- Title
-
Zebrafish Dkk1 functions in forebrain specification and axial mesendoderm formation
- Authors
- Hashimoto, H., Itoh, M., Yamanaka, Y., Yamashita, S., Shimizu, T., Solnica-Krezel, L., Hibi, M., and Hirano, T.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
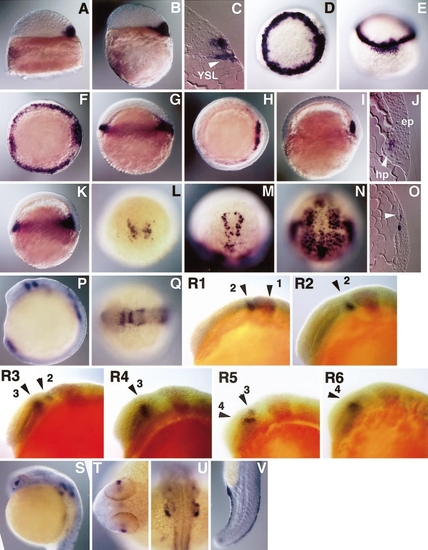
Expression of dkk1 mRNA during development. (A) High-stage, lateral view, dorsal to the right. (B, C) Sphere stage, lateral view, dorsal to the right (B) and sagittal section (C). (D, E) The 30% epiboly stage, animal pole view, dorsal to the right (D) and dorsal view (E). (F, G) The 50% epiboly stage, animal pole view, dorsal to the right (F) and lateral view, dorsal to the right (G). (H, I, J) Shield stage, animal pole view, dorsal to the right (H), lateral view, dorsal to the right (I), and sagittal section (J). (K, L) The 65% epiboly stage, lateral view, dorsal to the right (K) and dorsal view (L). (M, N, O) The 90% epiboly stage, animal pole view, anterior to the top (M), dorsal view (N), and sagittal section (O). (P, Q) Midsegmentation stage, lateral view, dorsal to the right (P) and animal pole view, anterior to the left (Q). (R1–6) Segmentation stage, lateral views, anterior to the left. dkk1 (purple) and eng3 (red) expression. Arrow heads (1– 4) indicate expression domains of dkk1. R1, 5-somite stage; R2, 7-somite stage; R3, 9-somite stage; R4, 11-somite stage; R5, 13-somite stage; R6, 15-somite stage. (S, T, U, V) 24 hpf, lateral view with dorsal right (S), animal pole view of forebrain region (T) and hindbrain region (U), and lateral view of tail region (V). epi, epiblast; hp, hypoblast; YSL, yolk syncytial layer. |
|
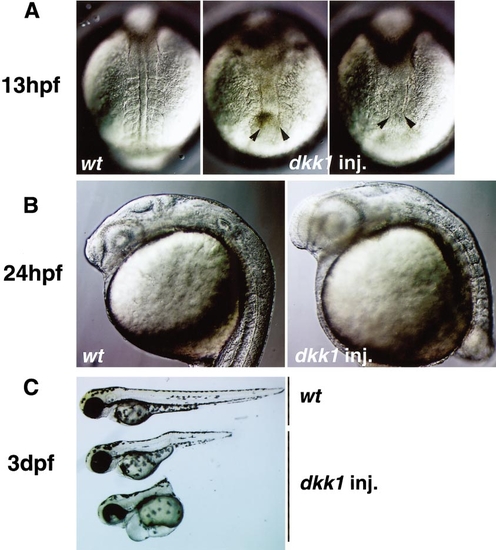
Effects of Dkk1 overexpression on zebrafish development. The embryos injected with 25 pg of dkk1 RNA were analyzed by microscopic observation at 13 hpf (A), 24 hpf (B), and 3 dpf (C). Typical phenotypes are shown. (A) Uninjected (left panel) and dkk1 RNA-injected embryos (middle and right) at 13 hpf (the 8-somite stage for wild-type embryos). Dorsal views. Note expansion of notochord and reduction and malformation of somites in the injected embryos, compared to uninjected embryos. In severely affected embryos (right), somites were not apparent. (B) Uninjected (left) and dkk1 RNA-injected embryos (right) at 24 hpf. Lateral views. The injected embryos had enlarged heads and eyes and shortened anterior-posterior axes. (C) Uninjected (top) and dkk1 RNA-injected embryos (middle, mildly affected embryo; lower, severely affected embryo) at 3 dpf. Lateral views. |
|
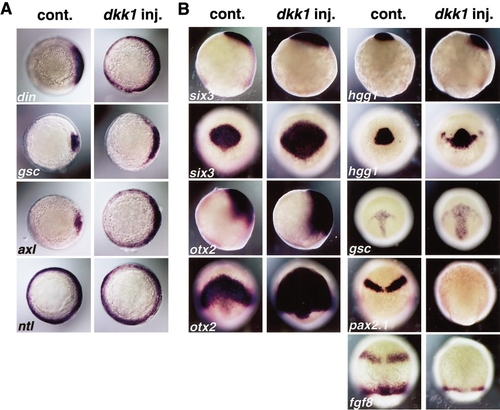
Overexpression of dkk1 RNA results in an enlargement of the forebrain and axial mesendoderm. (A) The embryos injected with 25 pg of dkk1 RNA at 6 hpf (shield stage) exhibited an expanded expression domain of dorsal mesendodermal markers (right panels), compared to an uninjected embryo (left panels). din, chordin; gsc, goosecoid; axl, axial; ntl, no tail. (B) In embryos injected with dkk1 RNA (right panels) at late-gastrula stages (90% epiboly), expression domains of anterior neuroectoderm markers, six3 and otx2, as well as prechordal mesendoderm markers, hgg1 and gsc, were enlarged compared to uninjected siblings (left panels). In contrast, expression of pax2.1 and fgf8, observed in prospective MHB of control embryos, was not detected in embryos injected with dkk1 RNA. |
