- Title
-
Electroporation-based methods for in vivo, whole mount and primary culture analysis of zebrafish brain development
- Authors
- Hendricks, M., and Jesuthasan, S.
- Source
- Full text @ Neural Dev.
|
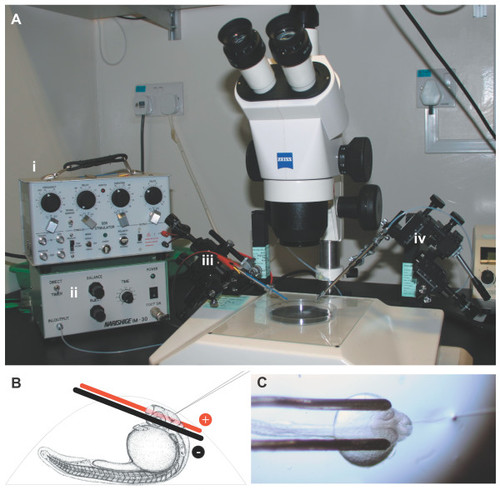
Electroporation apparatus. (a) The electroporation equipment assembled on a dissecting microscope: the Grass SD9 stimulator (i) and air pressure injector (ii) are connected to two micromanipulators controlling the electrodes (iii) and microinjection needle (iv). (b) Side view schematic of a 1 dpf zebrafish mounted in an agarose drop with the electrodes and injection needle in position. Electrodes are not drawn to scale. (c) Top view of an embryo mounted for electroporation, with electrodes in position and microinjection needle inserted into the brain ventricle. |
|
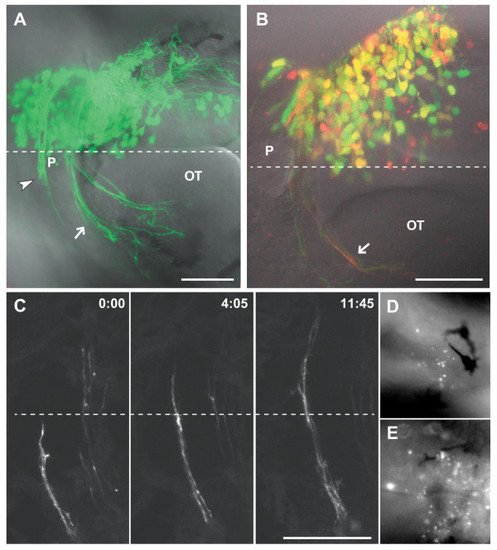
Results of electroporation at 2 dpf. (a) A 2 dpf embryo after electroporation at 24 hpf with 0.7 mg/ml each pHuC:GAL4/pUAS:EGFP. Axons of the developing habenular (arrowhead) and posterior (arrow) commissures are visible. (b) A 2 dpf embryo electroporated with 0.5 mg/ml each pHuC:GAL4/pUAS:EGFP/pUAS:mCherry. The mCherry channel (red) is less well resolved compared to EGFP (green) due to suboptimal excitation with a 543 nm laser line. Approximately 60% of cells express both transgenes at high levels (yellow). (c) Time series of commissural axons in the habenular commissure. Images were collected at room temperature, and growth cone migration is slower than normal. (d,e) Acridine orange staining two hours after electroporation shows higher levels of scattered cell death bilaterally in the brains of electroporated embryos (e) compared to unelectroporated siblings (d). Dorsal views, anterior to the left. Dashed lines indicate the midline. Time is hours:minutes. Scale bars = 50 μm. OT, optic tecum; P, pineal organ. |
|
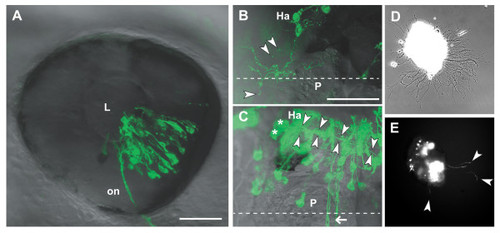
Analysis of transfected neurons in vivo and in vitro. (a) The eye of a 2 dpf embryo electroporated with pHuC:GAL4/pUAS:dnRyk-EGFP. Cells in multiple retinal layers are transfected in a distinct segment according to electrode positioning and injection site. Retinal ganglion cell axons are visible in the optic nerve (on). (b) A habenular (Ha) neuron contransfected with pHuC:GAL4/pUAS:dnEphB3-EGFP shows ectopic processes branching over the medial epithalamus, including the pineal organ (P). Extracellular exosome-like vesicles (arrowheads) are visible around the soma and processes. (c) Two habenular neurons (asterisks) expressing EGFP show the normal ventro-posterior projection into the fasciculus retroflexus (arrowheads). Commissural axons (arrow) are not derived from the habenula. (d) Bright field phase contrast and (e) fluorescence images of a 2 dpf forebrain explant from an embryo electroporated with pHuC:GAL4/pUAS:EGFP after 12 hours in culture. EGFP positive neurons and axons (arrowheads) can be tracked over time. Anterior is to the left in (a) (lateral), (b,c) (dorsal). Dashed lines indicate the midline. Scale bars = 50 μm. L, lens. |
|
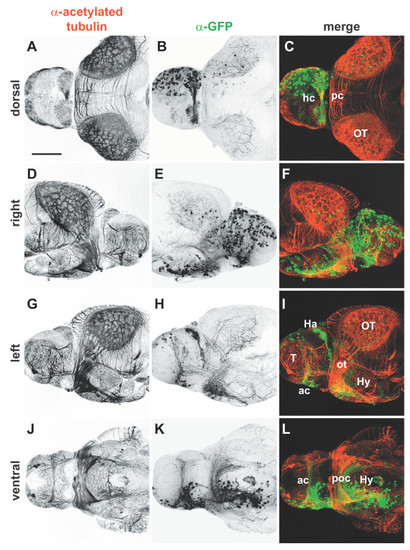
Whole mount immunocytochemistry of electroporated brains. Isolated 4 dpf brains from embryos in which pHuC:GAL4/pUAS:EGFP were unilaterally electroporated into the right forebrain. Brains were stained with (a,d,g,j) anti-acetylated tubulin to label axons (red) and (b,e,h,k) anti-GFP to mark transfected cells (green); (c,f,i,l) merged images. Widespread expression of EGFP is seen in neuronal cell bodies of the right telencephalon and diencephalon (b,e). All major commissures contain labeled fibers and contralateral axonal projections can be seen in detail in left and ventral views (h,k). Anterior is to right in (d-f), to the left in all other panels. Scale bar = 100 µm. Ac, anterior commissure; Ha, habenula; hc, habenular commissure; Hy, hypothalamus; ot, optic tract; OT, optic tectum; pc, posterior commissure; poc, postoptic commissure; T, telencephalon. |