- Title
-
FoxH1 negatively modulates flk1 gene expression and vascular formation in zebrafish
- Authors
- Choi, J., Dong, L., Ahn, J., Dao, D., Hammerschmidt, M., and Chen, J.N.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
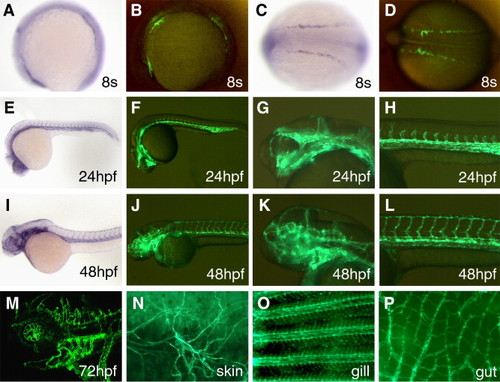
GFP expression in TG(flk1:GFP)la116 embryos. (A–D) GFP signals driven by the flk(6.4)-GFP transgene can be detected in TG(flk1:GFP)la116 embryos as early as the 8-somite stage. flk1 expression is detected in three patches of cells by in situ hybridization (A). A similar pattern is seen in TG(flk1:GFP)la116 embryos (B). Lateral views are shown in panels A and B and the dorsal views are shown in panels C and D. Anterior to the left. (E–H) GFP expression pattern of TG(flk1:GFP)la116 embryos at 24 hpf (F) resembles the flk1 pattern detected by in situ hybridization (E). Higher magnification images of the head and trunk are shown in panels G and H, respectively. (I–L) GFP expression pattern of TG(flk1:GFP)la116 embryos at 48 hpf (J) resembles the flk1 pattern detected by in situ hybridization (I). Higher magnification images of the head and trunk are shown in panels K and L, respectively. (M) Confocal image of GFP expression in endothelial cells in the brain and brachial arches in 3-day-old TG(flk1:GFP)la116 embryos. (N–P) GFP expression remains active in adult TG(flk1:GFP)la116 fish. Images show GFP signals in endothelial cells in the skin (N), gill (O) and gut (P). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
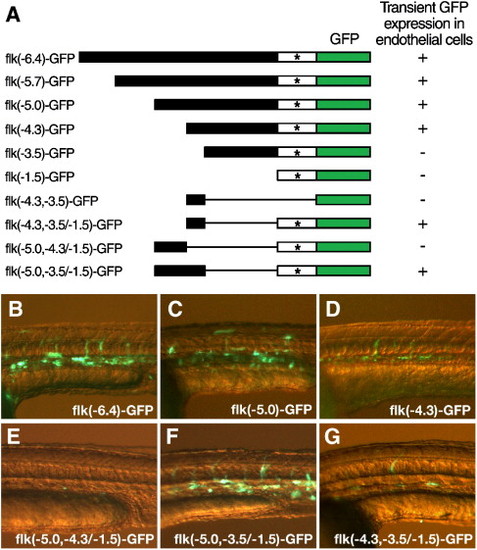
Deletion analysis of the flk1 regulatory region identifies a highly conserved element that is necessary for endothelial expression. (A) Schematic diagram of the deletion constructs of flk1-GFP reporter. Linearized DNA of each construct was injected in wild type zebrafish embryos at the 1-cell stage. GFP expression in injected embryos was analyzed after 1 day of development. The transient endothelial expression directed by each construct is summarized by a plus (endothelial expression) or a minus (no detectable endothelial expression) to the right of the line representing each construct. * marks the transcription initiation site of flk1. (B–G) Transient GFP expression in endothelial cells of 1-day-old embryos injected with flk(- 6.4)-GFP (B), flk(- 5.0)-GFP (C), flk(- 4.3)-GFP (D), flk(- 5.0, - 4.3/- 1.5)-GFP (E), flk(- 5.0, - 3.5/- 1.5)-GFP (F) or flk(- 4.3, - 3.5/- 1.5)-GFP (G). |
|
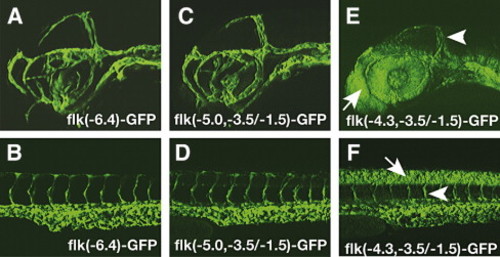
Transgenic analysis of the flk1 regulatory region identifies a 1.5-kb minimal endothelial specific enhancer. (A–B) GFP expression patterns in the brain (A) and trunk (B) of 2-day-old TG(flk1:GFP)la116 embryos. (C–D) GFP expression patterns of 2-day-old embryos carrying germ line integrated flk(-5.0, -3.5/-1.5)-GFP transgene resembles the patterns observed in TG(flk1:GFP)la116. (E–F) Embryos carrying germ line integrated flk(-4.3, -3.5/-1.5)-GFP have GFP expression in endothelial cells (arrowhead) as well as neural tissues. Arrows point to GFP positive cells in forebrain in panel E and to GFP positive cells in neural tube in panel F. |
|
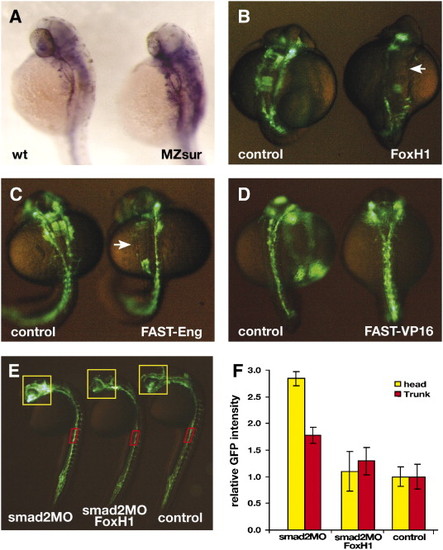
FoxH1 modulates vascular formation in zebrafish. (A) flk1 is expressed in the developing vasculature of embryos at 32 hpf (left). The expression level of flk1 is elevated in MZsur embryos (right). (B) Injection of FoxH1 mRNA disrupts zebrafish vascular formation. Embryos were analyzed at the 18-somite stage. (C) Injection of mRNA encoding the FAST-Eng chimeric protein disrupts vascular formation (right), resembling the phenotype of FoxH1 overexpression. Embryos were analyzed at the 23-somite stage. (D) Injection of mRNA encoding FAST-VP16 chimeric protein does not disrupt the GFP expression pattern in TG(flk1:GFP)la116 embryos. Embryos were analyzed at the 18-somite stage. Arrows point to patches of endothelial cells missing in FoxH1 or FAST-Eng mRNA-injected embryo. (E) Lateral view of the un-injected (right), smad2MO and FoxH1 mRNA co-injected (middle) and smad2MO-injected (left) TG(flk1:GFP)la116 embryos at 24 hpf. (F) Graph represents relative GFP intensities within the region of interests (indicated by the yellow and red boxes in panel E). |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 304(2), Choi, J., Dong, L., Ahn, J., Dao, D., Hammerschmidt, M., and Chen, J.N., FoxH1 negatively modulates flk1 gene expression and vascular formation in zebrafish, 735-744, Copyright (2007) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.