- Title
-
Dispersion of cyclin B mRNA aggregation is coupled with translational activation of the mRNA during zebrafish oocyte maturation
- Authors
- Kondo, T., Kotani, T., and Yamashita, M.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
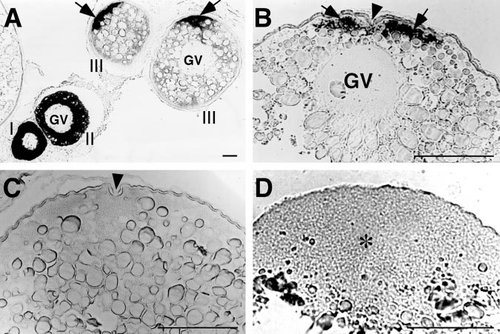
Localization of cyclin B mRNA (arrows) during zebrafish oocyte growth and maturation. GV, germinal vesicle. Scale, 100 μm. (A) Cyclin B mRNA during oocyte growth. Roman numerals show the stages of oocytes. Cyclin B mRNA is initially distributed throughout the cytoplasm of previtellogenic oocytes but translocated during oocyte growth to the future animal pole. (B) A full-grown immature oocyte showing localization of cyclin B mRNA along the cytoplasm at the animal pole identified by the presence of micropyle (indicated by arrowhead). (C) A mature oocyte treated with 17α,20β-DP showing the absence of cyclin B mRNA along the cytoplasm at the animal pole (arrowhead indicates the micropyle as a marker of the animal pole.). (D) A fertilized egg (30 min after spawning) showing the uniform distribution of cyclin B mRNA in the blastodisc (indicated by asterisk). |
|
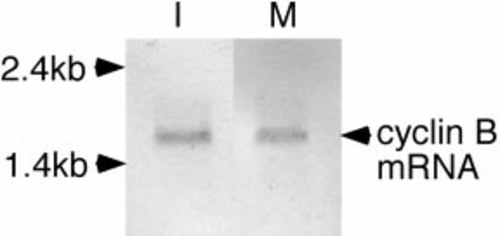
Presence of cyclin B mRNA in immature (I) and mature (M) zebrafish oocytes. Total RNA (5 μg) isolated from the oocytes was probed with DIG-labeled cyclin B antisense RNA. |
|
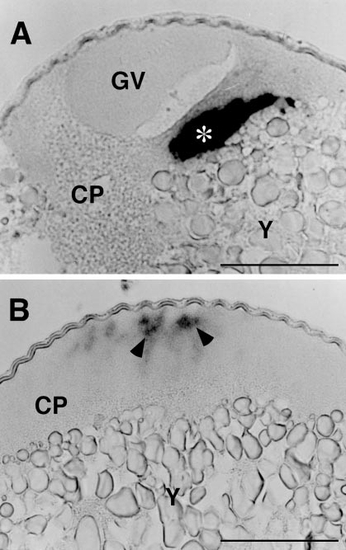
Cyclin B mRNA in immature (A) and mature (B) oocytes stratified by centrifugation on a Ficoll density gradient. The centrifugation segregated the oocyte cytoplasm (CP), including the germinal vesicle (GV), from the metaplasm consisting mainly of yolk (Y). Although cyclin B mRNA was seen in the cytoplasmic layer of both immature and mature oocytes, it exists as an aggregated form (asterisk) in immature oocytes and as indistinct matter (arrowheads) in mature oocytes. Scale, 100 μm. |
|
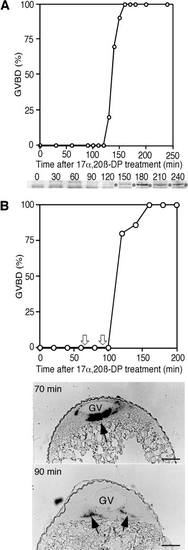
Cyclin B mRNA, cyclin B protein, and GVBD during 17α,20β-DP-induced oocyte maturation. (A) Time course of GVBD and cyclin B protein synthesis during oocyte maturation, indicating that both occur almost simultaneously 120 min after 17α,20β-DP treatment. Cyclin B proteins on the blot are indicated by asterisks. (B) Time course of GVBD and cyclin B mRNA dispersion. Oocytes collected at 70 and 90 min after 17α,20β-DP treatment (indicated by white arrows) were stratified by centrifugation in a density gradient of Ficoll. Aggregation is seen in an oocyte collected at 70 min, while it was diffused in the oocytes at 90 min just prior to the initiation of cyclin B synthesis and GVBD. Black arrows indicate cyclin B mRNA. GV, germinal vesicle. Scale, 100 μm. |
