- Title
-
Regulation of dharma/bozozok by the Wnt Pathway
- Authors
- Ryu, S.-L., Fujii, R., Yamanaka, Y., Shimizu, T., Yabe, T., Hirata, T., Hibi, M., and Hirano, T.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
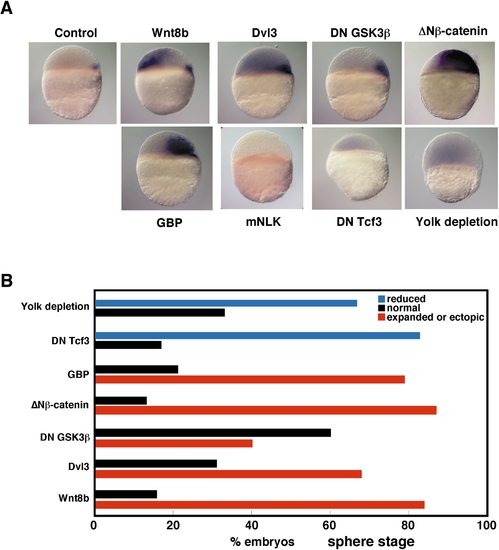
Regulation of dharma by Wnt signals. Synthetic RNAs for Wnt8b (200 pg), Dvl3 (520 pg), DN GSK3β (480 pg), an activated form of β-catenin (ΔNβ-catenin, 100 pg), GBP (480 pg), mNLK (100 pg), or DN Tcf3 (100 pg) were injected into one-cell-stage embryos. For yolk depletion, the vegetal yolk mass was removed at the one-cell stage. The embryos were fixed at the sphere stage (4 hpf) and the dharma transcripts were detected by whole-mount in situ hybridization. (A) In situ data representing each condition. (B) The proportions of embryos displaying reduced, normal, and expanded expression of dharma are shown as percentages. |
|
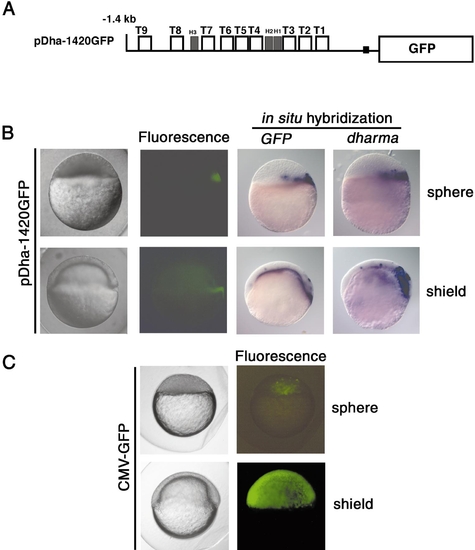
The -1.4-kbp promoter can recapitulate dharma expression. (A) Schematic representation of the -1.4-kbp promoter region of dharma and the GFP reporter construct (pDha-1420). (B, C) GFP expression. 50 pg of pDha-1420 GFP (B) or 25 pg of pCS2+GFP (C, CMV-GFP) plasmid DNAwas injected into one-cell-stage embryos, and expression of GFP proteins was detected by fluorescence microscopy and in situ hybridization with antisense GFP and dharma probes (B). Embryos shown are sphere stage (upper row) and shield stage (lower row). |
|
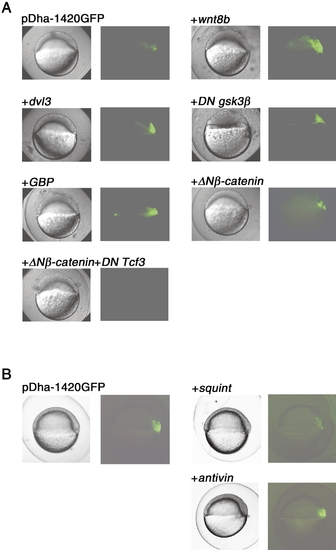
The dharma promoter can be regulated by Wnt but not Nodal signal. (A) pDha-1420 GFP plasmid DNA was coinjected with synthetic RNAs for wnt8b (200 pg), dvl3 (520 pg), DN gsk3β (480 pg), GBP (480 pg), ΔNβ-catenin (100 pg), ΔNβ-catenin (100 pg), and DN Tcf3 (100 pg) as indicated. Expression of GFP was detected at the 30% epiboly stage except for DN GSK3β RNA-injected embryos (sphere stage). (B) pDha-1420 GFP plasmid DNA was coinjected with synthetic RNAs for squint (1 pg) and antivin (5 pg) as indicated. Expression of GFP was detected at the shield stage. The squint RNA- and antivin RNA-injected embryos displayed a severely dorsalized phenotype and a cyclops;squint-like phenotype at pharyngula period, respectively (data not shown). Lateral view and dorsal is to the right. |
|
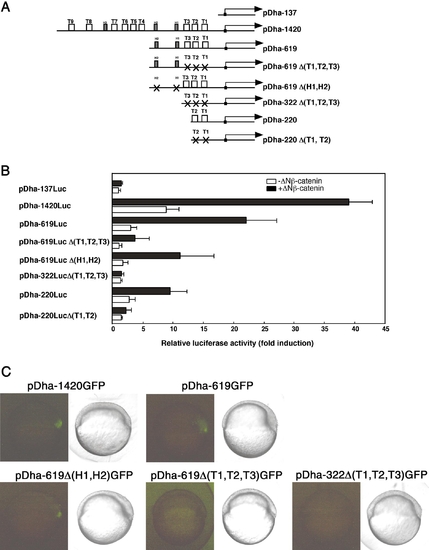
Tcf/Lef-binding sites are required for β-catenin-dependent and dorsal expression of dharma. (A) Schematic representation of deletion and point mutants for the reporter constructs. Mutations in the consensus sequences are indicated in Fig. 2. (B) β-Catenin-dependent expression. The luciferase reporter plasmid was injected with (closed bars) or without (open bars) ΔNβ-catenin RNA (300 pg) and the luciferase activities for various promoter mutants in the constructs were determined as described in Fig. 5. The averages and standard deviations from triplicate samples are shown. (C) Dorsal expression. The mutant GFP reporter plasmids were injected at the one-cell-stage and the expression of GFP was detected at the shield stage. Lateral view and dorsal is to the right. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 231(2), Ryu, S.-L., Fujii, R., Yamanaka, Y., Shimizu, T., Yabe, T., Hirata, T., Hibi, M., and Hirano, T., Regulation of dharma/bozozok by the Wnt Pathway, 397-409, Copyright (2001) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.