|
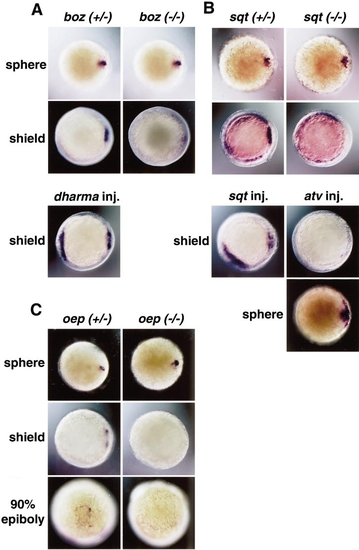
Maintenance of dkk1 expression depends on bozozok/dharma and Nodal signals. (A) dkk1 expression in dorsal marginal blastoderm and dorsal YSL was detected at the sphere stage in both bozm168 heterozygous (left) and homozygous (right) embryos. dkk1 expression in the embryonic shield was observed at the shield stage in bozm168 heterozygous embryos (left), but could not be detected in bozm168 homozygous embryos (right). When 5 pg of dharma RNA was injected to one blastomere (located in the lateral position) of 8-cell stage embryos, about a half of the dharma RNA-injected embryos exhibited expansion of dkk1 expression in the dorsal side, and the rest of them exhibited an ectopic expression of dkk1 at the shield stage (lower panel). Animal pole views, dorsal to the right. (B) dkk1 expression was normal at the sphere stage in both sqtcz35 heterozygous (left) and homozygous (right) embryos. dkk1 expression in the embryonic shield was observed at the shield stage in sqtcz35 heterozygous embryos (left), but could not be detected in sqtcz35 homozygous embryos (right). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
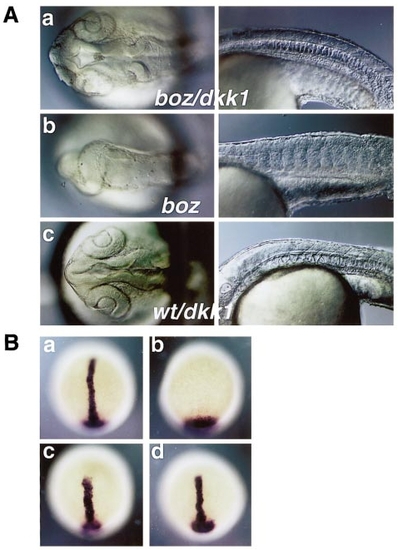
Overexpression of dkk1 rescues the phenotypes of bozm168 mutants. (A) bozm168 homozygous embryos did not have anterior neuroectoderm structures (b, left) or notochord (b, right). bozm168 homozygous (a) or wild-type embryos (c) injected with 5 pg of dkk1 RNA had enlarged separated eyes and anterior neuroectoderm structures (left panels), and notochord (right panels). Animal pole views for head region (left panels) and lateral views for trunk (right panels). (B) ntl expression was detected in dorsal midline at the tail-bud stage in the bozm168 heterozygous embryos (a), but ntl expression domain stayed in the tail bud and ntl transcripts were not detected in dorsal midline in bozm168 homozygous embryos (b). Shorter and wider ntl expression domain was detected in bozm168 heterozygous (c) and homozygous (d) embryos injected with dkk1 RNA, compared to the heterozygous uninjected embryos (a). |
|
Overexpression of dkk1 promotes anterior neuroectoderm development in the absence of dorso-anterior mesendoderm. (A) Embryos injected with 5 pg of antivin (atv) RNA lack most of mesoderm and endoderm except tail region, but contained a cyclopic eye (a). Embryos coinjected with 5 pg of atv and 20 pg of dkk1 RNA displayed enlarged head structures (b) with an enlarged cyclopic eye (c) which expresses six3 in a higher level (e), compared to an eye in the atv RNA-injected embryos (d). (B) Expression of gsc in the embryonic shield was not detected in either the atv RNA-injected embryos (a) or the atv and dkk1 RNA-injected embryos (b), compared to uninjected shield-stage embryos (c). Animal pole views, dorsal to the right. However, expression of six3 at 9 hpf was expanded in the atv and dkk1 RNA-injected embryos (e, g), compared to the atv RNA-injected embryos (d, f). (d, e) Lateral views, dorsal to the right. (f, g) Dorso-anterior views. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 217(1), Hashimoto, H., Itoh, M., Yamanaka, Y., Yamashita, S., Shimizu, T., Solnica-Krezel, L., Hibi, M., and Hirano, T., Zebrafish Dkk1 functions in forebrain specification and axial mesendoderm formation, 138-152, Copyright (2000) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.