|
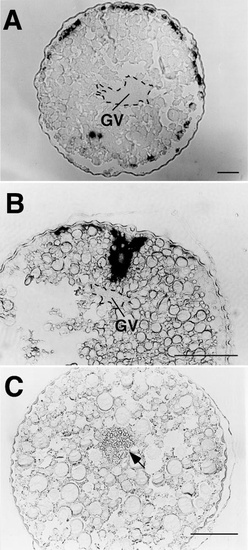
Cyclin B mRNA in full-grown oocytes treated with 1 (A, B) or 10 μg/ml (C) cytochalasin B. In the oocytes treated with 1 μg/ml cytochalasin B, the aggregation of cyclin B mRNA is seen as various forms depending on batches of oocytes (the aggregation was segregated into pieces scattered in the cytoplasm as in A or only deformed without apparent segregation as in B), whereas it was completely dispersed in the oocytes treated with 10 μg/ml cytochalasin B (C). Note that 10 μg/ml cytochalasin B induced GVBD in situ without migration of the germinal vesicle (indicated by arrow). GV, germinal vesicle (marked by broken lines). Scale, 100 μm. |
|
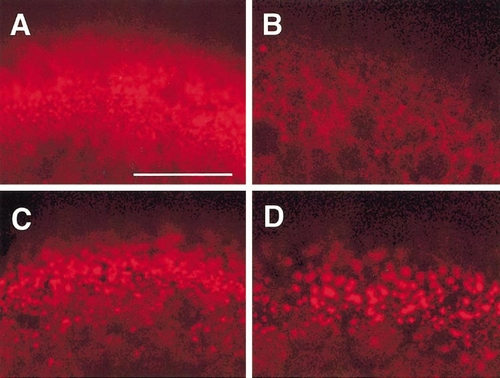
Microfilaments in full-grown immature (A), 17α,20β-DP-induced mature (B), and cytochalasin B-treated (C, D) oocytes, as revealed by confocal microscopy with rhodamine–phalloidin. Immature oocytes were treated with 1 (C) or 10 μg/ml (D) cytochalasin B. Dense meshwork of microfilaments is present in the cortical cytoplasm of immature oocytes (A) but not in mature oocytes (B). Cytochalasin B disrupts the microfilament meshwork partially at 1 μg/ml (C) and more extensively at 10 μg/ml (D). Scale, 50 μm. |
|
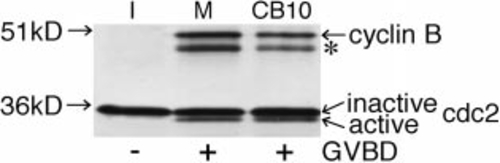
Anti-Cdc2 and anti-cyclin B immunoblots of Suc1- precipitates from oocyte extracts, showing Cdc2 and cyclin B forming a complex with Cdc2. An inactive Cdc2, but not cyclin B, is seen in immature oocytes (I). In addition to the inactive Cdc2, an active Cdc2 and cyclin B forming a complex with it are seen in mature (M) and cytochalasin B (10 μg/ml)-treated (CB10) oocytes, both of which underwent GVBD. The asterisk indicates a proteolytic product of cyclin B during Suc1-precipitation. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 229(2), Kondo, T., Kotani, T., and Yamashita, M., Dispersion of cyclin B mRNA aggregation is coupled with translational activation of the mRNA during zebrafish oocyte maturation, 421-431, Copyright (2001) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.