- Title
-
Production of maternal-zygotic mutant zebrafish by germ-line replacement
- Authors
- Ciruna, B., Weidinger, G., Knaut, H., Thisse, B., Thisse, C., Raz, E., and Schier, A.F.
- Source
- Full text @ Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA
|
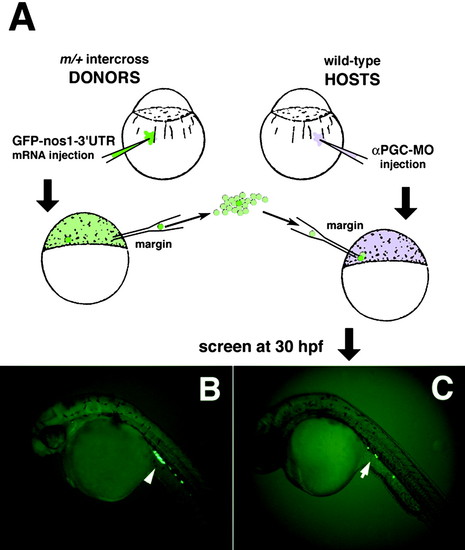
Germ-line replacement strategy using a GFP-nos1-3′UTR labeling technique. (A) Overview of transplantation strategy showing the transfer of cells from the margin of GFP-nos1-3′UTR-labeled mutant donor embryos into the margin of αPGC-MO-injected WT hosts. "m" refers to any zygotic mutation, in this case milte273. (B) At 30 hpf, PGCs from injected control milix embryos are specifically labeled with GFP (arrowhead). (C) Host embryos were screened at 30 hpf for the presence of GFP-labeled donor PGCs and their normal migration into the gonadal mesoderm at the anterior region of the yolk extension (arrow). |
|
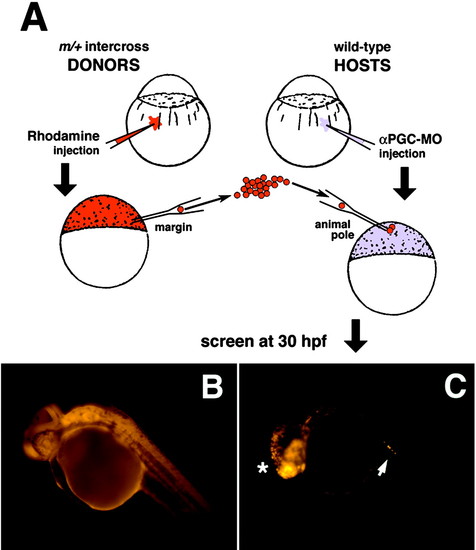
Germ-line replacement strategy using the rhodamine-dextran labeling technique. (A) Overview of transplantation strategy showing the transfer of cells from the margin of rhodamine-dextran-labeled mutant donor embryos into the animal pole of αPGC-MO-injected WT hosts. (B) At 30 hpf, all cells within control donor embryos are efficiently labeled with rhodamine-dextran. (C) Chimeric host embryo at 30 hpf showing somatic contribution of rhodamine-dextran-labeled donor cells to anterior neuroectoderm lineages (*). Host embryos were screened for the presence of labeled donor PGCs that had migrated successfully into the gonadal mesoderm (arrow). |
|
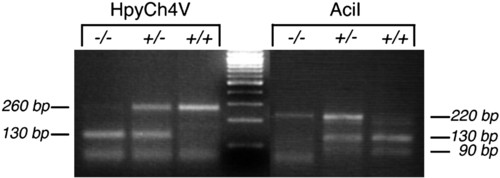
PCR genotyping of mil-mutant and WT embryos. Shown is 3% agarose gel resolution of HpyCh4V and AciI digestion products of PCR fragments amplified from genomic DNA prepared from milte273/milte273, milte273/+, and +/+ embryos. |