- Title
-
Characterization and expression patterns of the MAPK family in zebrafish
- Authors
- Krens, S.F., He, S., Spaink, H.P., and Snaar-Jagalska, B.E.
- Source
- Full text @ Gene Expr. Patterns
|
Unrooted phylogenetic tree of the zebrafish MAPK family to other vertebrates. The tree was constructed by neighbor-joining analysis based on an alignment of the amino acid sequences of the complete predicted and sequencing verified coding sequences. The numbers indicate the occurrence of nodes during bootstrap analysis. The bootstrap values are given as percentages of 10,000 reiterations and only values above 80 are shown. h, human; m, mouse; r, rat; z, zebrafish. |
|
Amino acid alignment of the proteins-region around the characteristic MAPK dual-phosphorylation domain of the zebrafish MAPK orthologs. Identical residues are indicated with black boxes, strongly conserved in dark gray and similar residues are boxed light grey. The phosphorylated amino acids of the dual-phosphorylation site and the intermediate amino acid, designating the mapk to a subfamily, are indicated with ▼ and *, respectively. |
|
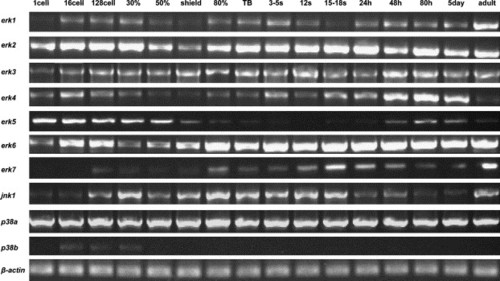
Temporal expression patterns of zebrafish MAPKs by RT-PCR analysis through zebrafish development. RNAs used for amplification were isolated from indicated stages. To obtain specific expression patterns, primers flanking the full coding sequences were used, but for erk7, where primers specific for the distinct c-terminus of the erk7 gene were used. Erk4, erk5, erk7, jnk1 and p38b showed dynamic expression levels through zebrafish development compared to erk1, erk2, erk3, erk6 and p38a. β-Actin (β-ACT) was used as a control for constitutive expression. |
|
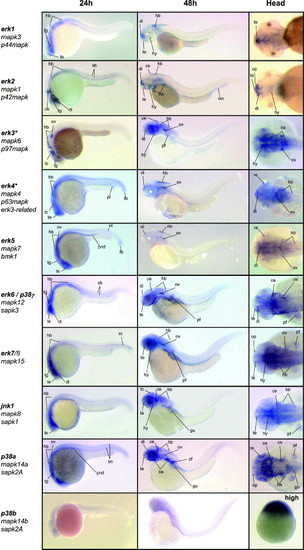
Expression patterns of the zebrafish MAPK genes by in situ hybridization. The first two columns show 24 and 48 hpf old zebrafish, lateral view, anterior to left, dorsal to top. The third column shows a dorsal view of the head region, anterior to left, at 48 hpf. All MAPK genes are indicated with all known names. MAPKs erk3 and erk4 are indicated with an astrix (*) because of their alternative dual phosphorylation site (SEG). All MAPK were expressed and showed distinct expression patterns at 24 and 48 hpf, but p38b. Therefore the dorsal head-image is replaced for an of the expression patterns at high stage (∼3.5 hpf), where p38b was expressed in the whole animal pole. ce, cerebellum; di, diencephalon; gu, gut; hb, hindbrain; hy, hypothalamus; nt, notochord, op, olfactory pit / placode; pf, pectoral fin; pnd, pronephric ducts; pr, proctodaeum re, retina; sb, somite boundary; tb, tail bud; tc, tectum; te, telencephalon; tg, tegmentum; tm, tail muscle. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
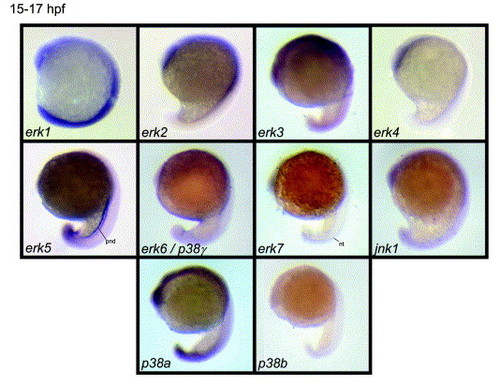
Expression patterns obtained for the zebrafish mapk genes by in situ hybridization at 15–17 hpf. Lateral view, anterior to top, dorsal to right. Almost all mapk showed a ubiquitously expression, however expression for erk5 was already enriched in the pronephric ducts and erk7 expression was enriched in the notochord. p38b was not expressed at this stage. nt, notochord; pnd, pronephric ducts EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
Reprinted from Gene expression patterns : GEP, 6(8), Krens, S.F., He, S., Spaink, H.P., and Snaar-Jagalska, B.E., Characterization and expression patterns of the MAPK family in zebrafish, 1019-1026, Copyright (2006) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Gene Expr. Patterns