expression at stage 25. Note that Hoxd13 domain lies posterior to Hoxd12 domain (compare with panel A). Dashed lines mark the approximate planes of the section showed in panels E and F. (E) Transverse section showing Hoxd13 expression in the visceral mesoderm and gut endoderm. Note absence of Hoxd13 expression in the anterior part of pelvic fin. (F) Transverse section showing Hoxd13 expression in the posterior part of the fin, visceral mesoderm and ventral endoderm. Arrowheads mark expression in endoderm (contrast with absence of Hoxd12 in endoderm in panel C). (G) Transverse section throughout the pelvic fins at stage 30 showing Hoxd13 expression in the cloacal epithelium (arrowheads). |