- Title
-
Transgenic zebrafish produced by retroviral infection of in vitro-cultured sperm
- Authors
- Kurita, K., Burgess, S.M., and Sakai, N.
- Source
- Full text @ Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA
|
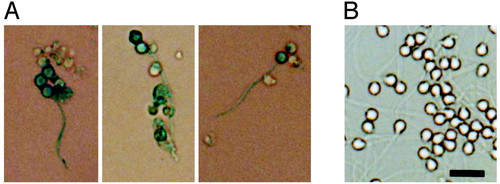
Retroviral infection of sperm cultured in vitro. (A) Detection of lacZ expression in infected sperm after 12 days of culture and (B) normal control sperm subjected to 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-β-D-galactoside staining. (Scale bar: 10 μm.) |
|
Detection of transgenesis in fish created from infected in vitro sperm cultures. (A) PCR analysis using DNA extracted from individual founder fish. Two pairs of primers were used for PCR analysis of genomic DNA, one specific to the proviral DNA and a second specific to the zebrafish Wnt5a. The numbered lanes show the PCR products generated with DNA from individuals in a part of each experiment of Table 1 to screen the positive. Lane PC shows the positive control PCR products generated with DNA from a zebrafish cell line that contains a proviral insertion. (B) Photos of transgenic zebrafish from infected in vitro sperm cultures. The WT cultured sperm were used to fertilize extruded eggs of the albino type. |
|
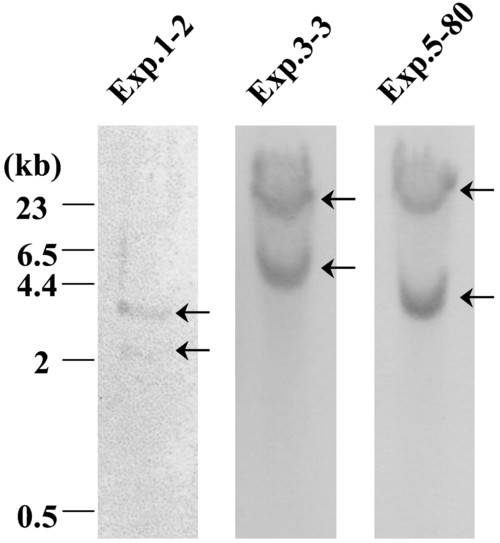
Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA from individual PCR-positive founder fish. Genomic DNA samples were digested with BglII. The number of each lane corresponds to the founder's number in the PCR experiment. The hybridization pattern in each lane shows a single copy insertion and different genomic locus for each lane, indicating independent integrations. |
|
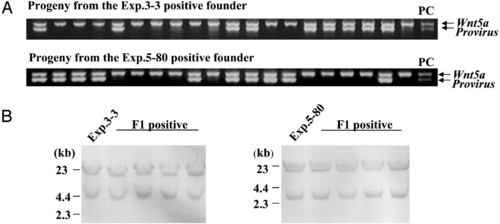
Analysis of transmission of the retroviral insertion into progenies by PCR and Southern blot hybridization. (A) PCR analysis with DNA extracted from progeny of each positive founder fish in experiments 3 and 5. Almost half of the progeny are positive for the provirus, indicating the transgene is not mosaic in the founder fish. (B) Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA from a positive founder fish and four individual PCR-positive progeny. Genomic DNA samples were digested with BglII. All PCR-positive progenies show the identical integration site to the parent. |